How does ES6 define classes?
In ES6, class (class) was introduced as a template for objects, and classes can be defined through the "class" keyword. The essence of class is function, which can be regarded as syntactic sugar, making the writing of object prototypes clearer and more like the syntax of object-oriented programming.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, ECMAScript version 6, Dell G3 computer.
ES6 Class
In ES6, class (class) is introduced as a template for objects and can be defined through the "class" keyword kind.
The essence of class is function.
Basically, the ES6 class can be regarded as just a syntax sugar. Most of its functions can be achieved by ES5. The new class writing method only makes the object prototype writing method clearer and more object-oriented. It’s just programming syntax.
Basic usage
Class definition
Class expressions can be anonymous or named.
// 匿名类
let Example = class {
constructor(a) {
this.a = a;
}
}
// 命名类
let Example = class Example {
constructor(a) {
this.a = a;
}
}Class declaration
class Example {
constructor(a) {
this.a = a;
}
}Note: Repeatable declarations are not allowed.
class Example{}
class Example{}
// Uncaught SyntaxError: Identifier 'Example' has already been
// declared
let Example1 = class{}
class Example{}
// Uncaught SyntaxError: Identifier 'Example' has already been
// declaredNote:
The class definition will not be promoted, which means that the class must be defined before accessing, otherwise an error will be reported.
Methods in the class do not require the function keyword.
Semicolons cannot be added between methods.
new Example();
class Example {}Body of the class
Attributes
prototype
ES6 Medium , the prototype still exists. Although methods can be defined directly from the class, the methods are actually still defined on the prototype. Override method/Add method during initialization
Example.prototype={
//methods
}Add method
Object.assign(Example.prototype,{
//methods
})Static attributes
Static attributes: attributes of the class itself, that is, attributes directly defined inside the class (Class. propname ), no instantiation is required. ES6 stipulates that there are only static methods inside Class and no static attributes.
class Example {
// 新提案
static a = 2;
}
// 目前可行写法
Example.b = 2;Public properties
class Example{}
Example.prototype.a = 2;Instance properties
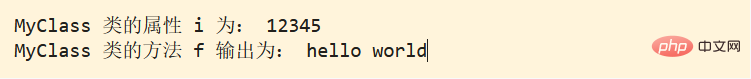
Instance properties: Properties defined on the instance object (this).
class Example {
a = 2;
constructor () {
console.log(this.a);
}
}name attribute
Returns the class name following class (when it exists).
let Example=class Exam {
constructor(a) {
this.a = a;
}
}
console.log(Example.name); // Exam
let Example=class {
constructor(a) {
this.a = a;
}
}
console.log(Example.name); // ExampleMethod
constructor method
The constructor method is the default method of the class and is called when creating an instantiated object of the class.
class Example{
constructor(){
console.log('我是constructor');
}
}
new Example(); // 我是constructorReturn object
class Test {
constructor(){
// 默认返回实例对象 this
}
}
console.log(new Test() instanceof Test); // true
class Example {
constructor(){
// 指定返回对象
return new Test();
}
}
console.log(new Example() instanceof Example); // falseStatic method
class Example{
static sum(a, b) {
console.log(a+b);
}
}
Example.sum(1, 2); // 3Prototype method
class Example {
sum(a, b) {
console.log(a + b);
}
}
let exam = new Example();
exam.sum(1, 2); // 3Instance method
class Example {
constructor() {
this.sum = (a, b) => {
console.log(a + b);
}
}
}Class The instantiation of
new
#class must be instantiated through the new keyword.
class Example {}
let exam1 = Example();
// Class constructor Example cannot be invoked without 'new'Instantiated object
Shared prototype object
class Example {
constructor(a, b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
console.log('Example');
}
sum() {
return this.a + this.b;
}
}
let exam1 = new Example(2, 1);
let exam2 = new Example(3, 1);
// __proto__ 已废弃,不建议使用
// console.log(exam1.__proto__ == exam2.__proto__);
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(exam1) === Object.getPrototypeOf(exam2));// true
Object.getPrototypeOf(exam1).sub = function() {
return this.a - this.b;
}
console.log(exam1.sub()); // 1
console.log(exam2.sub()); // 2[Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front end】
The above is the detailed content of How does ES6 define classes?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to use classes and methods in Python
Apr 21, 2023 pm 02:28 PM
How to use classes and methods in Python
Apr 21, 2023 pm 02:28 PM
Concepts and instances of classes and methods Class (Class): used to describe a collection of objects with the same properties and methods. It defines the properties and methods common to every object in the collection. Objects are instances of classes. Method: Function defined in the class. Class construction method __init__(): The class has a special method (construction method) named init(), which is automatically called when the class is instantiated. Instance variables: In the declaration of a class, attributes are represented by variables. Such variables are called instance variables. An instance variable is a variable modified with self. Instantiation: Create an instance of a class, a specific object of the class. Inheritance: that is, a derived class (derivedclass) inherits the base class (baseclass)
 Naming conventions in PHP: How to use camel case naming for classes, methods and variables
Jul 30, 2023 pm 02:43 PM
Naming conventions in PHP: How to use camel case naming for classes, methods and variables
Jul 30, 2023 pm 02:43 PM
Naming conventions in PHP: How to use camelCase notation to name classes, methods, and variables In PHP programming, good naming conventions are an important coding practice. It improves code readability and maintainability, and makes teamwork smoother. In this article, we will explore a common naming convention: camelCase and provide some examples of how to use it in PHP to name classes, methods, and variables. 1. What is camel case nomenclature? CamelCase is a common naming convention in which the first letter of each word is capitalized,
 PHP error: Unable to declare class repeatedly, solution!
