Detailed explanation of Oracle classic skills RAC
This article brings you relevant knowledge about Oracle, which mainly introduces RAC related issues. Oracle Real Application Cluster is used to realize multi-machine shared database in a cluster environment to ensure High availability of the application, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended tutorial: "Oracle Tutorial"
There are usually two general directions to deal with the increasing business volume, one is One is vertical expansion, which is to increase the CPU computing power, memory capacity, disk carrying capacity, etc. of a single server; the other is horizontal expansion, which is to increase processing power by increasing the number of servers. The former has many problems such as business interruption and expansion limit. Especially with the rapid development of Internet services, a single server can hardly meet the business load requirements. Therefore, horizontal expansion is currently the more popular method.
What is Oracle RAC?
Oracle Real Application Cluster (RAC, real-time application cluster) is used to realize multi-machine shared database in a cluster environment to ensure high availability of applications; at the same time, it can automatically realize parallel processing and load balancing, and It can achieve fault tolerance and breakpoint-free recovery of the database when it fails. It is the core technology of Oracle database to support network computing environment.
Shared Storage Multi-Active Cluster
In this architecture, multiple nodes in the cluster run the same database instance, and the data is completely consistent, and no matter where the user starts from Node access, the data obtained are the same. The figure below is a schematic diagram of Oracle RAC. A cluster is formed by 3 nodes, and they share data. 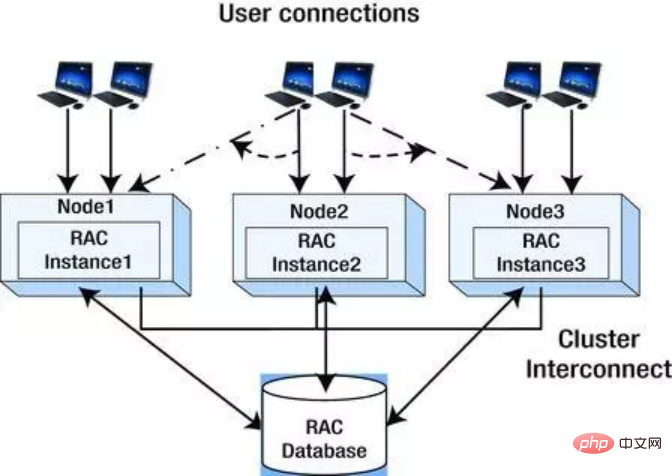
The characteristics of RAC can be summarized as follows:
- Nodes are interconnected and displayed as a server;
- Cluster software hides the internal structure ;
- The disk is shared;
- Each machine uses the same operating system;
- Multiple instances access the same database;
- Each node There is an example;
- Database files support physical or logical access;
- The reading and writing of data are controlled by software.
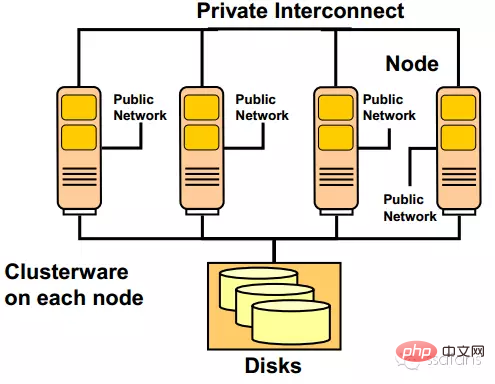
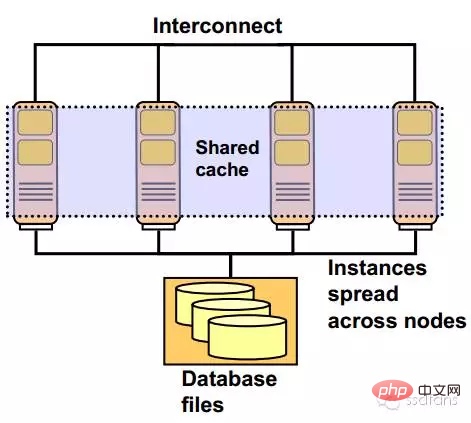
The difference between Oracle RAC and a single database server
As shown below, the main difference is that RAC is a clustered database. Managed through cluster software. 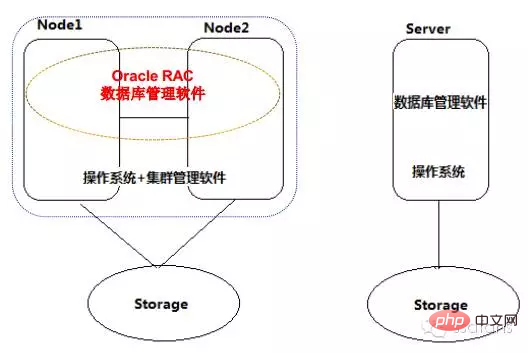
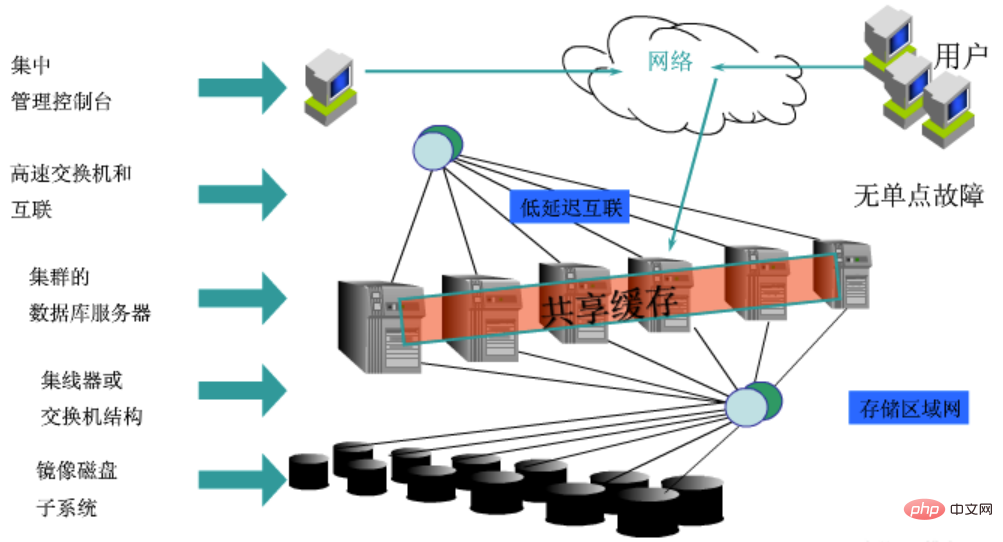
Oracle RAC hardware architecture
In order to ensure the availability of the entire cluster, Oracle RAC has many requirements for hardware during deployment. At the network level, Oracle RAC has a total of three network systems, namely the external access network, the internal private network and the storage network.
