
In mysql, you can limit the number of queries by using the "LIMIT" keyword in the SELECT query statement. This keyword can specify which record the query results start to be displayed and how many records are displayed in total; the syntax "SELECT {*|Field column name} FROM data table LIMIT initial position, number of records;".

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, mysql8 version, Dell G3 computer.
When there are tens of thousands of data in the data table, querying all the data in the table at one time will reduce the speed of data return and put a lot of pressure on the database server. This requires limiting the number of queries.
In mysql, you can limit the number of queries by using the "LIMIT" keyword in the SELECT query statement.
Mysql Limit keyword is used to limit the number of query results. You can specify which record the query results start to display and how many records are displayed in total.
For example, if there is a large table with 10 million data, querying all the data at one time will take up a lot of resources and cause the query results to be very slow. In this case, you can use Limit to obtain the specified number of items at a time. , only get the number of items we need.
Statements to limit the number of queries:
SELECT {* | 字段列名}
FROM 数据表名
LIMIT 初始位置,记录数;Among them,
"Initial position" indicates which record to start displaying and can be omitted. The first record is at position 0 and the second record is at position 1. The subsequent records are deduced in sequence.
"Number of records" indicates the number of records displayed.
Note: The two parameters after LIMIT must be positive integers.
Example:
Do not specify the starting location
The default is not to specify the starting location The starting position will be obtained from the first one, such as the following statement: Get three pieces of data from the students table
SELECT * FROM students LIMIT 3;
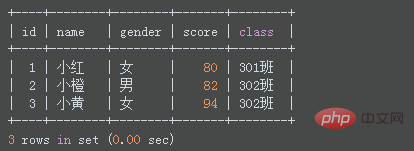
If the value of "number of records" is less than the total number of query results, it will Starting from the first record, display the specified number of records. If the value of "Number of records" is greater than the total number of query results, all the queried records will be displayed directly.
Specify the starting position
The starting position is the number from which the data should be obtained, such as the following one Statement: Get two pieces of data starting from the first piece.
SELECT * FROM students LIMIT 0,2;

[Related recommendations: mysql video tutorial]
The above is the detailed content of How to limit the number of queries in mysql. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!