Aug 25, 2023 pm 04:13 PM
PHP error: Unable to declare class repeatedly, solution!
Aug 25, 2023 pm 04:13 PM
PHP error: Unable to declare class repeatedly, solution! It is common for developers to encounter problems. In PHP development, we often encounter a common error: the class cannot be declared repeatedly. This problem seems simple, but if not solved in time, the code will not execute correctly. This article will introduce the cause of this problem and provide a solution for your reference. When we define a class in PHP code, if the same class is defined multiple times in the same file or multiple files, an error that the class cannot be declared repeatedly will occur. This is
 Replace the class name of an element using jQuery
Feb 24, 2024 pm 11:03 PM
Replace the class name of an element using jQuery
Feb 24, 2024 pm 11:03 PM
jQuery is a classic JavaScript library that is widely used in web development. It simplifies operations such as handling events, manipulating DOM elements, and performing animations on web pages. When using jQuery, you often encounter situations where you need to replace the class name of an element. This article will introduce some practical methods and specific code examples. 1. Use the removeClass() and addClass() methods jQuery provides the removeClass() method for deletion
 Detailed explanation of PHP Class usage: Make your code clearer and easier to read
Mar 10, 2024 pm 12:03 PM
Detailed explanation of PHP Class usage: Make your code clearer and easier to read
Mar 10, 2024 pm 12:03 PM
When writing PHP code, using classes is a very common practice. By using classes, we can encapsulate related functions and data in a single unit, making the code clearer, easier to read, and easier to maintain. This article will introduce the usage of PHPClass in detail and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand how to apply classes to optimize code in actual projects. 1. Create and use classes In PHP, you can use the keyword class to define a class and define properties and methods in the class.
 Packaging technology and application in PHP
Oct 12, 2023 pm 01:43 PM
Packaging technology and application in PHP
Oct 12, 2023 pm 01:43 PM
Encapsulation technology and application encapsulation in PHP is an important concept in object-oriented programming. It refers to encapsulating data and operations on data together in order to provide a unified access interface to external programs. In PHP, encapsulation can be achieved through access control modifiers and class definitions. This article will introduce encapsulation technology in PHP and its application scenarios, and provide some specific code examples. 1. Encapsulated access control modifiers In PHP, encapsulation is mainly achieved through access control modifiers. PHP provides three access control modifiers,
 Vue error: Unable to use v-bind to bind class and style correctly, how to solve it?
Aug 26, 2023 pm 10:58 PM
Vue error: Unable to use v-bind to bind class and style correctly, how to solve it?
Aug 26, 2023 pm 10:58 PM
Vue error: Unable to use v-bind to bind class and style correctly, how to solve it? In Vue development, we often use the v-bind instruction to dynamically bind class and style, but sometimes we may encounter some problems, such as being unable to correctly use v-bind to bind class and style. In this article, I will explain the cause of this problem and provide you with a solution. First, let’s understand the v-bind directive. v-bind is used to bind V
 How SpringBoot encrypts and protects class files through custom classloader
May 11, 2023 pm 09:07 PM
How SpringBoot encrypts and protects class files through custom classloader
May 11, 2023 pm 09:07 PM
Background Recently, key business codes have been encrypted for the company framework to prevent the engineering code from being easily restored through decompilation tools such as jd-gui. The configuration and use of the related obfuscation scheme are relatively complex and there are many problems for the springboot project, so the class files are encrypted and then passed The custom classloder is decrypted and loaded. This solution is not absolutely safe. It only increases the difficulty of decompilation. It prevents gentlemen but not villains. The overall encryption protection flow chart is shown in the figure below. Maven plug-in encryption uses custom maven plug-in to compile. The class file specified is encrypted, and the encrypted class file is copied to the specified path. Here, it is saved to resource/corecla.