Needless to say more about external access to the network, I believe everyone understands it. The internal private network is mainly used for internal use of the Oracle cluster, including data transmission, heartbeat and cluster management. This part of the network requires dual switches and dual physical links during deployment to ensure that cluster abnormalities will not be caused by link failures. Behind is the storage network, which is used by the RAC cluster to access storage resources. This part is also link redundant. 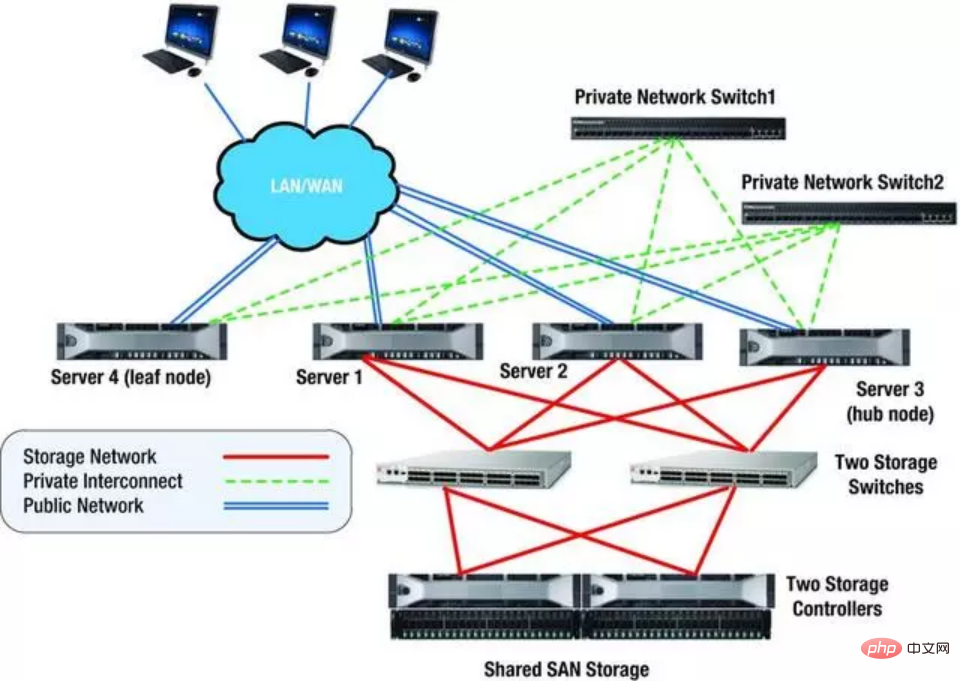
Another example is the figure below, which is a two-node RAC system. It can be seen that redundancy is implemented from the host to the switch. No matter which device fails, the business will not Affected. Shared storage comes with RAID redundancy. 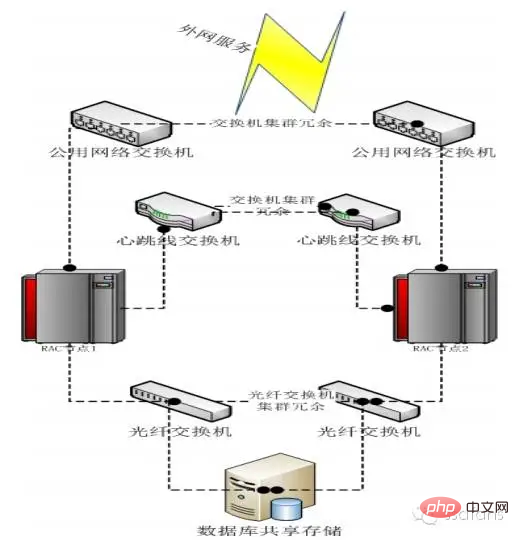
Among them, the host is called a node (Node). They must have the same CPU, memory and other configurations. Each one must have at least two network cards to access the internal and external networks, and an HBA card to connect to the shared storage, but more Most are connected to FC storage arrays through FC switches. Shared storage is the core of the RAC architecture. Most files are in shared storage, and many functions are developed for the security of shared storage. Generally, the optical fiber is connected through the FC interface and runs the SCSI protocol.
Oracle RAC software architecture
As shown below, it is a two-node RAC system. Oracle RDBMS is the database software, and Oracle Clusterware is the cluster software. The drivers are mainly network cards, HBA cards, ASMLib, etc.
Each node must have the same operating system and the version must be consistent, including patch numbers, etc. For example, operating system: RHEL AS 4.8 64bit, Linux kernel version: 2.6.9-89.EL. 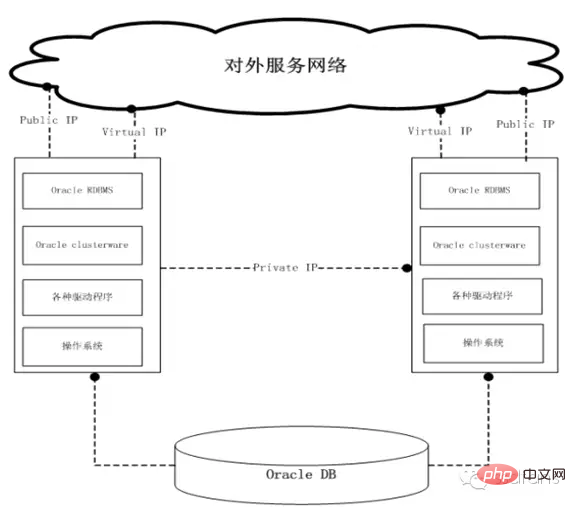
In order to understand Oracle RAC more deeply, let's take a look at the composition of its internal software modules. There are not many differences at the entire database level. The main additions are the following: virtual IP (VIP), ASM, Clusterware and quorum disk. These new components work together to complete Oracle's multi-active cluster function.
