
es6 Method of traversing an array: 1. Use forEach() to call a function for each element in the array; 2. Use map() to call the specified callback function for each element of the array; 3. Using filter(), a callback function will be called to filter the elements in the array and return all elements that meet the conditions; 4. Use some() to traverse the array to detect whether there are elements with specified conditions in the array; 5. Use every() can determine whether all array elements meet the conditions; 6. Use reduce().

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, ECMAScript version 6, Dell G3 computer.
Declare an object that needs to be traversed
The following code refers to this object
let data = {
code: 1,
list: [{
id: 23,
title: "女装1",
price: 300
},
{
id: 24,
title: "女装2",
price: 200
},
{
id: 27,
title: "男装1",
price: 100
},
{
id: 29,
title: "男装2",
price: 400
},
{
id: 230,
title: "女装3",
price: 600
},
{
id: 40,
title: "童装1",
price: 700
}
]
}ForEach, you cannot use break and continue statements
// 有二个参数 第一个参数是数值 第二个参数是索引值
data.list.forEach(function(item,index){
console.log(item,index)
//输出结果是{
// {id: 23, title: "女装1", price: 300} 0
// {id: 24, title: "女装2", price: 200} 1
// {id: 27, title: "男装1", price: 100} 2
// {id: 29, title: "男装2", price: 400} 3
// {id: 230, title: "女装3", price: 600} 4
// {id: 40, title: "童装1", price: 700} 5
// }
}) //map 映射
//遍历数据并返回一个新的数组 对数据的处理会返回原先对应的位置
let arr = [2, 3, 6];
let newArr = arr.map(function (val, index) {
// 第一个参数是值 第二个参数是索引值
console.log(arr)
})**Traverse the data and return a new array. Processing the data will return the original corresponding position
To add a code block map, you cannot parse the same block-level scope
{}{} represents different block-level scopes and is written in different places**
// 浅拷贝
// 浅拷贝是指a把值 给了b 当b的值改变 a b 的值同时改变。
{
let arr = [2, 3, 6];
let newArr = arr.map(function (index, val) {
// 第一个参数是索引值 第二个参数是值 })
console.log(arr)// 0: 2
// 1: 3
// 2: 6 }
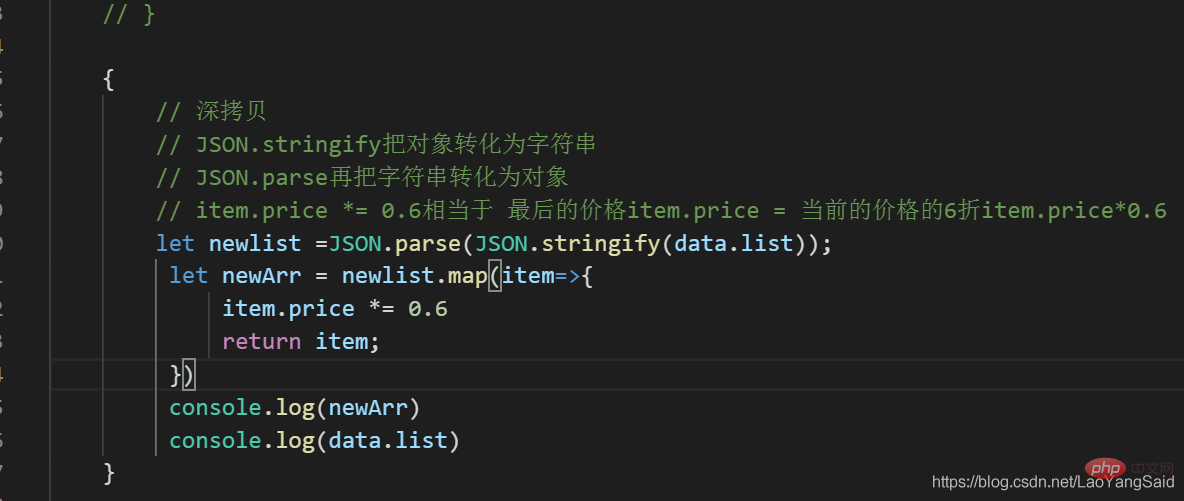
{
// 浅拷贝
// 浅拷贝是指a把值 给了b 当b的值改变 a b 的值同时改变。
let newArr = data.list.map((item, index) => {
item.price = item.price * .6
return item;
});
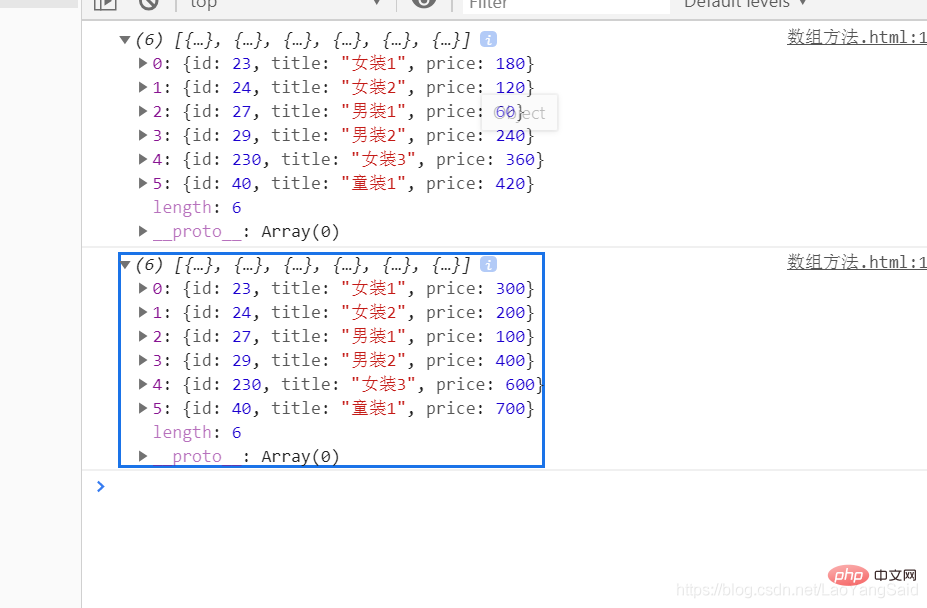
console.log(newArr)//打印的结果价格都是改变的,一样的{
// 0: {id: 23, title: "女装1", price: 180}
// 1: {id: 24, title: "女装2", price: 120}
// 2: {id: 27, title: "男装1", price: 60}
// 3: {id: 29, title: "男装2", price: 240}
