Summarize 10 tips to improve Redis performance
This article brings you relevant knowledge about Redis, which mainly introduces some tips to improve redis performance, including pipeline, enabling IO multi-threading, avoiding big keys, etc. ,I hope everyone has to help.

Recommended learning: Redis tutorial
01 Using pipeline
Redis is TCP based on the request-response model server. Means a single request RTT (round trip time), depends on the current network conditions. This results in a single Redis request potentially being very fast, e.g. over a local loop network card. May be very slow, such as in a poor network environment.
On the other hand, every Redis request-response involves read and write system calls. It may even trigger multiple epoll_wait system calls (Linux platform). This causes Redis to constantly switch between user mode and kernel mode.
static int connSocketRead(connection *conn, void *buf, size_t buf_len) {
// read 系统调用
int ret = read(conn->fd, buf, buf_len);}static int connSocketWrite(connection *conn, const void *data, size_t data_len) {
// write 系统调用
int ret = write(conn->fd, data, data_len);}int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags) {
// 事件触发,Linux 下为 epoll_wait 系统调用
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);}So, how to save round trip time and system calls? Batch processing is a good idea.
For this purpose, Redis provides "pipeline". The principle of pipeline is very simple. Multiple commands are packaged into "one command" and sent. After Redis receives it, it parses it into multiple commands for execution. Finally, multiple results are packaged and returned.
「Pipeline can effectively improve Redis performance」.
However, there are a few things you need to pay attention to when using pipeline
"Pipeline cannot guarantee atomicity". During the execution of a pipeline command, commands initiated by other clients may be executed. Remember, a pipeline just batches commands. To ensure atomicity, use MULTI or Lua scripts.
「Don’t use too many pipeline commands at a time」. When using pipeline, Redis will temporarily store the response results of pipeline commands in the memory Reply buffer and wait for all commands to be executed before returning. If there are too many pipeline commands, it may occupy more memory. A single pipeline can be split into multiple pipelines.
02 Enable IO multi-threading
Before the "Redis 6" version, Redis was "single-threaded" Reading and parsing , execute orders. Starting from Redis 6, IO multi-threading was introduced.
The IO thread is responsible for reading commands, parsing commands, and returning results. When enabled, it can effectively improve IO performance.
I drew a schematic diagram for your reference
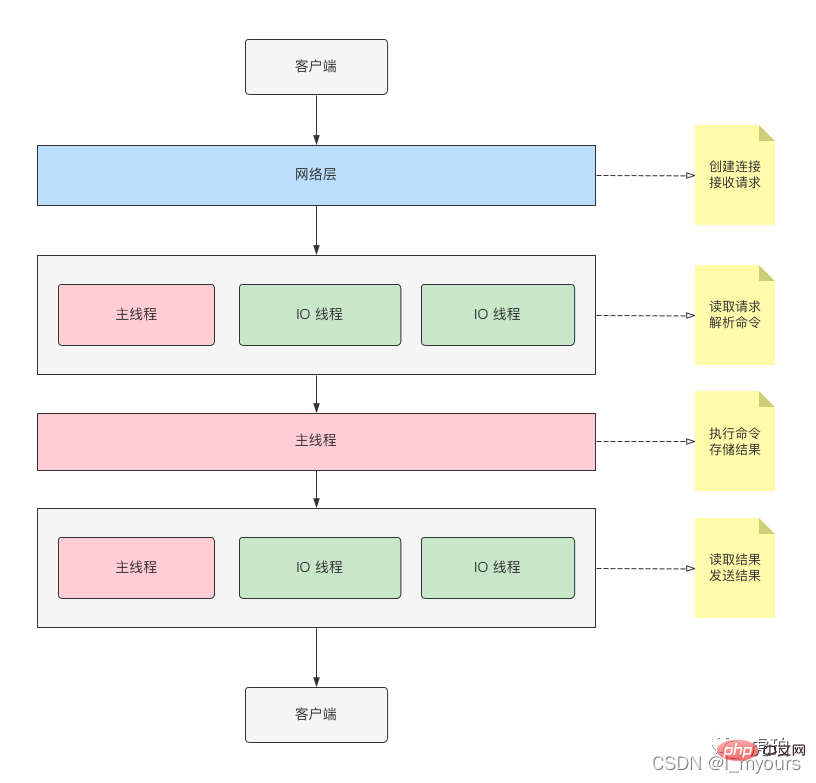
As shown in the figure above, the main thread and IO thread will jointly participate in the reading, parsing and result response of commands.
But the one that executes the command is "main thread".
