
This article brings you relevant knowledge about mysql, which mainly introduces the various lock mechanism issues in mysql. Locks are used by the database to ensure the consistency of data. A rule designed to make shared resources orderly when accessed concurrently. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended learning: mysql tutorial
If you want to ensure data security in multi-threads How is accuracy achieved? That's right, through synchronization. Synchronization is equivalent to locking. What are the benefits of adding a lock? When one thread is actually manipulating data, other threads can only wait. When a thread completes execution, the lock is released. Only other threads can perform operations!
The function of the lock in our MySQL database is also similar. In the isolation of transaction processing, problems such as dirty reads, non-repeatable reads, and phantom reads may occur. Therefore, the role of locks can also be solved. these questions!
In a database, data is a resource shared and accessed by many users. How to ensure the consistency and effectiveness of concurrent data access is a problem that all databases must solve. Due to the characteristics of MySQL's own architecture, In different storage engines, locking mechanisms are designed to face specific scenarios. Therefore, the differences in engines lead to very different locking mechanisms.
In order to ensure the consistency of data, the database uses a rule designed by using various shared resources to become orderly when accessed concurrently.
For example: When purchasing a product on an e-commerce website, there is only one product in the product list, and at this time two people are buying it at the same time, so who can buy it is a key issue.
Transactions will be used here to perform a series of operations:
First take out the item data from the product table
Then insert the order
After payment, Then insert the payment table information
Update the quantity of goods in the product table
In the above process, the lock can be used to protect the product quantity data information and achieve isolation, that is, only the first user is allowed to complete The entire purchase process, while other users can only wait, thus solving the conflict problem in concurrency.
Classification by operation:
Shared lock: also called read lock. For the same data, multiple transaction read operations can be locked at the same time without affecting each other, but the data records cannot be modified.
Exclusive lock: also called write lock. Before the current operation is completed, reading and writing of other operations will be blocked
Classified by granularity:
Table-level lock: During the operation, the entire operation will be locked surface. The overhead is small and locking is fast; deadlock will not occur; the locking force is strong, the probability of lock conflict is high, and the concurrency is the lowest. Prefer MyISAM storage engine!
Row-level lock: During operation, the current operation row will be locked. The overhead is large and locking is slow; deadlocks may occur; the locking granularity is small, the probability of lock conflicts is low, and the concurrency is high. Prefer InnoDB storage engine!
Page-level lock: The lock granularity, the probability of conflict, and the cost of locking are between table locks and row locks. Deadlocks will occur and concurrency performance is average.
Classification by usage:
Pessimistic lock: Every time you query the data, you think that others will modify it. It is very pessimistic, so you add a lock when querying.
Optimistic lock: Every time you query the data, you think that others will not modify it. You are very optimistic, but when updating, you will judge whether others have updated the data during this period.
Different storage engine support Lock
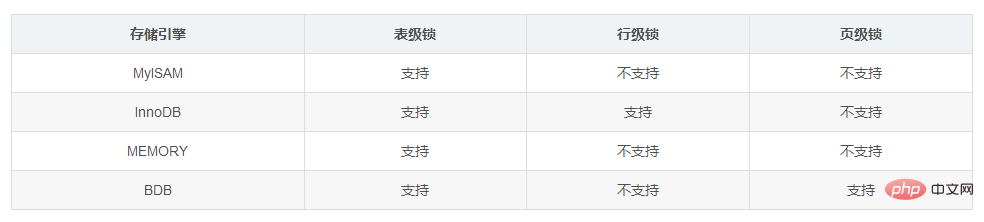