// 4: {id: 230, title: "女装3", price: 360}
// 5: {id: 40, title: "童装1", price: 420}
// }
console.log(data.list)//同上 }
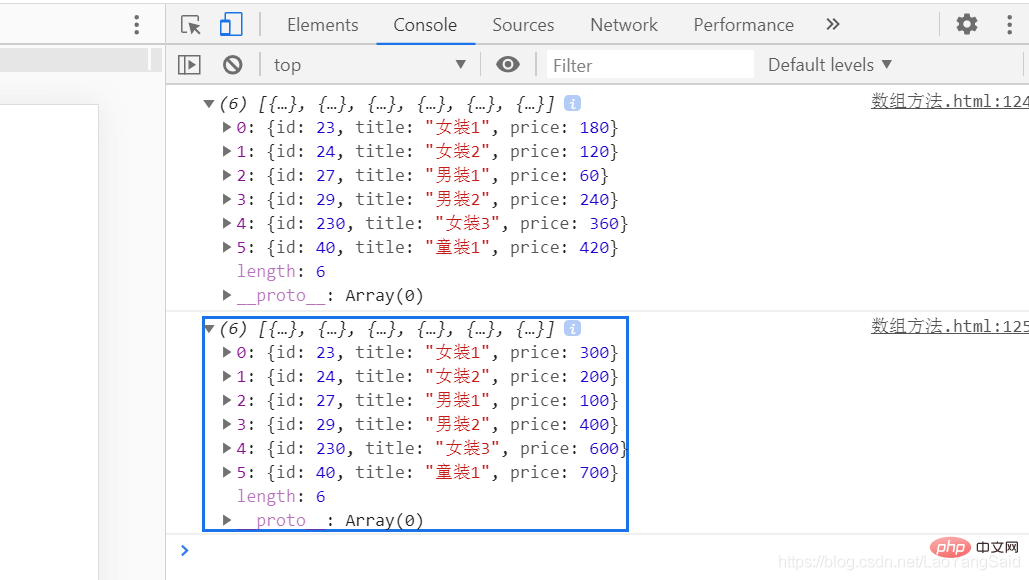
The output result is a deep copy. No matter which value of a b changes, the final result will not change with the change of a b
// Deep copy 2 (simple and crude)
filter will call a callback function to filter the elements in the array and return All elements that meet the conditions
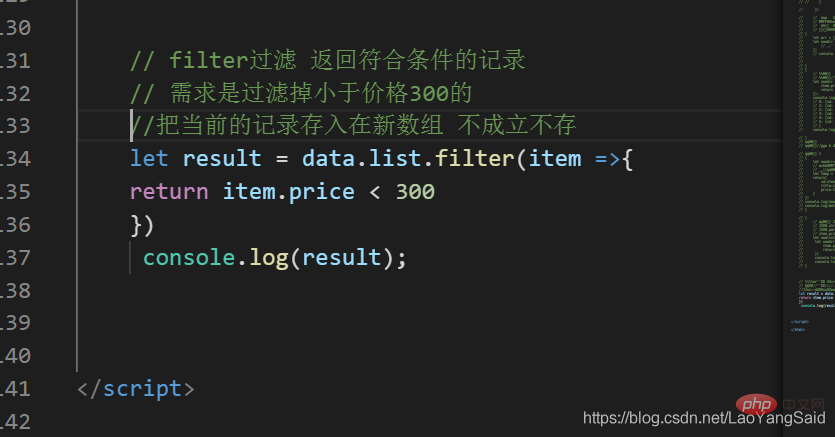
Filter out those with a price less than 300 and print them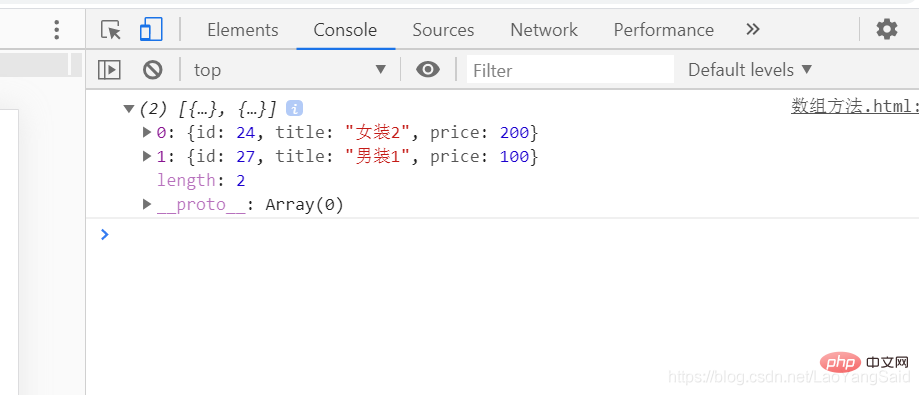
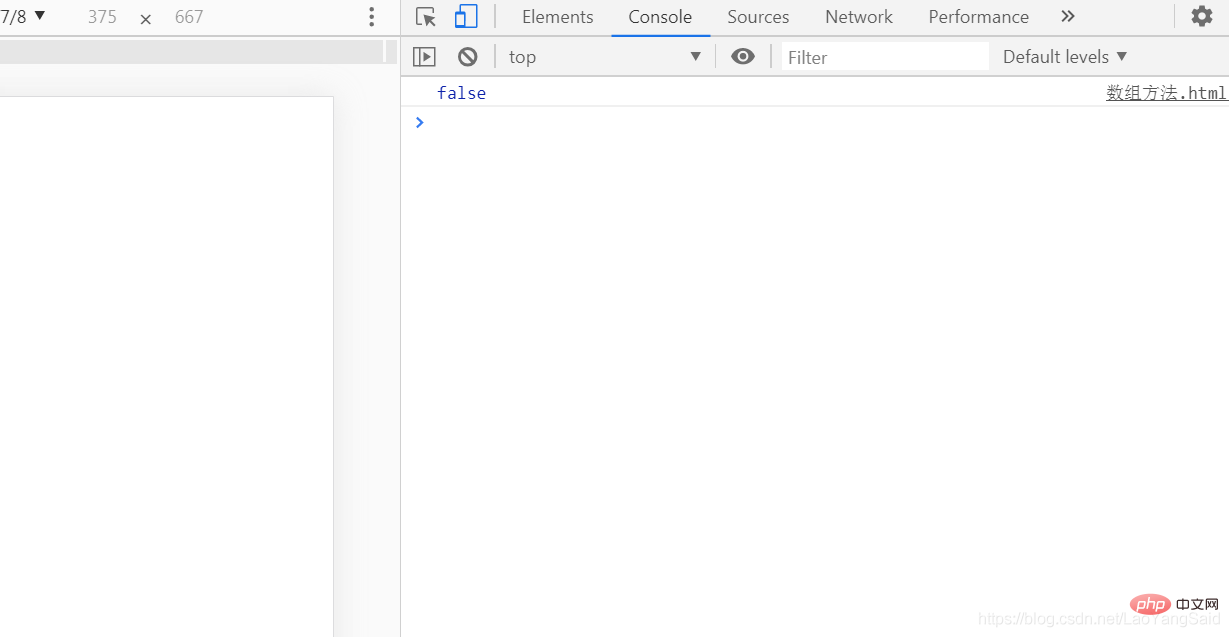
The function is to detect whether the element of the specified condition exists in the array; if the specified element exists, the returned result is true, if the specified element does not exist, the returned result is false


The every method is used to determine whether any element in the array meets the judgment conditions. The judgment is also completed in the function body of the callback function, and the callback function returns a Boolean value. If the callback function returns false at a certain time, the entire every method returns false and the traversal ends.
