A brief analysis of the life cycle hook mounted in vue
本篇文章带大家了解一下vue中的生命周期钩子,介绍一下vue中的mounted钩子,希望对大家有所帮助!

注:阅读本文需要对vue的patch流程有较清晰的理解,如果不清楚patch流程,建议先了解清楚这个流程再阅读本文,否则可能会感觉云里雾里。【相关推荐:vuejs视频教程】
聊之前我们先看一个场景
<div id="app">
<aC />
<bC />
</div>如上所示,App.vue文件里面有两个子组件,互为兄弟关系
组件里面自各有created和mounted两个生命周期钩子,a表示组件名 C是created的缩写
// a组件
created() {
console.log('aC')
},
mounted() {
debugger
console.log('aM')
},
// b组件
created() {
console.log('bC')
},
mounted() {
debugger
console.log('bM')
},请问打印顺序是什么?各位读者可以先脑补一下,后面看看对不对。
如果对vue patch流程比较熟悉的读者,可能会认为顺序是aC→aM→bC→BM,也就是a组件先创建,再挂载,然后到b组件重复以上流程。因为从patch的方法里面可以知道,组件created后,再走到insert进父容器的过程,是一个同步的流程,只有这个流程走完后,才会遍历到b组件,走b组件的渲染流程。
实际上浏览器打印出来的顺序是aC→bC→aM→bM,也就是两个created先执行,才到mounted执行,和上面的分析相悖。这里先说原因,子组件从created到insert进父容器的过程还是同步的,但是insert进父容器后,也可以理解为子组件mounted,并没有马上调用mounted生命周期钩子。下面从源码角度分析一下:
先大概回顾一下子组件渲染流程,patch函数调用createElm创建真实element,createElm里面通过createComponent判断当前vnode是否组件vnode,是则进入组件渲染流程
function createComponent (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm) {
var i = vnode.data;
if (isDef(i)) {
var isReactivated = isDef(vnode.componentInstance) && i.keepAlive;
if (isDef(i = i.hook) && isDef(i = i.init)) {
i(vnode, false /* hydrating */);
}
if (isDef(vnode.componentInstance)) {
initComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
// 最终组件创建完后会走到这里 把组件对应的el插入到父节点
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm);
if (isTrue(isReactivated)) {
reactivateComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm);
}
return true
}
}
}createComponent里面就把组件对应的el插入到父节点,最后会返回到patch调用栈,调用
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, isInitialPatch);
因为子组件有vnode.parent所以会走一个分支,但是我们也看看第二个分支调用的insert是什么
function invokeInsertHook (vnode, queue, initial) {
// delay insert hooks for component root nodes, invoke them after the
// element is really inserted
if (isTrue(initial) && isDef(vnode.parent)) {
vnode.parent.data.pendingInsert = queue;
} else {
for (var i = 0; i < queue.length; ++i) {
queue[i].data.hook.insert(queue[i]);
}
}
}这个insert是挂在vnode.data.hook上,在组件创建过程中,createComponent方法里面有一个调用
installComponentHooks,在这里把insert钩子注入了。这个方法实际定义在componentVNodeHooks对象里面,可以看到这个insert里面调用了callHook(componentInstance, 'mounted'),这里实际上就是调用子组件的mounted生命周期。
insert: function insert (vnode) {
var context = vnode.context;
var componentInstance = vnode.componentInstance;
if (!componentInstance._isMounted) {
componentInstance._isMounted = true;
callHook(componentInstance, 'mounted');
}
if (vnode.data.keepAlive) {
if (context._isMounted) {
// vue-router#1212
// During updates, a kept-alive component's child components may
// change, so directly walking the tree here may call activated hooks
// on incorrect children. Instead we push them into a queue which will
// be processed after the whole patch process ended.