The IO thread is closed by default. You can modify the following configuration in redis.conf to enable it.
io-threads 4 io-threads-do-reads yes
"io-threads" is the number of IO threads (including the main thread). I suggest you set different values according to the machine for stress testing and get the optimal value.
03 Avoid big key
Redis execution command is single-threaded, which means that there is a risk of blocking when Redis operates "big key".
Big key usually means that the value stored in Redis is too large. Including:
- A single value is too large. Such as 200M size String.
- There are too many collection elements. For example, there are hundreds or tens of millions of data in List, Hash, Set, and ZSet.
For example, suppose we have a 200M String key named "foo".
Execute the following command
127.0.0.1:6379> GET foo
When the result is returned, Redis will allocate 200m of memory and perform a memcpy copy.
void _addReplyProtoToList(client *c, const char *s, size_t len) {
...
if (len) {
/* Create a new node, make sure it is allocated to at
* least PROTO_REPLY_CHUNK_BYTES */
size_t size = len size = zmalloc_usable_size(tail) - sizeof(clientReplyBlock);
tail->used = len;
// 内存拷贝
memcpy(tail->buf, s, len);
listAddNodeTail(c->reply, tail);
c->reply_bytes += tail->size;
closeClientOnOutputBufferLimitReached(c, 1);
}}And the Redis output buf is 16k
// server.h#define PROTO_REPLY_CHUNK_BYTES (16*1024) /* 16k output buffer */typedef struct client {
...
char buf[PROTO_REPLY_CHUNK_BYTES];} client;This means that Redis cannot return response data in a single time and needs to register a "writable event", thus triggering multiple write system calls.
There are two time-consuming points here:
- Allocate large memory (may also release memory, such as DEL command)
- Trigger multiple writable events (frequent Execute system calls, such as write, epoll_wait)
So, how to find the big key?
If simple commands appear in the slow log, such as GET, SET, and DEL, there is a high probability that a big key appears.
127.0.0.1:6379> SLOWLOG GET 3) (integer) 201323 // 单位微妙 4) 1) "GET" 2) "foo"
Secondly, you can use the Redis analysis tool to find the big key.
$ redis-cli --bigkeys -i 0.1 ... [00.00%] Biggest string found so far '"foo"' with 209715200 bytes -------- summary ------- Sampled 1 keys in the keyspace! Total key length in bytes is 3 (avg len 3.00) Biggest string found '"foo"' has 209715200 bytes 1 strings with 209715200 bytes (100.00% of keys, avg size 209715200.00) 0 lists with 0 items (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00) 0 hashs with 0 fields (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00) 0 streams with 0 entries (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00) 0 sets with 0 members (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00) 0 zsets with 0 members (00.00% of keys, avg size 0.00)
Regarding big keys, we have the following suggestions:
1. Try to avoid big keys in business. When a big key appears, you have to judge whether the design is reasonable or whether a bug has occurred.
2. Split the big key into multiple small keys.
3. Use alternative commands.
If the Redis version is greater than 4.0, you can use the UNLINK command instead of DEL. If the Redis version is greater than 6.0, the lazy-free mechanism can be turned on. The memory release operation will be executed on the background thread.
LRANGE, HGETALL, etc. are replaced with LSCAN and HSCAN to obtain in batches.
But I still recommend avoiding big keys in business.
04 Avoid executing commands with high time complexity
We know that Redis executes commands in a "single thread". Executing commands with high time complexity is likely to block other requests.
复杂度高的命令和元素数量有关。通常有以下两种场景。
元素太多,消耗 IO 资源。如 HGETALL、LRANGE,时间复杂度为 O(N)。
计算过于复杂,消费 CPU 资源。如 ZUNIONSTORE,时间复杂度为 O(N)+O(M log(M))
Redis 官方手册,标记了命令执行的时间复杂度。建议你在使用不熟悉的命令前,先查看手册,留意时间复杂度。
实际业务中,你应该尽量避免时间复杂度高的命令。如果必须要用,有两点建议
保证操作的元素数量,尽可能少。
读写分离。复杂命令通常是读请求,可以放到「slave」结点执行。
05 使用惰性删除 Lazy free
key 过期或是使用 DEL 删除命令时,Redis 除了从全局 hash 表移除对象外,还会将对象分配的内存释放。当遇到 big key 时,释放内存会造成主线程阻塞。
为此,Redis 4.0 引入了 UNLINK 命令,将释放对象内存操作放入 bio 后台线程执行。从而有效减少主线程阻塞。
Redis 6.0 更进一步,引入了 Lazy-free 相关配置。当开启配置后,key 过期和 DEL 命令内部,会将「释放对象」操作「异步执行」。
void delCommand(client *c) {
delGenericCommand(c,server.lazyfree_lazy_user_del);}void delGenericCommand(client *c, int lazy) {
int numdel = 0, j;
for (j = 1; j argc; j++) {
expireIfNeeded(c->db,c->argv[j]);
// 开启 lazy free 则使用异步删除
int deleted = lazy ? dbAsyncDelete(c->db,c->argv[j]) :
dbSyncDelete(c->db,c->argv[j]);
...
