 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)
Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)
Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)
This article brings you relevant knowledge about python. It mainly introduces machine learning and deep learning library summary, which contains a large number of examples. Let’s take a look at it together. I hope it will help Everyone is helpful.

Recommended learning: python video tutorial
Preface
Currently, with The popularity of artificial intelligence has attracted the attention of many industries to artificial intelligence, and has also ushered in waves of artificial intelligence learning craze. Although the principles behind artificial intelligence cannot be introduced in detail in a short article, Like all disciplines, we do not need to "invent the wheel" from scratch. We can quickly build artificial intelligence models by using rich artificial intelligence frameworks to get started with the trend of artificial intelligence.
Artificial intelligence refers to a series of technologies that enable machines to process information like humans; machine learning is the process of using computer programming to learn from historical data and predict new data; neural networks are based on the biological brain Computer models of machine learning for structure and features; deep learning is a subset of machine learning that processes large amounts of unstructured data such as human speech, text, and images. Therefore, these concepts are hierarchically interdependent, with artificial intelligence being the broadest term and deep learning being the most specific: To have a preliminary understanding of the
Python library, you can choose a library that can meet your needs for learning, and give a brief and comprehensive introduction to the currently more common artificial intelligence libraries. 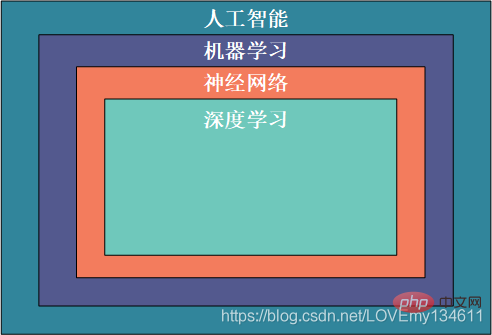
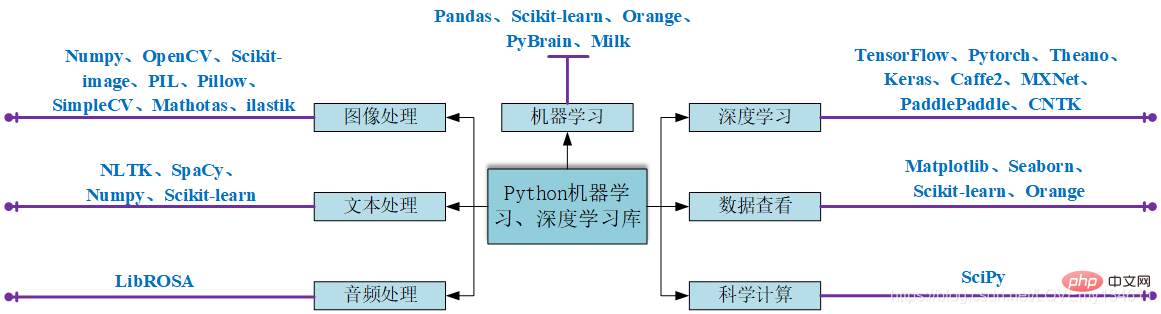
1. Numpy
NumPy(Numerical Python) is an extension library of Python
, which supports a large number of dimensional array and matrix operations. In addition, it also provides a large amount of mathematics for array operations. Function library,Numpy is written in C language at the bottom. Objects are stored directly in the array instead of object pointers, so its operation efficiency is much higher than pure Python generation code. We can compare the speed of calculating the sin value of the list between pure Python and using the Numpy library in the example:
import numpy as npimport mathimport randomimport time
start = time.time()for i in range(10):
list_1 = list(range(1,10000))
for j in range(len(list_1)):
list_1[j] = math.sin(list_1[j])print("使用纯Python用时{}s".format(time.time()-start))start = time.time()for i in range(10):
list_1 = np.array(np.arange(1,10000))
list_1 = np.sin(list_1)print("使用Numpy用时{}s".format(time.time()-start)) From the following running results, you can See that using the Numpy library is faster than code written in pure Python: 使用纯Python用时0.017444372177124023s 使用Numpy用时0.001619577407836914s
2, Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)
Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) It is a cross-platform computer vision library that can run on Linux, Windows and Mac OS operating systems. It is lightweight and efficient - composed of a series of C functions and a small number of C classes. It also provides a Python
interface to implement many common algorithms in image processing and computer vision. The following code attempts to use some simple filters, including image smoothing, Gaussian blur, etc.: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">import numpy as npimport cv2 as cvfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv.imread('h89817032p0.png')kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.float32)/25dst = cv.filter2D(img,-1,kernel)blur_1 = cv.GaussianBlur(img,(5,5),0)blur_2 = cv.bilateralFilter(img,9,75,75)plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))plt.subplot(221),plt.imshow(img[:,:,::-1]),plt.title('Original')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.subplot(222),plt.imshow(dst[:,:,::-1]),plt.title('Averaging')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.subplot(223),plt.imshow(blur_1[:,:,::-1]),plt.title('Gaussian')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.subplot(224),plt.imshow(blur_1[:,:,::-1]),plt.title('Bilateral')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.show()</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>
You can refer to Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) image processing basics (transformation and denoising ) to learn more about Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) image processing operations.
