In Oracle, you can use the SELECT statement and the DISTINCT keyword to achieve query deduplication, filter duplicate rows in the query result set, and ensure that the value of the specified column or columns returned after the query operation is unique; The syntax is "SELECT DISTINCT field name FROM data table name;".

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Oracle 11g version, Dell G3 computer.
In Oracle, you can use the SELECT statement and the DISTINCT keyword to achieve query deduplication.
Use the DISTINCT clause in the SELECT statement to filter duplicate rows in the result set. It ensures that the values returned in the specified column or columns in the SELECT clause are unique.
The following explains the syntax of the SELECT DISTINCT statement:
SELECT DISTINCT column_name FROM table_name;
In the above syntax, the column_name column of the table_name table The values in will be compared to filter out duplicates.
To retrieve unique data based on multiple columns, simply specify a list of columns in the SELECT clause, as follows:
SELECT DISTINCT column_1, column_2, ... FROM table_name;
In this syntax, ## The combination of values in #column_1, column_2, and column_n is used to determine the uniqueness of the data. The
DISTINCT clause can only be used in the SELECT statement.
DISTINCT is not a synonym for the SQL standard UNIQUE. It is a good habit to always use DISTINCT instead of UNIQUE.
SELECT DISTINCT to see how it works.
contacts) table in the sample database:

SELECT first_name FROM contacts ORDER BY first_name;
319 rows, indicating that the contact (contacts) table has 319 rows.
DISTINCT keyword to the SELECT statement above, as follows:
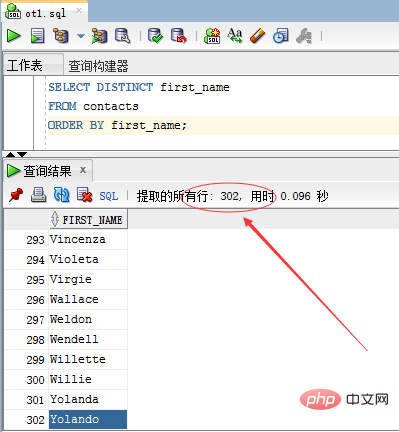
SELECT DISTINCT first_name FROM contacts ORDER BY first_name;

302 rows, indicating the contact (contacts) table There are 17 rows that are duplicates and they have been filtered.
order_items table below. The structure of the table is as follows:
order_items table:
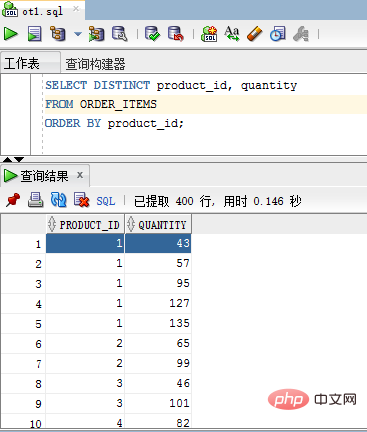
SELECT DISTINCT product_id, quantity FROM ORDER_ITEMS ORDER BY product_id;

product_id and quantity columns are both used to evaluate the uniqueness of the rows in the result set.
DISTINCT treats NULL values as duplicate values. If you use the SELECT DISTINCT statement to query data from a column with multiple NULL values, the result set contains only one NULL value.
locations table in the sample database, the structure is as follows -
stateRetrieve data with multiple NULL values in the column:
SELECT DISTINCT state FROM locations ORDER BY state NULLS FIRST;
NULL value is returned.
Oracle Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to perform query deduplication in oracle. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!