}}建议至少升级到 Redis 6,并开启 Lazy-free。
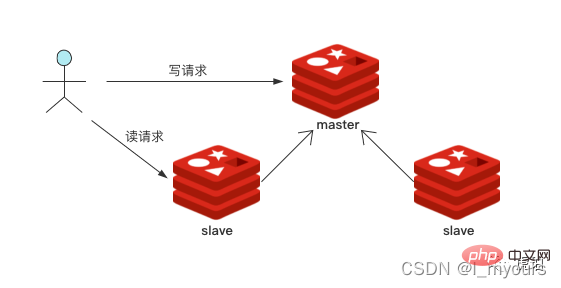
06 读写分离
Redis 通过副本,实现「主-从」运行模式,是故障切换的基石,用来提高系统运行可靠性。也支持读写分离,提高读性能。
你可以部署一个主结点,多个从结点。将读命令分散到从结点中,从而减轻主结点压力,提升性能。
07 绑定 CPU
Redis 6.0 开始支持绑定 CPU,可以有效减少线程上下文切换。
CPU 亲和性(CPU Affinity)是一种调度属性,它将一个进程或线程,「绑定」到一个或一组 CPU 上。也称为 CPU 绑定。
设置 CPU 亲和性可以一定程度避免 CPU 上下文切换,提高 CPU L1、L2 Cache 命中率。
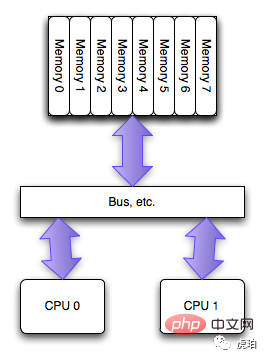
早期「SMP」架构下,每个 CPU 通过 BUS 总线共享资源。CPU 绑定意义不大。
而在当前主流的「NUMA」架构下,每个 CPU 有自己的本地内存。访问本地内存有更快的速度。而访问其他 CPU 内存会导致较大的延迟。这时,CPU 绑定对系统运行速度的提升有较大的意义。
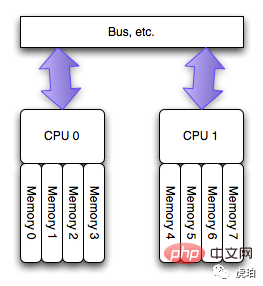
现实中的 NUMA 架构比上图更复杂,通常会将 CPU 分组,若干个 CPU 分配一组内存,称为 「node」。
你可以通过 「numactl -H 」 命令来查看 NUMA 硬件信息。
$ numactl -H available: 2 nodes (0-1)node 0 cpus: 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 node 0 size: 32143 MB node 0 free: 26681 MB node 1 cpus: 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 node 1 size: 32309 MB node 1 free: 24958 MB node distances: node 0 1 0: 10 21 1: 21 10
上图中可以得知该机器有 40 个 CPU,分组为 2 个 node。
node distances 是一个二维矩阵,表示 node 之间 「访问距离」,10 为基准值。上述命令中可以得知,node 自身访问,距离是 10。跨 node 访问,如 node 0 访问 node 1 距离为 21。说明该机器「跨 node 访问速度」比「node 自身访问速度」慢 2.1 倍。
其实,早在 2015 年,有人提出 Redis 需要支持设置 CPU 亲和性,而当时的 Redis 还没有支持 IO 多线程,该提议搁置。
而 Redis 6.0 引入 IO 多线程。同时,也支持了设置 CPU 亲和性。
我画了一张 Redis 6.0 线程家族供你参考。

上图可分为 3 个模块
- 主线程和 IO 线程:负责命令读取、解析、结果返回。命令执行由主线程完成。
- bio 线程:负责执行耗时的异步任务,如 close fd。
- 后台进程:fork 子进程来执行耗时的命令。
Redis 支持分别配置上述模块的 CPU 亲和度。你可以在 redis.conf 找到以下配置(该配置需手动开启)。