 3. Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)
3. Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)
scikit-image is an image processing library based on scipy
, which uses images asnumpyArray processing. For example, you can use scikit-image to change the image ratio. scikit-image provides
rescale, resize and downscale_local_mean and other functions.
from skimage import data, color, iofrom skimage.transform import rescale, resize, downscale_local_mean
image = color.rgb2gray(io.imread('h89817032p0.png'))image_rescaled = rescale(image, 0.25, anti_aliasing=False)image_resized = resize(image, (image.shape[0] // 4, image.shape[1] // 4),
anti_aliasing=True)image_downscaled = downscale_local_mean(image, (4, 3))plt.figure(figsize=(20,20))plt.subplot(221),plt.imshow(image, cmap='gray'),plt.title('Original')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.subplot(222),plt.imshow(image_rescaled, cmap='gray'),plt.title('Rescaled')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.subplot(223),plt.imshow(image_resized, cmap='gray'),plt.title('Resized')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.subplot(224),plt.imshow(image_downscaled, cmap='gray'),plt.title('Downscaled')plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])plt.show()
Python Imaging Library(PIL) has become Python
is the de facto image processing standard library. This is becausePIL is very powerful, but the API is very simple and easy to use. However, since PIL only supports Python 2.7 and is in disrepair, a group of volunteers created a compatible version based on PIL, named
Pillow supports the latest Python 3.x and adds many new features. Therefore, we can skip PIL and directly install and use Pillow. 5. Pillow
Pillow to generate a letter verification code image: from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont, ImageFilterimport random# 随机字母:def rndChar():
return chr(random.randint(65, 90))# 随机颜色1:def rndColor():
return (random.randint(64, 255), random.randint(64, 255), random.randint(64, 255))# 随机颜色2:def rndColor2():
return (random.randint(32, 127), random.randint(32, 127), random.randint(32, 127))# 240 x 60:width = 60 * 6height = 60 * 6image = Image.new('RGB', (width, height), (255, 255, 255))# 创建Font对象:font = ImageFont.truetype('/usr/share/fonts/wps-office/simhei.ttf', 60)# 创建Draw对象:draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)# 填充每个像素:for x in range(width):
for y in range(height):
draw.point((x, y), fill=rndColor())# 输出文字:for t in range(6):
draw.text((60 * t + 10, 150), rndChar(), font=font, fill=rndColor2())# 模糊:image = image.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR)image.save('code.jpg', 'jpeg')Copy after login
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont, ImageFilterimport random# 随机字母:def rndChar():
return chr(random.randint(65, 90))# 随机颜色1:def rndColor():
return (random.randint(64, 255), random.randint(64, 255), random.randint(64, 255))# 随机颜色2:def rndColor2():
return (random.randint(32, 127), random.randint(32, 127), random.randint(32, 127))# 240 x 60:width = 60 * 6height = 60 * 6image = Image.new('RGB', (width, height), (255, 255, 255))# 创建Font对象:font = ImageFont.truetype('/usr/share/fonts/wps-office/simhei.ttf', 60)# 创建Draw对象:draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)# 填充每个像素:for x in range(width):
for y in range(height):
draw.point((x, y), fill=rndColor())# 输出文字:for t in range(6):
draw.text((60 * t + 10, 150), rndChar(), font=font, fill=rndColor2())# 模糊:image = image.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR)image.save('code.jpg', 'jpeg')<h3 id="SimpleCV">6、 SimpleCV</h3>
