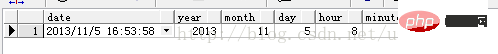What are the functions of oracle?
Oracle's functions include: 1. String functions, including ASCII(), CONCAT(), etc.; 2. Numeric functions, including ABS(), COS(), etc.; 3. Date functions, including EXTRACT( ), ROUND(), etc.; 4. Conversion functions, including TO_CHAR(), TO_DATE(), etc.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Oracle 11g version, Dell G3 computer.
Oracle SQL statements often use Oracle's own functions. These functions enrich the language functions of SQL and provide more operability for Oracle SQL. Oracle functions can accept zero or more input parameters and return an output result. There are two main types of functions used in Oracle database:
1. Single-row function: When each function is applied to the records of the table, only the column values in one row can be entered as input. parameters (or constants), and returns a result.
For example 1: MOD(X,Y) is a remainder function that returns the remainder of X divided by Y, where X and Y can be column values or constants.
For example 2: TO_CHAR(X,'YYYYMMDD') is a function that converts time type to string, where X can be a column of a certain time type (date) in the row, or it can be a time type constant .
Commonly used single-line functions are generally in the following categories:
String functions: operate on strings, such as: TO_CHAR(), SUBSTR(), DECODE() etc.
Numeric function: performs calculations or operations on numerical values and returns a number. For example: ABS(), MOD(), ROUND(), etc.
Conversion function: Convert one data type to another type: for example: TO_CHAR(), TO_NUMBER(), TO_DATE(), etc.
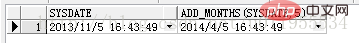
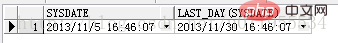
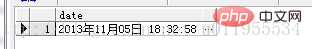
Date function: A function that operates on time and date. For example: TRUNC(), SYSDATE(), ADD_MONTHS(), etc.
2. Aggregation function: Aggregation function can operate on multiple rows of data at the same time and return a result. For example, SUM(x) returns the sum of the x columns in the result set.
1. String function
Character function accepts character parameters, which can be columns in the table or a string expression.
Commonly used character functions:
Function |
Description |
ASCII(X) |
Returns the ASCII code of character X |
CONCAT(X,Y) |
Connect strings X and Y |
| ##INSTR(X,STR[, START][,N) | Search str from X, you can specify starting from start, or you can specify starting from n |
| Returns the length of X | |
| X is converted to lowercase | |
| X is converted to uppercase | |
| Truncate the trim_str string from the left side of X, default Truncate spaces | |
| Truncate the trim_str string to the right of X , spaces are truncated by default | ##TRIM([TRIM_STR FROM]X) |
Truncate both sides of X trim_str string, spaces are truncated by default |
REPLACE(X,old,new) |
in X Find old and replace it with new |
SUBSTR(X,start[,length]) |
Return X String, starting from start, intercepting length characters, default length, default to the end |
Examples of the above functions: |
Example result |
SELECT ASCII ('a') FROM dual; | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ##97 | ##SELECT CONCAT('Hello','world') FROM dual; |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ##SELECT INSTR('Hello world','or') FROM dual; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ##SELECT LENGTH('Hello') FROM dual; | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ##SELECT LOWER('Hello') FROM dual; | hello | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SELECT UPPER('hello') FROM dual; | HELLO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SELECT LTRIM('=Hello=','=') FROM dual; |
Hello= | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SELECT RTRIM('=Hello=','=') FROM dual; | =Hello | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SELECT TRIM('='FROM'=Hello=') FROM dual; | Hello | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SELECT REPLACE(' ABCDE','CD','AAA')FROM dual; | ABAAAE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
##SELECT SUBSTR('ABCDE ',2,3) FROM dual; |
BCD |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2. Numeric function Numeric function accepts numeric parameters. The parameter can come from a column in the table, or it can be a numeric expression.
The above is the detailed content of What are the functions of oracle?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website! Statement of this Website
The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cn

Hot AI Tools
Undresser.AI UndressAI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos 
AI Clothes RemoverOnline AI tool for removing clothes from photos. 
Undress AI ToolUndress images for free 
Clothoff.ioAI clothes remover 
AI Hentai GeneratorGenerate AI Hentai for free. 