Virtual IP is the entrance for applications to access the database. This IP is not bound to any server, but can drift between any servers in the cluster. Due to this feature, when a server crash occurs, the database cluster can ensure that services are provided to the outside world through the same interface. 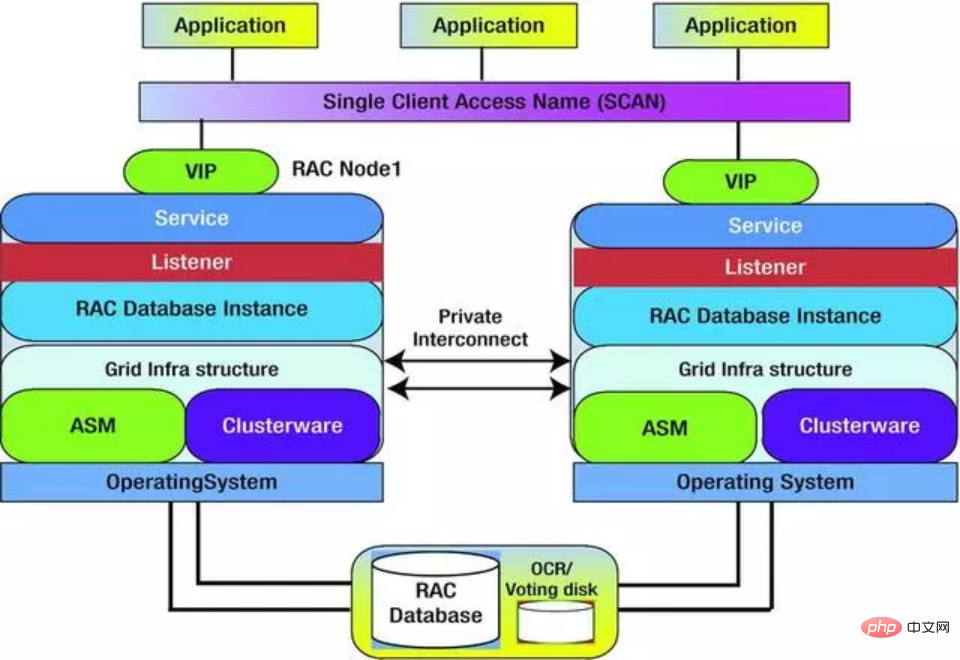
ASM and Clusterware implement cluster management functions. ASM implements disk management to avoid the risk of data inconsistency caused by simultaneous disk access, while Clusterware is used to manage the software processes and resource scheduling of Oracle clusters. .
The quorum disk is used to determine the abnormality of servers in the cluster. The nodes in the cluster mark their own health status by regularly updating the data in specific areas of the quorum disk. Other nodes can determine whether the node is down based on this data.