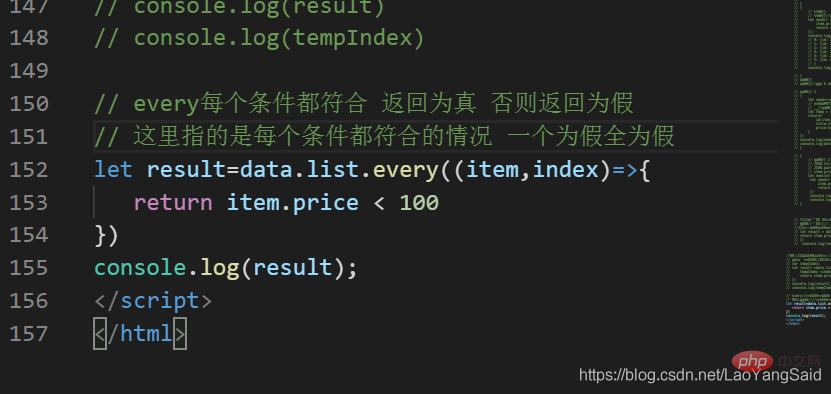
This is the output information
Output The sum is sum val (numeric value)
// reduce 用来实现累加的效果 (常用于写购物车价格的累加)
// 声明一个数组 数组里面放数字 让其里面的数字显示为累加的总和
// let arr=[200,200,100]
// let result =arr.reduce((sum,val,index)=>{
// 200+200 index
// 400+100 index
// sum是总加后的和 val是变量里面的值 index为索引值
// console.log(sum,val,index)
// return sum +val;
// })
// console.log(result)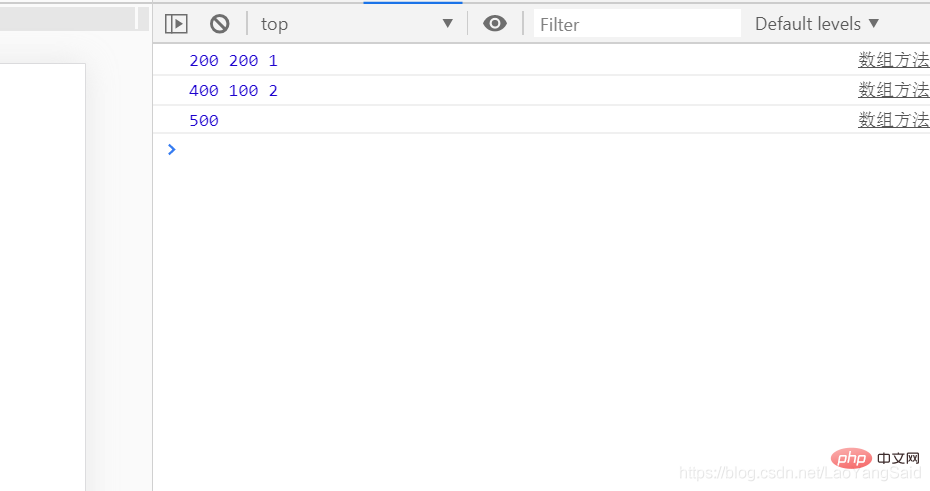
[Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end】
The above is the detailed content of What are the methods for traversing arrays in es6. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!