queueActivatedComponent(componentInstance);
} else {
activateChildComponent(componentInstance, true /* direct */);
}
}
},再来看看这个方法,子组件走第一个分支,仅仅执行了一行代码vnode.parent.data.pendingInsert = queue , 这个queue实际是在patch 开始时候,定义的insertedVnodeQueue。这里的逻辑就是把当前的insertedVnodeQueue,挂在parent的vnode data的pendingInsert上。
function invokeInsertHook (vnode, queue, initial) {
// delay insert hooks for component root nodes, invoke them after the
// element is really inserted
if (isTrue(initial) && isDef(vnode.parent)) {
vnode.parent.data.pendingInsert = queue;
} else {
for (var i = 0; i < queue.length; ++i) {
queue[i].data.hook.insert(queue[i]);
}
}
}
// 在patch 开始时候 定义了insertedVnodeQueue为一个空数组
var insertedVnodeQueue = [];源码里面再搜索insertedVnodeQueue ,可以看到有这样一段逻辑,initComponent还是在createComponent里面调用的
function initComponent (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) {
if (isDef(vnode.data.pendingInsert)) {
insertedVnodeQueue.push.apply(insertedVnodeQueue, vnode.data.pendingInsert);
vnode.data.pendingInsert = null;
}
vnode.elm = vnode.componentInstance.$el;
if (isPatchable(vnode)) {
// ⚠️注意这个方法
invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue);
setScope(vnode);
} else {
// empty component root.
// skip all element-related modules except for ref (#3455)
registerRef(vnode);
// make sure to invoke the insert hook
insertedVnodeQueue.push(vnode);
}
}insertedVnodeQueue.push.apply(insertedVnodeQueue, vnode.data.pendingInsert) 重点看这一行代码,把 vnode.data.pendingInsert这个数组每一项push到当前vnode的insertedVnodeQueue中,注意这里是通过apply的方式,所以是把 vnode.data.pendingInsert这个数组每一项都push,而不是push pendingInsert这个列表进去。也就是说在这里,组件把他的子组件的insertedVnodeQueue里面的item收集了,因为渲染是一个深度递归的过程,所有最后根组件的insertedVnodeQueue能拿到所有子组件的insertedVnodeQueue里面的每一项。
从invokeInsertHook的queue[i].data.hook.insert(queue[i]) 这一行可以看出,insertedVnodeQueue里面的item应该是vnode。源码中搜索insertedVnodeQueue.push ,可以发现是invokeCreateHooks这个方法把当前vnode push了进去。
function invokeCreateHooks (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) {
for (var i$1 = 0; i$1 < cbs.create.length; ++i$1) {
cbs.create[i$1](emptyNode, vnode);
}
i = vnode.data.hook; // Reuse variable
