
This article brings you relevant knowledge about python, which mainly introduces the related issues of the "__missing__()" function. Let's take a look at this magic function together, hoping to Everyone is helpful.

Recommended learning: python learning tutorial
When fetching values from an ordinary dictionary, the key may not exist:
dd = {'name':'PythonCat'}
dd.get('age') # 结果:None
dd.get('age', 18) # 结果:18
dd['age'] # 报错 KeyError
dd.__getitem__('age') # 等同于 dd['age']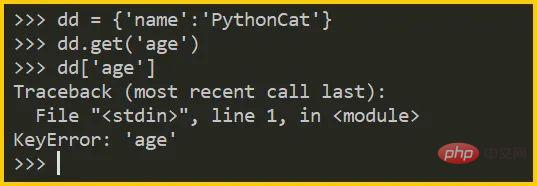
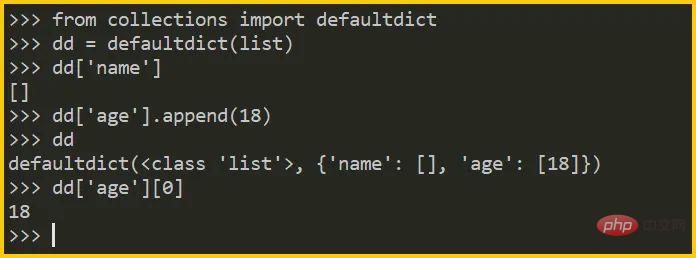
collections.defaultdict:
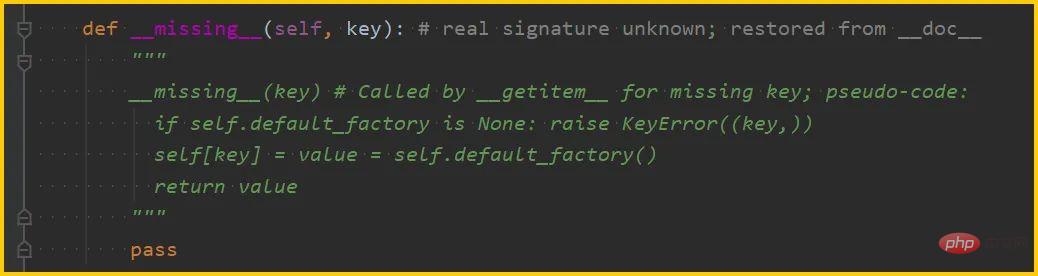
__missing__() is Called by __getitem__ when key is missing to avoid KeyError.
Another typical usage example iscollections.Counter, which is also a subclass of dict. When fetching uncounted keys, count 0 is returned:
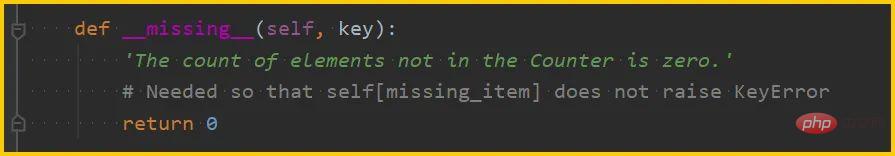
__getitem__() does not necessarily call __missing__() when it cannot get the value.
This is because it is not a necessary attribute of the built-in type and is not predefined in the dictionary base class. If you take the attribute value directly from the dict type, it will report that the attribute does not exist:AttributeError: type object 'object' has no attribute '__missing__'.


It is a method born in Magic methods in subclasses!
