
This article brings you relevant knowledge about java, which mainly introduces related issues about process control, including input and output, branch statements and loop statements, etc. I hope it will be helpful to everyone helpful.

Recommended study: "java tutorial"
Two input methods:
Method one: java.util.Scanner
The code is as follows:
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
var sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入姓名:");
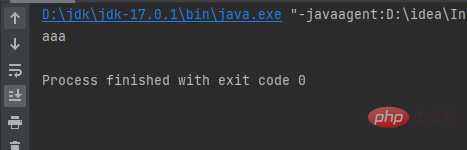
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.printf("%n欢迎你:%s", name);
}}Generate Scanner object , output "Please enter your name:", return the input string and assign it to name, output "%nWelcome %s" where %n means line break %s means name
Result: 
Method 2: JOptionPane If the input content is confirmed, the string value will be null. As long as it is not confirmed, it will be null
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String w = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("请输入词汇:");
System.out.println(w);
}}Result: 
Three ways to output on the console
Method one: System.out.print(); Output to the console
Method two: System.out.println(); Output to the console and wrap
Method 3: System.out.printf(); Format the output to the console
Code demonstration:
The first type is output directly without line breaks
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int w = 1;
int a = 2;
System.out.print(w);
System.out.print(a);
}}Result: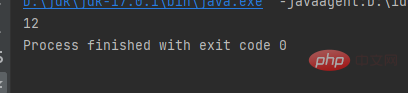
The second type is output with line breaks
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int w = 1;
int a = 2;
System.out.println(w);
System.out.println(a);
}} Result: 
The third formatted output
%d means an int type variable, which is to replace the first value with the value of w %d, the value of a replaces the second %d
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int w = 1;
int a = 2;
System.out.printf("w=%d a=%d", w, a);
}} Result: 
if() As long as the conditions in brackets are correct, it will return true, if it is wrong, it will return false
else means otherwise
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (1>2){
System.out.println("A");
}else {
System.out.println("B");
}
}}Multiple judgments are as follows : If the first judgment is incorrect, the next judgment will be made. When the return value is true, it will be executed. Otherwise, else
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (1 > 2) {
System.out.println("A");
} else if (1 > 0) {
System.out.println("B");
} else {
System.out.println("C");
}
}}switch multi-branch switch statement will be executed.
switch(w) w in parentheses is the judgment parameter, and the number after case is the value that matches w. When the value of w matches the value after the case, the statement in the current case is executed
break means to exit the current judgment, which means that there is no need to judge again later
default means the default value, when there is no match The default is this
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int w=1;
String wk = "";
switch (w) {
case 2:
wk = "星期一";
break;
case 3:
wk = "星期二";
break;
case 4:
wk = "星期三";
break;
case 5:
wk = "星期四";
break;
case 6:
wk = "星期五";
break;
case 7:
wk = "星期六";
break;
default:
wk = "星期日";
break;
}
System.out.println(wk);
}} result: 
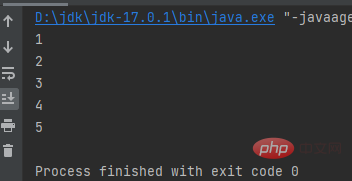
for ( int i = 0; i 5
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i <p> Result: <br><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/7aa0164809e23dcd8cf553ff03309c56-7.png" class="lazy" alt="Summarize and organize the process control of JAVA learning"></p><h2>for in</h2><blockquote><p>for in is mainly used to loop collections Or an array, use an array to demonstrate </p></blockquote><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int i : a) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}}i corresponds to the value in the table below of array a, which is equivalent to looping output a[0],a[1]a[2],a [3]The value of a[4]
- while(condition){}
Execute the statement if the conditions are met, exit if not.
public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
while (i <p>Result: <br><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/81a53db7ed1edb59950a1c21ae62f15c-9.png" class="lazy" alt="Summarize and organize the process control of JAVA learning"></p><blockquote><p>do while<br> Different from while, do while is executed once and then judged</p></blockquote><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">public class a {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
do {
i++;
System.out.println(i);
} while (i <blockquote><p>The output is executed first and then judged. Therefore, the condition i</p></blockquote><p>The result is:<br><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/81a53db7ed1edb59950a1c21ae62f15c-10.png" class="lazy" alt="Summarize and organize the process control of JAVA learning"></p><h2>break continue</h2><blockquote><p><strong>break;</strong> Terminate the current loop statement<br><strong>continue;</strong> End this loop and immediately prepare to start the next loop</p></blockquote><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">int i = 0;while (++i 10) break;}当i被2整除就跳过这一次,进行下一次循环。当i大于10就结束循环。
推荐学习:《java学习教程》
The above is the detailed content of Summarize and organize the process control of JAVA learning. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!