Logical structure
The following figure is the logical structure of Oracle RAC, and each component inside will be introduced in turn. 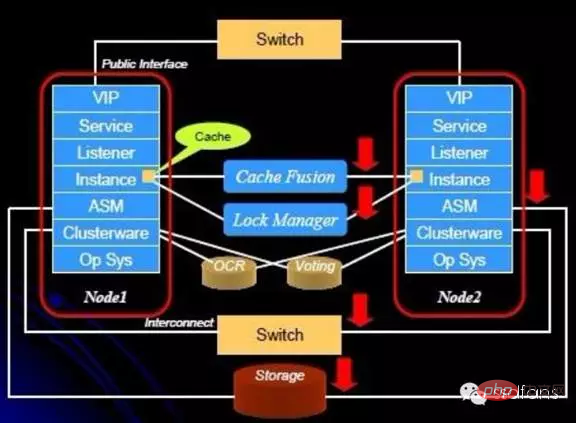
DLM: Concurrency Control
Each node has equal rights to access shared stored data, Oracle RAC uses Distribute Lock Management (DLM) for multiple nodes Control of concurrent access. The distributed lock manager is responsible for coordinating the competition for shared resources between nodes. When a node accesses data, it must first apply through DLM and confirm that it will not conflict with other nodes before it can be used.
OCR: Amnesia
Amnesia: If each node has a copy of the cluster configuration information, then an error will occur if there is no synchronization after modifying the configuration.
So, the cluster can only have one configuration information, shared by all nodes. Oracle RAC uses OCR Disk files to solve amnesia.
OCR Disk can only be modified by the Master node. Each node has a copy in the OCR Cache memory. When a node wants to modify the OCR Disk, it requests the Master node, and the OCR process on this node updates the local and other node OCR Cache contents. OCR Disk is backed up regularly every few hours.
Voting Disk: Split Brain
Split Brain: The nodes in the cluster use heartbeat detection to know whether the other party is good. If there is a problem with the heartbeat, both nodes will think that the other party is wrong. It will require exclusive data, which will destroy the consistency of the data.
Voting Disk is used to record the status of members between nodes. When a split-brain occurs, the one with the highest number of votes will be selected to gain control and other nodes will be kicked out.
IO isolation: The kicked-out node can no longer access data, so IO isolation is required. The mechanism of Oracle RAC is to restart the failed node.
Cache Fusion Lock
Database files are shared, and Cache Fusion Lock solves storage sharing and concurrent access control outside the cluster level.
Four kinds of networks
1.Public network: Use Public IP to provide external data query, database maintenance, and server maintenance.
2.Virtual network: Use Virtual IP to provide application connections, and the application uses this IP.
In the TCP/IP protocol, the TCP Header contains the source and destination ports, the IP header contains the source and destination IPs, and the application layer database monitor records the IP and port. When the TCP times out, it is known that there is a problem with the database or monitor. The TCP/IP protocol stack timeout is determined by the OS, and each OS has different definitions. To shorten the time to catch errors, Oracle RAC uses VIP. Virtual IP is floating and not bound to the physical network card. If a node fails, the VIP will be moved to a good node. However, the VIP cannot be found in the monitoring of the good node. The application will immediately detect the problem and switch to Other VIPs send connection requests.
3.Private network: Use Private IP for RAC heartbeat detection and Cache Fusion Lock, which requires high speed.
4. Storage network: composed of storage devices, HBA cards, and FC networks.
Oracle Clusterware
On a single machine, only the OS can handle upper-layer requests, but when there are multiple machines, the cluster management software Oracle Clusterware will intercept requests to other nodes before the OS kernel, and other The node's Clusterware communication completes the request.
Application layer: RDBMS
The application layer is composed of several CRS Resources. Each resource is a complete service composed of several processes. LMON (Lock Monitor) monitors CRS Resource and restarts and switches when abnormality occurs to ensure the high availability of Oracle RAC service.
Cache Fusion
Cache Fusion can be understood literally - cache fusion, in fact, is to uniformly manage the cache of each node, avoiding the need to operate the disk for every read, and accelerating IO performance . Because the Private network is very fast, it is faster than reading the disk. Time to read data blocks from different locations:
- Local Cache: 0.01 ms
- Network access to other node Cache: 2.5 ms
- Disk: 14 ms. But now with SSD or all-flash arrays on the storage side, the latency is around 1 ms. So with the all-flash array, Cache Fusion is probably meaningless.