Based on this, I have an immature guess: __getitem__() will determine whether the current object is a subclass of dict and whether it has __missing__(), and then call it (if This method also exists in the parent class, so it will not be judged first, but will be called directly). I mentioned this conjecture in the communication group, and some students quickly found the verification in the CPython source code: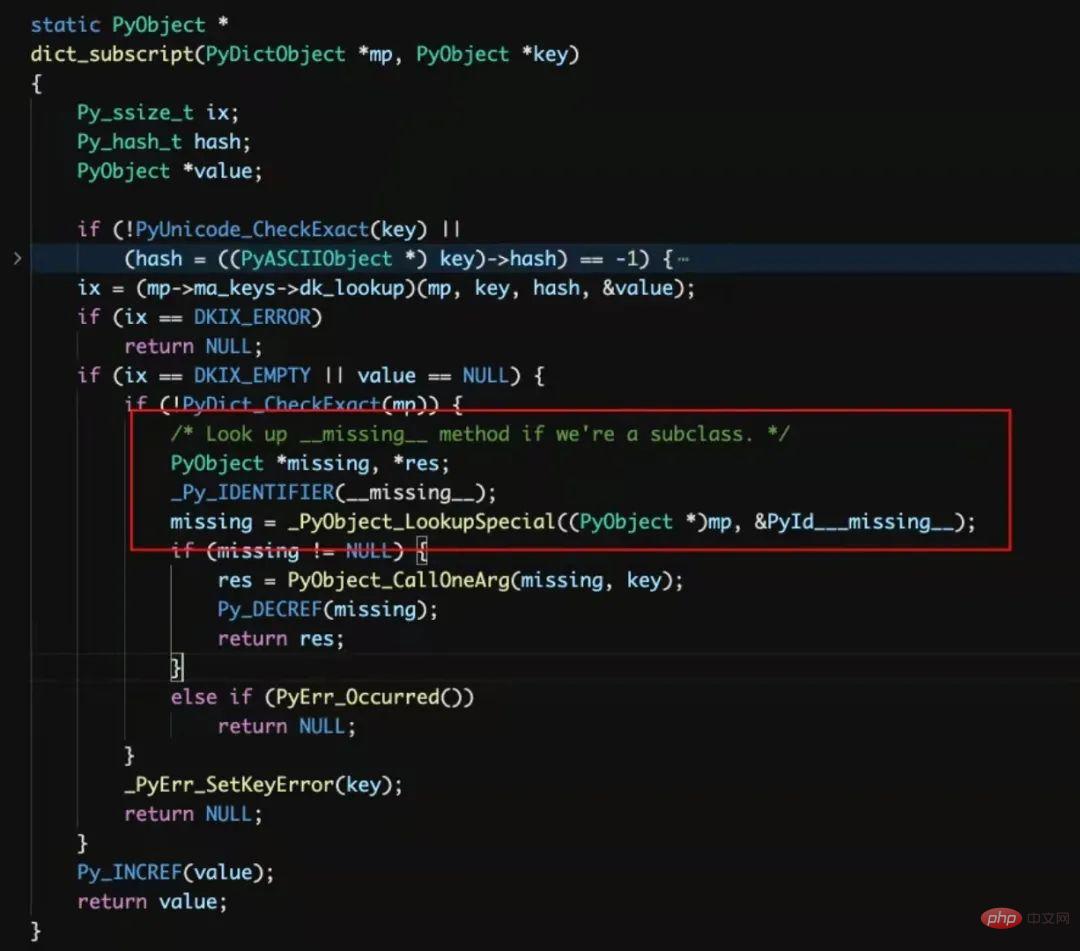
And this is interesting, Magic methods that only exist on subclasses of built-in types, Looking at the entire Python world, it is probably difficult to find a second example.
I suddenly had an association: this elusive __missing__() is like a magician who is good at "changing people into living beings". First, let the audience see him through the glass outside (that is, the official Document), however, when the door is opened, he is not inside (that is, the built-in type). After changing the props, he appears intact again (that is, a subclass of dict).
__missing__() is that in addition to the "magic" itself, it also requires a powerful "magic" "Talent driven.
In the last article, I found that the native magic methods are independent of each other. They may have the same core logic in the C language interface, but in the Python language interface, there is no calling relationship:
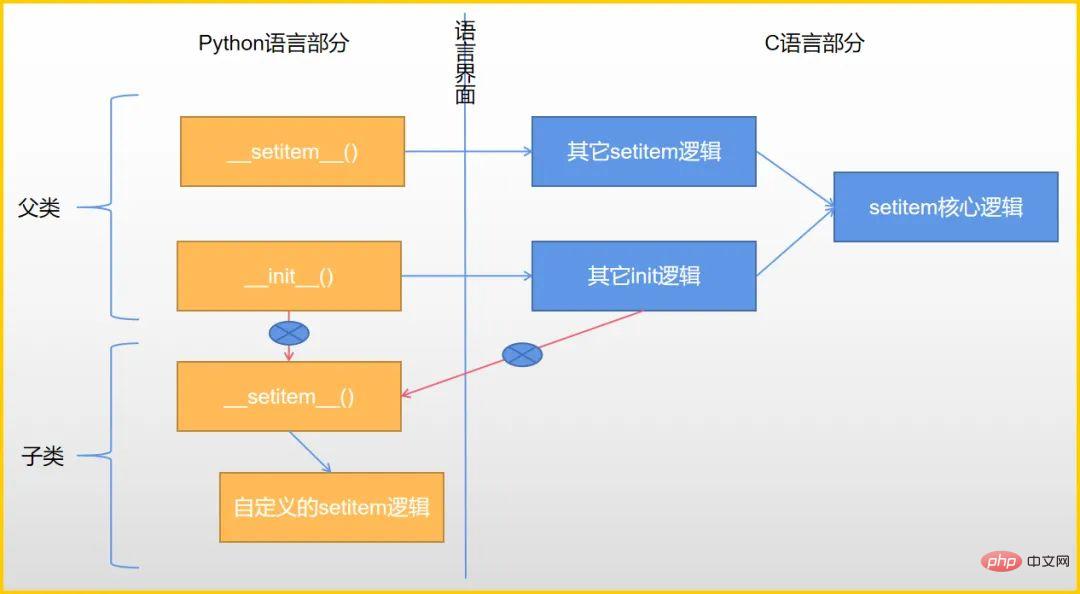
This kind of "no communication" behavior of magic methods violates the general code reuse principle, and also causes some strange behaviors in subclasses of built-in types. reason.