# IO 线程(包含主线程)绑定到 CPU 0、2、4、6 server_cpulist 0-7:2 # bio 线程绑定到 CPU 1、3 bio_cpulist 1,3 # aof rewrite 后台进程绑定到 CPU 8、9、10、11 aof_rewrite_cpulist 8-11 # bgsave 后台进程绑定到 CPU 1、10、11 bgsave_cpulist 1,10-11
我在上述机器,针对 IO 线程和主线程,进行如下测试:
首先,开启 IO 线程配置。
io-threads 4 # 主线程 + 3 个 IO 线程io-threads-do-reads yes # IO 线程开启读和解析命令功能
测试如下三种场景:
不开启 CPU 绑定配置。
绑定到不同 node。
「server_cpulist 0,1,2,3」绑定到相同 node。
「server_cpulist 0,2,4,6」
通过 redis-benchmark 对 get 命令进行基准测试,每种场景执行 3 次。
$ redis-benchmark -n 5000000 -c 50 -t get --threads 4
结果如下:
1.不开启 CPU 绑定配置
throughput summary: 248818.11 requests per second throughput summary: 248694.36 requests per second throughput summary: 249004.00 requests per second
2.绑定不同 node
throughput summary: 248880.03 requests per second throughput summary: 248447.20 requests per second throughput summary: 248818.11 requests per second
3.绑定相同 node
throughput summary: 284414.09 requests per second throughput summary: 284333.25 requests per second throughput summary: 265252.00 requests per second
根据测试结果,绑定到同一个 node,qps 大约提升 15%
使用绑定 CPU,你需要注意以下几点:
Linux 下,你可以使用 「numactl --hardware」 查看硬件布局,确保支持并开启 NUMA。
线程要尽可能分布在 「不同的 CPU,相同的 node」,设置 CPU 亲和度才有效。否则会造成频繁上下文切换和远距离内存访问。
你要熟悉 CPU 架构,做好充分的测试。否则可能适得其反,导致 Redis 性能下降。
08 合理配置持久化策略
Redis 支持两种持久化策略,RDB 和 AOF。
RDB 通过 fork 子进程,生成数据快照,二进制格式。
AOF 是增量日志,文本格式,通常较大。会通过 AOF rewrite 重写日志,节省空间。
除了手动执行「BGREWRITEAOF」命令外,以下 4 点也会触发 AOF 重写
执行「config set appendonly yes」命令
AOF 文件大小比例超出阈值,「auto-aof-rewrite-percentage」
AOF 文件大小绝对值超出阈值,「auto-aof-rewrite-min-size」
