 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 How to delete a non-empty directory in Linux
How to delete a non-empty directory in Linux
How to delete a non-empty directory in Linux
In Linux, you can execute the "rm -r directory name" statement to delete a non-empty directory. The rm command is used to permanently delete a specified file or directory in the file system. When this command is followed by the "-r" option, recursive deletion can be achieved, deleting the specified directory and all its contents, including all subdirectories and files.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux5.9.8 system, Dell G3 computer.
Common shell commands to delete directories are: rm
rm is a command line utility for deleting files and directories. Unlike the rmdir command, rm can delete both empty and non-empty directories. (The knowledge points about what the rmdir command is are added at the bottom!)
By default, without any options When used, rm will not delete the directory
as shown in the figure below:
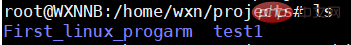
First, let’s check how many directories we have:
There are two=>They are: First_linux_progarm and test1
How to delete empty directories under Linux system?
##=>If you want to delete empty directories, please use -d(– dir) option. That is:
rm -d 目录名
How to delete a non-empty directory under the linux system?
=>If you want to delete a non-empty directory and all its contents, use the -r (–recursive or -R) option. That is:
rm -r 目录名
- -r
: Recursive deletion, mainly used to delete directories, can delete specified directories and Everything included, including all subdirectories and files.
As shown in the figure below:
#First use ls
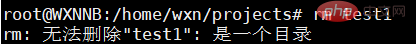
to check how many directories there are=>There are two First_linux_progarm and test1. #Use rmdir again to try to delete the First_linux_progarm directory => It shows that First_linux_progarm is not empty and cannot be deleted (
I will explain what the rmdir command is later). #At this point, we enable
rm -r First_linux_progarm. # Then use ls
to view the directory, only test1 is left.

Additional knowledge points: rmdir command is also deleted Directory shell command!
It’s just that
rmdir is a command line utility for deletingempty directories. Directories can only be deleted if the directory is empty. For example, to delete the directory named linuxmi, type:
rmdir linuxmi
If the directory
is not empty, an error will be reported : rmdir: 删除 'linuxmi' 失败: 目录非空
The above is the detailed content of How to delete a non-empty directory in Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to learn Linux basics?
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:32 AM
How to learn Linux basics?
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:32 AM
The methods for basic Linux learning from scratch include: 1. Understand the file system and command line interface, 2. Master basic commands such as ls, cd, mkdir, 3. Learn file operations, such as creating and editing files, 4. Explore advanced usage such as pipelines and grep commands, 5. Master debugging skills and performance optimization, 6. Continuously improve skills through practice and exploration.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 The 5 Pillars of Linux: Understanding Their Roles
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The 5 Pillars of Linux: Understanding Their Roles
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The five pillars of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. Shell, 4. File system, 5. System tools. The kernel manages hardware resources and provides basic services; the system library provides precompiled functions for applications; the shell is the interface for users to interact with the system; the file system organizes and stores data; and system tools are used for system management and maintenance.
 Where is the Redis restart service
Apr 10, 2025 pm 02:36 PM
Where is the Redis restart service
Apr 10, 2025 pm 02:36 PM
How to restart the Redis service in different operating systems: Linux/macOS: Use the systemctl command (systemctl restart redis-server) or the service command (service redis-server restart). Windows: Use the services.msc tool (enter "services.msc" in the Run dialog box and press Enter) and right-click the "Redis" service and select "Restart".
 How to view instance name of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to view instance name of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
There are three ways to view instance names in Oracle: use the "sqlplus" and "select instance_name from v$instance;" commands on the command line. Use the "show instance_name;" command in SQL*Plus. Check environment variables (ORACLE_SID on Linux) through the operating system's Task Manager, Oracle Enterprise Manager, or through the operating system.
 Monitor Redis Droplet with Redis Exporter Service
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
Monitor Redis Droplet with Redis Exporter Service
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:36 PM
Effective monitoring of Redis databases is critical to maintaining optimal performance, identifying potential bottlenecks, and ensuring overall system reliability. Redis Exporter Service is a powerful utility designed to monitor Redis databases using Prometheus. This tutorial will guide you through the complete setup and configuration of Redis Exporter Service, ensuring you seamlessly build monitoring solutions. By studying this tutorial, you will achieve fully operational monitoring settings
 What is Linux actually good for?
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:20 AM
What is Linux actually good for?
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Linux is suitable for servers, development environments, and embedded systems. 1. As a server operating system, Linux is stable and efficient, and is often used to deploy high-concurrency applications. 2. As a development environment, Linux provides efficient command line tools and package management systems to improve development efficiency. 3. In embedded systems, Linux is lightweight and customizable, suitable for environments with limited resources.