Official Python would rather provide new UserString, UserList, and UserDict subclasses than reuse magic methods. The only reasonable explanation seems to be that the cost of making magic methods call each other is too high.
However, for the special case __missing__(), Python has to compromise and have to pay this price!
__missing__() is a "second-class citizen" of magic methods. It has no independent calling entrance and can only be called passively by __getitem__(), that is, __missing__() depends on __getitem__().
Different from those "First-class citizens", such as __init__(), __enter__(), __len__(), __eq__(), etc., they are either in the object life cycle or execution A certain node in the process is triggered, or is triggered by a built-in function or operator. These are relatively independent events and have no dependencies.
__missing__() depends on __getitem__() to achieve method calling; and __getitem__() also depends on __missing__() to achieve complete functionality.
In order to achieve this, __getitem__() opens a backdoor in the interpreter code, returning from the C language interface to the Python interface to call the specific method named "__missing__".
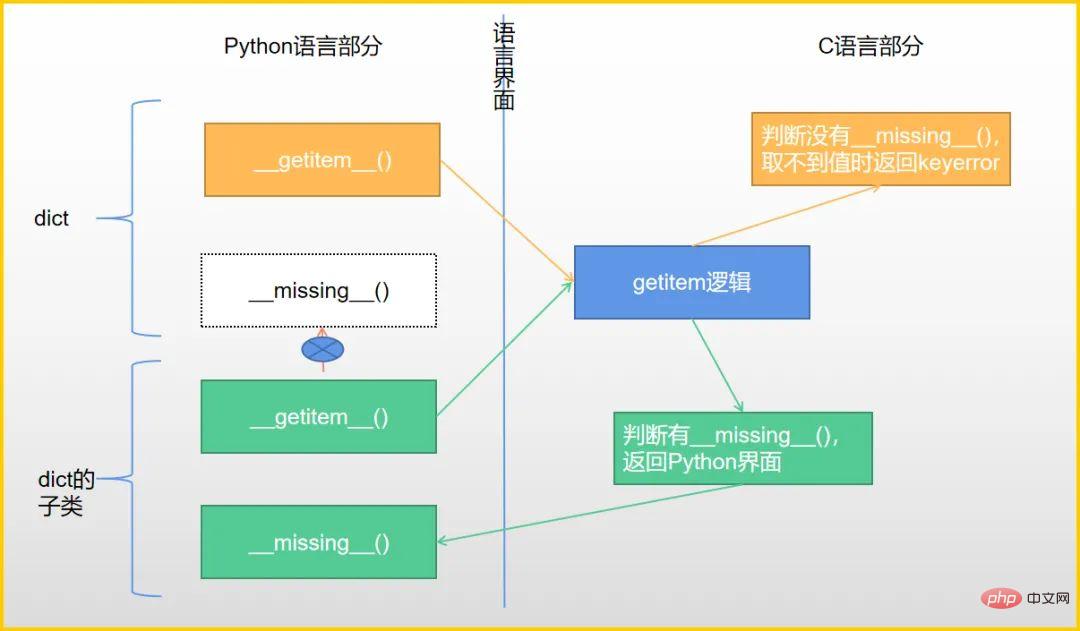
And this is the real "magic". So far, __missing__() seems to be the only magic method that enjoys such treatment!
Python's dictionary provides two built-in methods for obtaining values, namely __getitem__() and get(). When the value does not exist, their processing strategy is Different: The former will report an error KeyError, while the latter will return None.
Why does Python provide two different methods? Or you should ask, why does Python handle these two methods differently?
This may have a very complicated (or very simple) explanation, which I will not delve into in this article.
But one thing is certain: that is, the method of simply and crudely throwing KeyError with the native dict type is insufficient.
In order to give dictionary types more powerful performance (or let __getitem__() behave like get()), Python allows subclasses of dictionaries to define __missing__() for __getitem__() Find the call.
This article combs the implementation principle of __missing__(), revealing that it is not an inconspicuous existence, on the contrary, It is the only one that breaks the barriers between magic methods and supports being used by other magic methods. Special case of magic method call!
In order to maintain the independence of magic methods, Python took great pains to introduce derived classes such as UserString, UserList, and UserDict, but for __missing__(), it chose to compromise.
Recommended learning: python tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Python magic function learning __missing__. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!