主从复制完成 RDB 加载
RDB 和 AOF,都是在主线程中触发执行。虽然具体执行,会通过 fork 交给后台子进程。但 fork 操作,会拷贝进程数据结构、页表等,当实例内存较大时,会影响性能。
AOF 支持以下三种策略。
appendfsync no:由操作系统决定执行 fsync 时机。 对 Linux 来说,通常每 30 秒执行一次 fsync,将缓冲区中的数据刷到磁盘上。如果 Redis qps 过高或写 big key,可能导致 buffer 写满,从而频繁触发 fsync。
appendfsync everysec: 每秒执行一次 fsync。
appendfsync always: 每次「写」会调用一次 fsync,性能影响较大。
AOF 和 RDB 都会对磁盘 IO 造成较高的压力。其中,AOF rewrite 会将 Redis hash 表所有数据进行遍历并写磁盘。对性能会产生一定的影响。
线上业务 Redis 通常是高可用的。如果对缓存数据丢失不敏感。考虑关闭 RDB 和 AOF 以提升性能。
如果无法关闭,有以下几点建议:
RDB 选择业务低峰期做,通常为凌晨。保持单个实例内存不超过 32 G。太大的内存会导致 fork 耗时增加。
AOF 选择 appendfsync no 或者 appendfsync everysec。
AOF auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 配置大一些,如 2G。避免频繁触发 rewrite。
AOF 可以仅在从节点开启,减轻主节点压力。
根据本地测试,不开启 AOF,写性能大约能提升 20% 左右。
09 使用长连接
Redis 是基于 TCP 协议,请求-响应式服务器。使用短连接会导致频繁的创建连接。
短连接有以下几个慢速操作:
创建连接时,TCP 会执行三次握手、慢启动等策略。
Redis 会触发新建/断开连接事件,执行分配/销毁客户端等耗时操作。
如果你使用的是 Redis Cluster,新建连接时,客户端会拉取 slots 信息初始化。建立连接速度更慢。
所以,相对于性能快速的 Redis,创建连接是十分慢速的操作。
「建议使用连接池,并合理设置连接池大小」。
但使用长连接时,需要留意一点,要有「自动重连」策略。避免因网络异常,导致连接失效,影响正常业务。
10 关闭 SWAP
SWAP 是内存交换技术。将内存按页,复制到预先设定的磁盘空间上。
内存是快速的,昂贵的。而磁盘是低速的,廉价的。
通常使用 SWAP 越多,系统性能越低。
Redis 是内存数据库,使用 SWAP 会导致性能快速下降。
建议留有足够内存,并关闭 SWAP。
总结
以上就是今天为大家分享的 「提升 Redis 性能的 10 个手段」。
我绘制了思维导图,方便大家记忆。
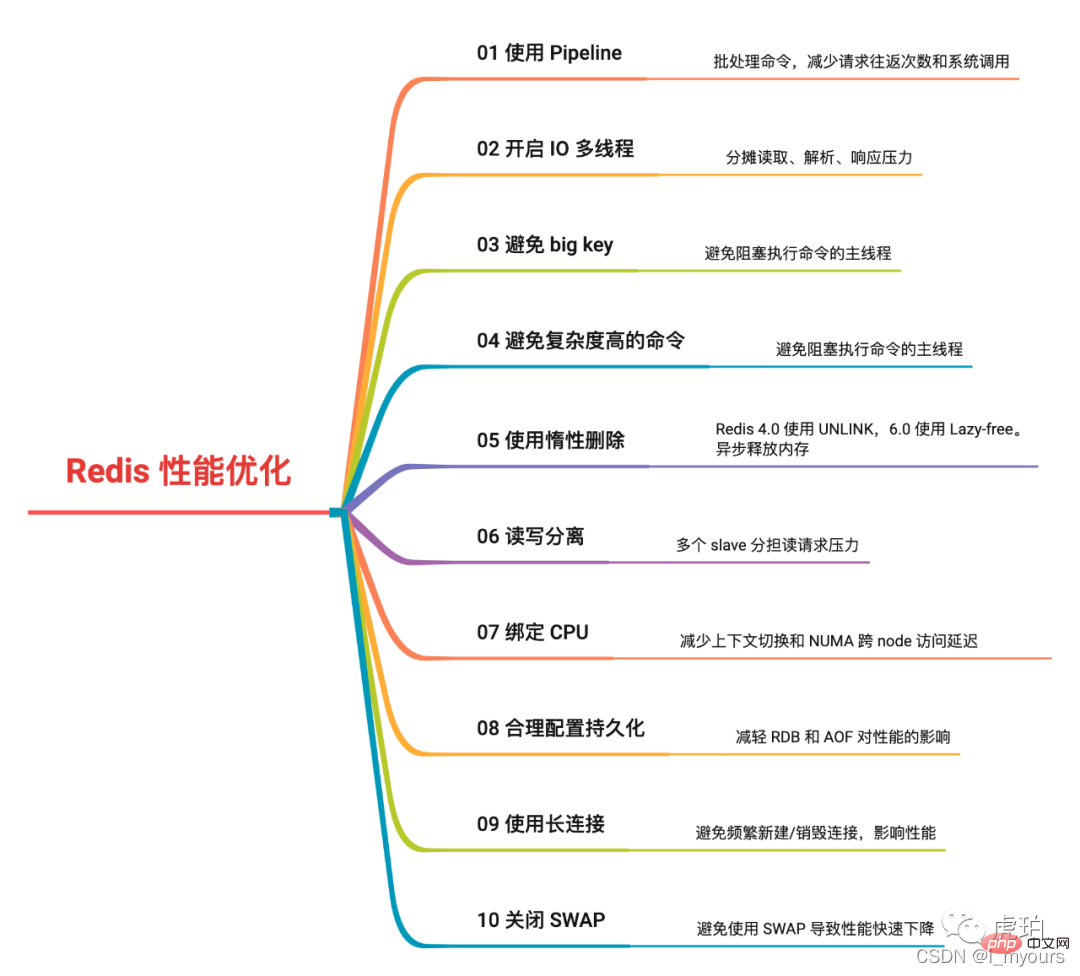
可以看到,性能优化并不容易,需要我们了解很多底层知识,并做出充分测试。在不同机器、不同系统、不同配置下,Redis 都会有不同的性能表现。
推荐学习:Redis学习教程
The above is the detailed content of Summarize 10 tips to improve Redis performance. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