Hot Article
Assassin's Creed Shadows: Seashell Riddle Solution
3 weeks ago
By DDD
What's New in Windows 11 KB5054979 & How to Fix Update Issues
2 weeks ago
By DDD
Where to find the Crane Control Keycard in Atomfall
3 weeks ago
By DDD
Saving in R.E.P.O. Explained (And Save Files)
1 months ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌

Hot Tools
Notepad++7.3.1Easy-to-use and free code editor 
SublimeText3 Chinese versionChinese version, very easy to use 
Zend Studio 13.0.1Powerful PHP integrated development environment 
Dreamweaver CS6Visual web development tools 
SublimeText3 Mac versionGod-level code editing software (SublimeText3) 
Hot Topics
CakePHP Tutorial
 1385
1385
 52
52
 How to check tablespace size of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
How to check tablespace size of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
To query the Oracle tablespace size, follow the following steps: Determine the tablespace name by running the query: SELECT tablespace_name FROM dba_tablespaces; Query the tablespace size by running the query: SELECT sum(bytes) AS total_size, sum(bytes_free) AS available_space, sum(bytes) - sum(bytes_free) AS used_space FROM dba_data_files WHERE tablespace_  How to uninstall Oracle installation failed
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to uninstall Oracle installation failed
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Uninstall method for Oracle installation failure: Close Oracle service, delete Oracle program files and registry keys, uninstall Oracle environment variables, and restart the computer. If the uninstall fails, you can uninstall manually using the Oracle Universal Uninstall Tool.  How to encrypt oracle view
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to encrypt oracle view
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
Oracle View Encryption allows you to encrypt data in the view, thereby enhancing the security of sensitive information. The steps include: 1) creating the master encryption key (MEk); 2) creating an encrypted view, specifying the view and MEk to be encrypted; 3) authorizing users to access the encrypted view. How encrypted views work: When a user querys for an encrypted view, Oracle uses MEk to decrypt data, ensuring that only authorized users can access readable data.  How to view instance name of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to view instance name of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
There are three ways to view instance names in Oracle: use the "sqlplus" and "select instance_name from v$instance;" commands on the command line. Use the "show instance_name;" command in SQL*Plus. Check environment variables (ORACLE_SID on Linux) through the operating system's Task Manager, Oracle Enterprise Manager, or through the operating system.  How to solve the problem of closing oracle cursor
Apr 11, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to solve the problem of closing oracle cursor
Apr 11, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
The method to solve the Oracle cursor closure problem includes: explicitly closing the cursor using the CLOSE statement. Declare the cursor in the FOR UPDATE clause so that it automatically closes after the scope is ended. Declare the cursor in the USING clause so that it automatically closes when the associated PL/SQL variable is closed. Use exception handling to ensure that the cursor is closed in any exception situation. Use the connection pool to automatically close the cursor. Disable automatic submission and delay cursor closing.  How to delete all data from oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:36 PM
How to delete all data from oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:36 PM
Deleting all data in Oracle requires the following steps: 1. Establish a connection; 2. Disable foreign key constraints; 3. Delete table data; 4. Submit transactions; 5. Enable foreign key constraints (optional). Be sure to back up the database before execution to prevent data loss.  How to check invalid numbers of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to check invalid numbers of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
Oracle Invalid numeric errors may be caused by data type mismatch, numeric overflow, data conversion errors, or data corruption. Troubleshooting steps include checking data types, detecting digital overflows, checking data conversions, checking data corruption, and exploring other possible solutions such as configuring the NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS parameter and enabling data verification logging.  How to create oracle dynamic sql
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:06 AM
How to create oracle dynamic sql
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:06 AM
SQL statements can be created and executed based on runtime input by using Oracle's dynamic SQL. The steps include: preparing an empty string variable to store dynamically generated SQL statements. Use the EXECUTE IMMEDIATE or PREPARE statement to compile and execute dynamic SQL statements. Use bind variable to pass user input or other dynamic values to dynamic SQL. Use EXECUTE IMMEDIATE or EXECUTE to execute dynamic SQL statements. 
|