Multiple shared locks can be shared. If there is a key, InnoDB defaults to a row lock. If not, it will Upgraded to table lock, when row lock is used, multiple windows can modify the data of different rows. If they are in the same row, they need to wait for the submission of the first lock. Different rows can be modified directly, but if the other one wants to query, it must wait for the submission of subsequent modifications. The lock disappears after submission
Shared lock:
SELECT语句 LOCK IN SHARE MODE;
Window 1:
- 窗口1
/*
共享锁:数据可以被多个事务查询,但是不能修改
*/
-- 开启事务
START TRANSACTION;
-- 查询id为1的数据记录。加入共享锁
SELECT * FROM student WHERE id=1 LOCK IN SHARE MODE;
-- 查询分数为99分的数据记录。加入共享锁
SELECT * FROM student WHERE score=99 LOCK IN SHARE MODE;
-- 提交事务
COMMIT;Window 2:
-- 窗口2 -- 开启事务 START TRANSACTION; -- 查询id为1的数据记录(普通查询,可以查询) SELECT * FROM student WHERE id=1; -- 查询id为1的数据记录,并加入共享锁(可以查询。共享锁和共享锁兼容) SELECT * FROM student WHERE id=1 LOCK IN SHARE MODE; -- 修改id为1的姓名为张三三(不能修改,会出现锁的情况。只有窗口1提交事务后,才能修改成功) UPDATE student SET NAME='张三三' WHERE id = 1; -- 修改id为2的姓名为李四四(修改成功,InnoDB引擎默认是行锁) UPDATE student SET NAME='李四四' WHERE id = 2; -- 修改id为3的姓名为王五五(修改失败,InnoDB引擎如果不采用带索引的列加锁。则会提升为表锁) UPDATE student SET NAME='王五五' WHERE id = 3; -- 提交事务 COMMIT;
Exclusive lock:
When the exclusive lock is executed, other transactions can be queried normally, but no lock operations are allowed
-- 标准语法 SELECT语句 FOR UPDATE;
Window 1:
-- 窗口1
/*
排他锁:加锁的数据,不能被其他事务加锁查询或修改
*/
-- 开启事务
START TRANSACTION;
-- 查询id为1的数据记录,并加入排他锁
SELECT * FROM student WHERE id=1 FOR UPDATE;
-- 提交事务
COMMIT;Window 2:
-- 窗口2 -- 开启事务 START TRANSACTION; -- 查询id为1的数据记录(普通查询没问题) SELECT * FROM student WHERE id=1; -- 查询id为1的数据记录,并加入共享锁(不能查询。因为排他锁不能和其他锁共存) SELECT * FROM student WHERE id=1 LOCK IN SHARE MODE; -- 查询id为1的数据记录,并加入排他锁(不能查询。因为排他锁不能和其他锁共存) SELECT * FROM student WHERE id=1 FOR UPDATE; -- 修改id为1的姓名为张三(不能修改,会出现锁的情况。只有窗口1提交事务后,才能修改成功) UPDATE student SET NAME='张三' WHERE id=1; -- 提交事务 COMMIT;
MyISAM read lock:
MyISAM locks the entire table. When reading the lock, all transactions can be checked without unlocking, and no other operations, including its own transactions, are allowed. Operation
-- 加锁 LOCK TABLE 表名 READ; -- 解锁(将当前会话所有的表进行解锁) UNLOCK TABLES;
MyISAM write lock:
When writing the lock, other transactions cannot perform any operations as long as it is not unlocked. The own transaction can operate
-- 标准语法 -- 加锁 LOCK TABLE 表名 WRITE; -- 解锁(将当前会话所有的表进行解锁) UNLOCK TABLES;
Pessimistic lock :
is very pessimistic. It has a conservative attitude towards data being modified by the outside world and believes that the data will be modified at any time.
The data needs to be locked during the entire data processing. Pessimistic locking generally relies on the locking mechanism provided by relational databases.
Row locks and table locks are pessimistic locks regardless of whether they are read or write locks.
Optimistic lock:
就是很乐观,每次自己操作数据的时候认为没有人会来修改它,所以不去加锁。
但是在更新的时候会去判断在此期间数据有没有被修改。
需要用户自己去实现,不会发生并发抢占资源,只有在提交操作的时候检查是否违反数据完整性。
乐观锁的简单实现方式:
实现思想:加标记去比较,一样则执行,不同则不执行
方式一:版本号
给数据表中添加一个version列,每次更新后都将这个列的值加1。
读取数据时,将版本号读取出来,在执行更新的时候,比较版本号。
如果相同则执行更新,如果不相同,说明此条数据已经发生了变化。
用户自行根据这个通知来决定怎么处理,比如重新开始一遍,或者放弃本次更新。
-- 创建city表
CREATE TABLE city(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, -- 城市id
NAME VARCHAR(20), -- 城市名称
VERSION INT -- 版本号
);
-- 添加数据
INSERT INTO city VALUES (NULL,'北京',1),(NULL,'上海',1),(NULL,'广州',1),(NULL,'深圳',1);
-- 修改北京为北京市
-- 1.查询北京的version
SELECT VERSION FROM city WHERE NAME='北京';
-- 2.修改北京为北京市,版本号+1。并对比版本号
UPDATE city SET NAME='北京市',VERSION=VERSION+1 WHERE NAME='北京' AND VERSION=1;方式二:时间戳
和版本号方式基本一样,给数据表中添加一个列,名称无所谓,数据类型需要是timestamp
每次更新后都将最新时间插入到此列。
读取数据时,将时间读取出来,在执行更新的时候,比较时间。
如果相同则执行更新,如果不相同,说明此条数据已经发生了变化。
悲观锁和乐观锁使用前提:
对于读的操作远多于写的操作的时候,这时候一个更新操作加锁会阻塞所有的读取操作,降低了吞吐量。最后还要释放锁,锁是需要一些开销的,这时候可以选择乐观锁。
如果是读写比例差距不是非常大或者系统没有响应不及时,吞吐量瓶颈的问题,那就不要去使用乐观锁,它增加了复杂度,也带来了业务额外的风险。这时候可以选择悲观锁。
推荐学习:mysql学习教程
The above is the detailed content of Detailed analysis of mysql lock mechanism. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!