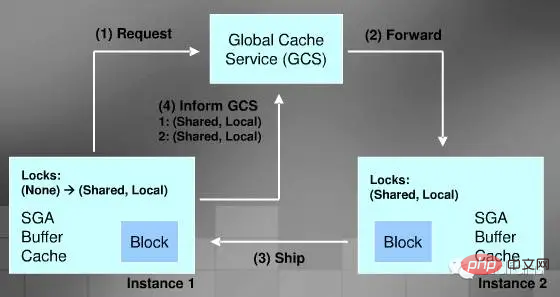
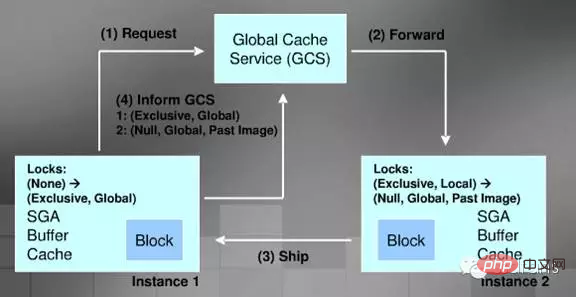
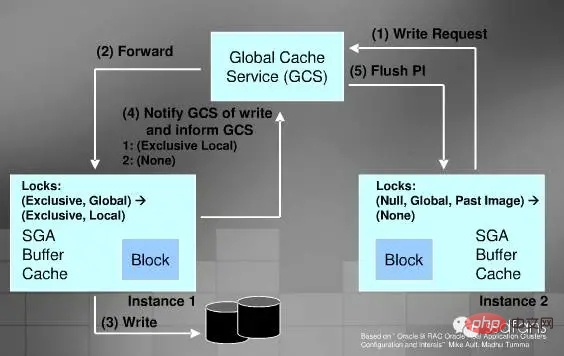
Cache Fusion is managed through GCS (Global Cache Service), which treats your Cache as one big Cache.
Read Cache process
- Load balancing cluster: allocate requests to different members according to a certain algorithm;
- High performance cluster (HPC, High Performance Cluster): adopted Awesome machines composed of specialized software and hardware such as vector processors, with powerful computing performance and extremely expensive prices, such as Tianhe Computer;
- High Reliability Cluster (HAC: High Available Cluster, Failover Cluster): Very good reliability , the hardware and software are very fault-tolerant, and the database clusters used daily fall into this category.
Dual-machine hot standby
Usually one of them is idle and on standby. If the one working fails, let him Alternate replacement.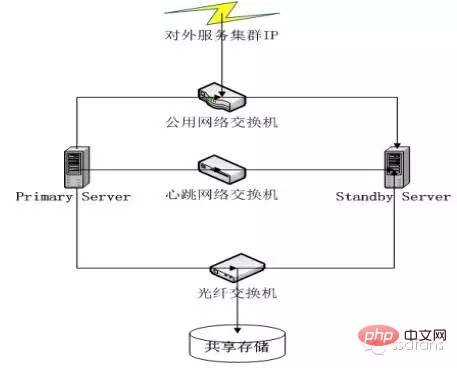
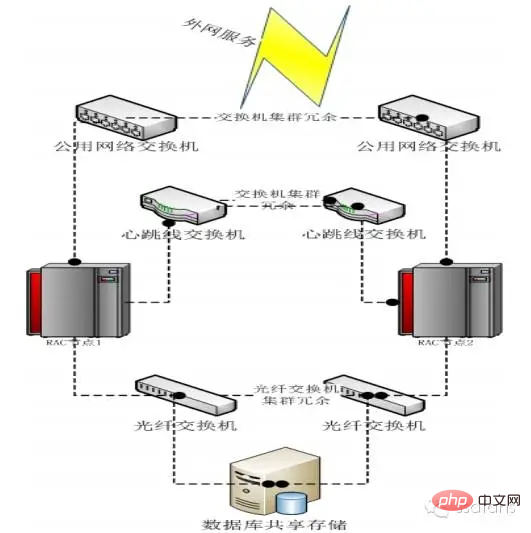
Dual-machine mutual backup

Dual-machine duplex
Oracle Learning Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Oracle classic skills RAC. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How long will Oracle database logs be kept?