if (isDef(i)) {
if (isDef(i.create)) { i.create(emptyNode, vnode); }
// 把当前vnode push 到了insertedVnodeQueue
if (isDef(i.insert)) { insertedVnodeQueue.push(vnode); }
}
}对于组件vnode来说,这个方法还是在initComponent中调用的。
到这里就很清晰,子组件insert进父节点后,并不会马上调用mounted钩子,而是把组件对应到vnode插入到父vnode的insertedVnodeQueue中,层层递归,最终根组件拿到所有子组件的vnode,再依次循环遍历,调用vnode的insert钩子,从而调用了mounted钩子。这里是先进先出的,第一个被push进去的第一个被拿出来调用,所以最深的那个子组件的mounted先执行。最后附上一张源码调试的图,可以清晰的看到根组件的insertedVnodeQueue是什么内容。
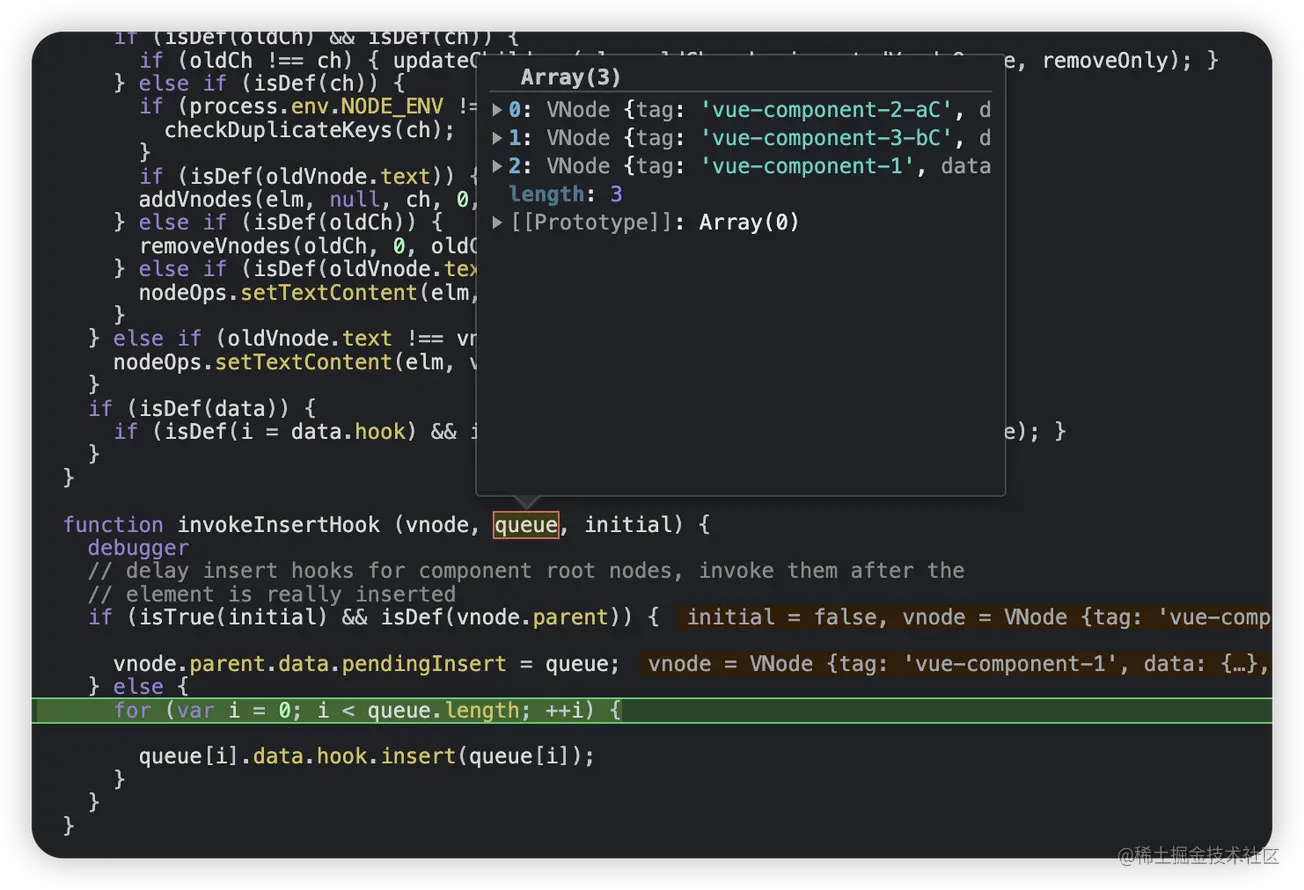
As for why vue is designed like this, it is because mounting is done first, then the parent. The child component is inserted into the parent node, but the parent node has not actually been inserted into the page. If the mounted of the child component is called immediately at this time, it will It may cause confusion for framework users, because when the subcomponent calls mounted, it is not actually rendered into the page, and it is certainly not possible to operate the DOM through document.querySelector at this time.
(Learning video sharing: vuejs tutorial, web front-end)
The above is the detailed content of A brief analysis of the life cycle hook mounted in vue. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
You can query the Vue version by using Vue Devtools to view the Vue tab in the browser's console. Use npm to run the "npm list -g vue" command. Find the Vue item in the "dependencies" object of the package.json file. For Vue CLI projects, run the "vue --version" command. Check the version information in the <script> tag in the HTML file that refers to the Vue file.
 How to pass parameters for vue function
Apr 08, 2025 am 07:36 AM
How to pass parameters for vue function
Apr 08, 2025 am 07:36 AM
There are two main ways to pass parameters to Vue.js functions: pass data using slots or bind a function with bind, and provide parameters: pass parameters using slots: pass data in component templates, accessed within components and used as parameters of the function. Pass parameters using bind binding: bind function in Vue.js instance and provide function parameters.




