Completely master JAVA process control
This article brings you relevant knowledge about java, which mainly introduces related issues about process control, including input and output, branch statements and loop statements, etc. I hope it will be helpful to you. Everyone is helpful.

java video tutorial"
Process control
JAVA input and output
Input
##Two input methods:Method 1: java.util.Scanner
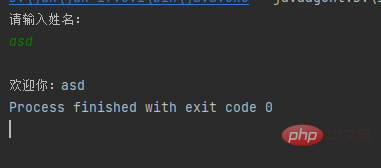
The code is as follows:Generate a Scanner object, output "Please enter your name:", return the input string and assign it to name, output "%nWelcome %s" where %n means line break %s means name
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { var sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入姓名:"); String name = sc.nextLine(); System.out.printf("%n欢迎你:%s", name); }}Copy after login
Result:
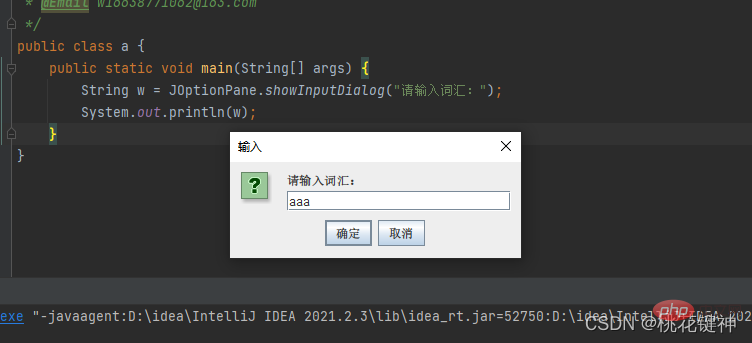
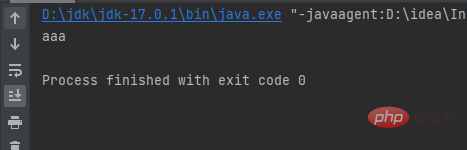
Result:public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { String w = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("请输入词汇:"); System.out.println(w); }}Copy after login
 Output
Output
Method one: System.out.print(); Output to the consoleCode demonstration:Method two: System.out.println(); Output to the console and wrap
Method 3: System.out.printf(); format the output to the console
The first method is direct without line breaks Output
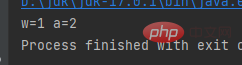
Result:public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int w = 1; int a = 2; System.out.print(w); System.out.print(a); }}Copy after login
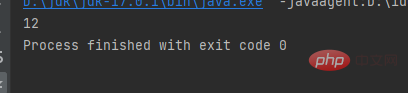
Result:public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int w = 1; int a = 2; System.out.println(w); System.out.println(a); }}Copy after login
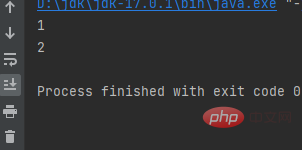
%d means an int type variable, which means replacing the first %d with the value of w and the second %d with the value of a
Result:public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int w = 1; int a = 2; System.out.printf("w=%d a=%d", w, a); }}Copy after login
if else
## if() The condition in the brackets will return true as long as it is correct, and false if it is wrong
else means otherwisepublic class a { public static void main(String[] args) { if (1>2){ System.out.println("A"); }else { System.out.println("B"); } }}Copy after login
Multiple judgments are as follows: First judgment If not, proceed to the next judgment, execute it when the return value is true, otherwise execute else
switch case defaultpublic class a { public static void main(String[] args) { if (1 > 2) { System.out.println("A"); } else if (1 > 0) { System.out.println("B"); } else { System.out.println("C"); } }}Copy after login
switch multi-branch switch Statement
switch(w) The w in the brackets is the judgment parameter, and the number after case is the value matching w. When the value of w matches the value after the case, the statement in the current case is executedbreak means to exit the current judgment, which means that there is no need to judge again laterdefault means the default value, when there is no match The default is this
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int w=1; String wk = ""; switch (w) { case 2: wk = "星期一"; break; case 3: wk = "星期二"; break; case 4: wk = "星期三"; break; case 5: wk = "星期四"; break; case 6: wk = "星期五"; break; case 7: wk = "星期六"; break; default: wk = "星期日"; break; } System.out.println(wk); }}Copy after login
result:
Loop statement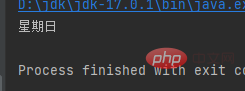
for ( int i = 0; i 5
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i <p> Result: </p>Copy after login
for in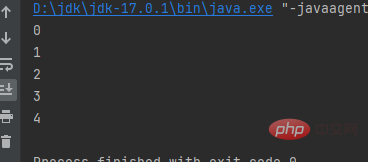
for in is mainly used to loop collections Or an array, use an array to demonstrate
i corresponds to the value in the table below of array a, which is equivalent to looping output a[0],a[1]a[2],a [3]The value of a[4]public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; for (int i : a) { System.out.println(i); } }}Copy after login
while do while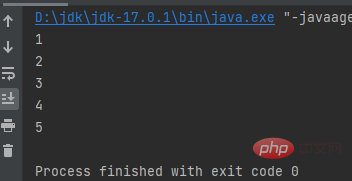
Execute the statement if the conditions are met, exit if not.
- Result:
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 0; while (iCopy after login
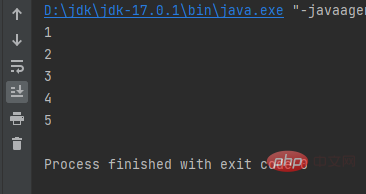 do while
do while
public class a { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 0; do { i++; System.out.println(i); } while (i <br>The output is executed first and then judged. Therefore, the condition i<blockquote><p> result: </p></blockquote><p></p><h3 id="break-continue">break continue</h3><blockquote><p><strong>break;</strong> 终止当前循环语句<br><strong>continue;</strong> 结束这一次循环,立即准备开启下一次循环</p></blockquote><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">int i = 0;while (++i 10) break;}Copy after login当i被2整除就跳过这一次,进行下一次循环。当i大于10就结束循环。
推荐学习:《java视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of Completely master JAVA process control. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