May 10, 2024 am 03:27 AM
How long will Oracle database logs be kept?
May 10, 2024 am 03:27 AM
The retention period of Oracle database logs depends on the log type and configuration, including: Redo logs: determined by the maximum size configured with the "LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST" parameter. Archived redo logs: Determined by the maximum size configured by the "DB_RECOVERY_FILE_DEST_SIZE" parameter. Online redo logs: not archived, lost when the database is restarted, and the retention period is consistent with the instance running time. Audit log: Configured by the "AUDIT_TRAIL" parameter, retained for 30 days by default.
 Function to calculate the number of days between two dates in oracle
May 08, 2024 pm 07:45 PM
Function to calculate the number of days between two dates in oracle
May 08, 2024 pm 07:45 PM
The function in Oracle to calculate the number of days between two dates is DATEDIFF(). The specific usage is as follows: Specify the time interval unit: interval (such as day, month, year) Specify two date values: date1 and date2DATEDIFF(interval, date1, date2) Return the difference in days
 The order of the oracle database startup steps is
May 10, 2024 am 01:48 AM
The order of the oracle database startup steps is
May 10, 2024 am 01:48 AM
The Oracle database startup sequence is: 1. Check the preconditions; 2. Start the listener; 3. Start the database instance; 4. Wait for the database to open; 5. Connect to the database; 6. Verify the database status; 7. Enable the service (if necessary ); 8. Test the connection.
 How to use interval in oracle
May 08, 2024 pm 07:54 PM
How to use interval in oracle
May 08, 2024 pm 07:54 PM
The INTERVAL data type in Oracle is used to represent time intervals. The syntax is INTERVAL <precision> <unit>. You can use addition, subtraction, multiplication and division operations to operate INTERVAL, which is suitable for scenarios such as storing time data and calculating date differences.
 How much memory does oracle require?
May 10, 2024 am 04:12 AM
How much memory does oracle require?
May 10, 2024 am 04:12 AM
The amount of memory required by Oracle depends on database size, activity level, and required performance level: for storing data buffers, index buffers, executing SQL statements, and managing the data dictionary cache. The exact amount is affected by database size, activity level, and required performance level. Best practices include setting the appropriate SGA size, sizing SGA components, using AMM, and monitoring memory usage.
 How to see the number of occurrences of a certain character in Oracle
May 09, 2024 pm 09:33 PM
How to see the number of occurrences of a certain character in Oracle
May 09, 2024 pm 09:33 PM
To find the number of occurrences of a character in Oracle, perform the following steps: Get the total length of a string; Get the length of the substring in which a character occurs; Count the number of occurrences of a character by subtracting the substring length from the total length.
 Oracle database server hardware configuration requirements
May 10, 2024 am 04:00 AM
Oracle database server hardware configuration requirements
May 10, 2024 am 04:00 AM
Oracle database server hardware configuration requirements: Processor: multi-core, with a main frequency of at least 2.5 GHz. For large databases, 32 cores or more are recommended. Memory: At least 8GB for small databases, 16-64GB for medium sizes, up to 512GB or more for large databases or heavy workloads. Storage: SSD or NVMe disks, RAID arrays for redundancy and performance. Network: High-speed network (10GbE or higher), dedicated network card, low-latency network. Others: Stable power supply, redundant components, compatible operating system and software, heat dissipation and cooling system.
 How to replace string in oracle
May 08, 2024 pm 07:24 PM
How to replace string in oracle
May 08, 2024 pm 07:24 PM
The method of replacing strings in Oracle is to use the REPLACE function. The syntax of this function is: REPLACE(string, search_string, replace_string). Usage steps: 1. Identify the substring to be replaced; 2. Determine the new string to replace the substring; 3. Use the REPLACE function to replace. Advanced usage includes: multiple replacements, case sensitivity, special character replacement, etc.