<p><code>SimpleCV 是一个用于构建计算机视觉应用程序的开源框架。使用它,可以访问高性能的计算机视觉库,如 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing),而不必首先了解位深度、文件格式、颜色空间、缓冲区管理、特征值或矩阵等术语。但其对于 Python3 的支持很差很差,在 Python3.7 中使用如下代码:
from SimpleCV import Image, Color, Display# load an image from imgurimg = Image('http://i.imgur.com/lfAeZ4n.png')# use a keypoint detector to find areas of interestfeats = img.findKeypoints()# draw the list of keypointsfeats.draw(color=Color.RED)# show the resulting image. img.show()# apply the stuff we found to the image.output = img.applyLayers()# save the results.output.save('juniperfeats.png')会报如下错误,因此不建议在 Python3 中使用:
SyntaxError: Missing parentheses in call to 'print'. Did you mean print('unit test')?7、 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)
Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 是一个快速计算机视觉算法库,其构建在 Numpy 之上,目前拥有超过100种图像处理和计算机视觉功能,并在不断增长。
使用 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 加载图像,并对像素进行操作:
import numpy as npimport mahotasimport mahotas.demosfrom mahotas.thresholding import soft_thresholdfrom matplotlib import pyplot as pltfrom os import path
f = mahotas.demos.load('lena', as_grey=True)f = f[128:,128:]plt.gray()# Show the data:print("Fraction of zeros in original image: {0}".format(np.mean(f==0)))plt.imshow(f)plt.show()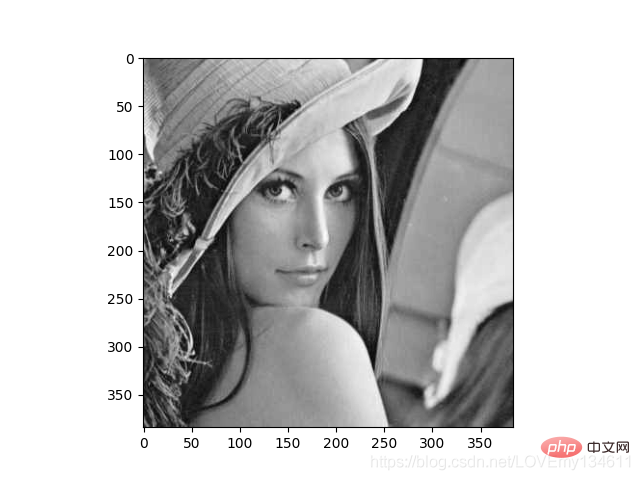
8、 Ilastik
Ilastik 能够给用户提供良好的基于机器学习的生物信息图像分析服务,利用机器学习算法,轻松地分割,分类,跟踪和计数细胞或其他实验数据。大多数操作都是交互式的,并不需要机器学习专业知识。可以参考https://www.ilastik.org/documentation/basics/installation.html进行安装使用。
9、 Scikit-learn
Scikit-learn 是针对 Python 编程语言的免费软件机器学习库。它具有各种分类,回归和聚类算法,包括支持向量机,随机森林,梯度提升,k均值和 DBSCAN 等多种机器学习算法。
使用Scikit-learn实现Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)算法:
import timeimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.cluster import MiniBatchIntroduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing), Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import pairwise_distances_argminfrom sklearn.datasets import make_blobs# Generate sample datanp.random.seed(0)batch_size = 45centers = [[1, 1], [-1, -1], [1, -1]]n_clusters = len(centers)X, labels_true = make_blobs(n_samples=3000, centers=centers, cluster_std=0.7)# Compute clustering with Meansk_means = Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)(init='k-means++', n_clusters=3, n_init=10)t0 = time.time()k_means.fit(X)t_batch = time.time() - t0# Compute clustering with MiniBatchIntroduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)mbk = MiniBatchIntroduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)(init='k-means++', n_clusters=3, batch_size=batch_size,
n_init=10, max_no_improvement=10, verbose=0)t0 = time.time()mbk.fit(X)t_mini_batch = time.time() - t0# Plot resultfig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3))fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.02, right=0.98, bottom=0.05, top=0.9)colors = ['#4EACC5', '#FF9C34', '#4E9A06']# We want to have the same colors for the same cluster from the# MiniBatchIntroduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) and the Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) algorithm. Let's pair the cluster centers per# closest one.k_means_cluster_centers = k_means.cluster_centers_
order = pairwise_distances_argmin(k_means.cluster_centers_,
mbk.cluster_centers_)mbk_means_cluster_centers = mbk.cluster_centers_[order]k_means_labels = pairwise_distances_argmin(X, k_means_cluster_centers)mbk_means_labels = pairwise_distances_argmin(X, mbk_means_cluster_centers)# Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)for k, col in zip(range(n_clusters), colors):
my_members = k_means_labels == k
cluster_center = k_means_cluster_centers[k]
plt.plot(X[my_members, 0], X[my_members, 1], 'w',
markerfacecolor=col, marker='.')
plt.plot(cluster_center[0], cluster_center[1], 'o', markerfacecolor=col,
markeredgecolor='k', markersize=6)plt.title('Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)')plt.xticks(())plt.yticks(())plt.show()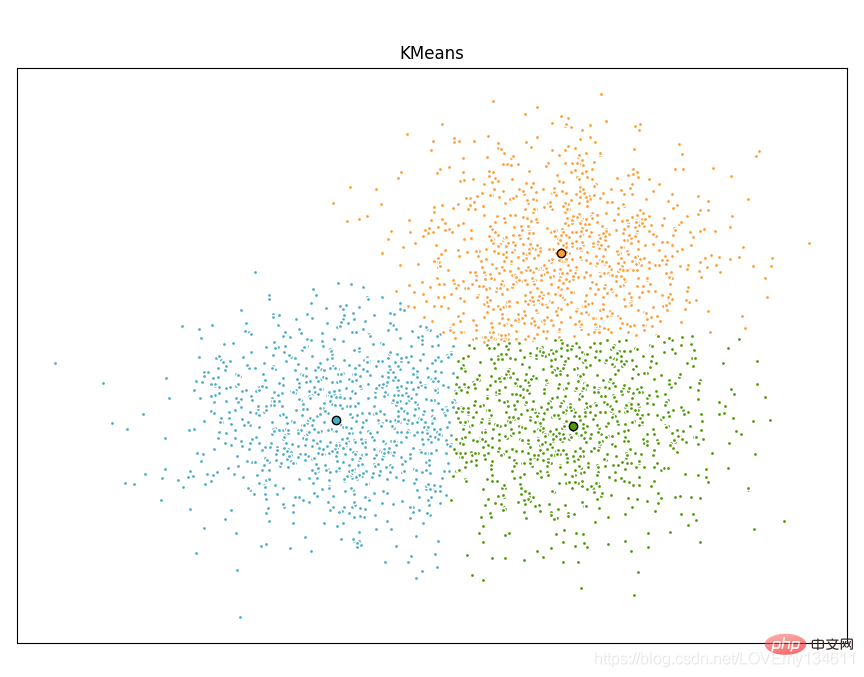
10、 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)
Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 库提供了许多用户友好和高效的数值计算,如数值积分、插值、优化、线性代数等。Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 库定义了许多数学物理的特殊函数,包括椭圆函数、贝塞尔函数、伽马函数、贝塔函数、超几何函数、抛物线圆柱函数等等。
from scipy import specialimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npdef drumhead_height(n, k, distance, angle, t):
kth_zero = special.jn_zeros(n, k)[-1]
return np.cos(t) * np.cos(n*angle) * special.jn(n, distance*kth_zero)theta = np.r_[0:2*np.pi:50j]radius = np.r_[0:1:50j]x = np.array([r * np.cos(theta) for r in radius])y = np.array([r * np.sin(theta) for r in radius])z = np.array([drumhead_height(1, 1, r, theta, 0.5) for r in radius])fig = plt.figure()ax = fig.add_axes(rect=(0, 0.05, 0.95, 0.95), projection='3d')ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='RdBu_r', vmin=-0.5, vmax=0.5)ax.set_xlabel('X')ax.set_ylabel('Y')ax.set_xticks(np.arange(-1, 1.1, 0.5))ax.set_yticks(np.arange(-1, 1.1, 0.5))ax.set_zlabel('Z')plt.show()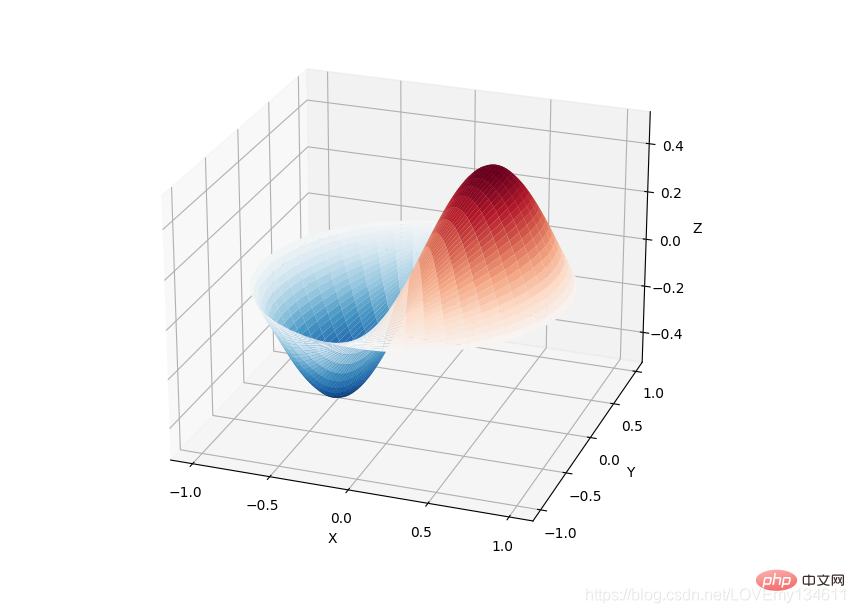
11、 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)
Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 是构建Python程序以处理自然语言的库。它为50多个语料库和词汇资源(如 WordNet )提供了易于使用的接口,以及一套用于分类、分词、词干、标记、解析和语义推理的文本处理库、工业级自然语言处理 (Natural Language Processing, NLP) 库的包装器。
Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)被称为 “a wonderful tool for teaching, and working in, computational linguistics using Python”。
import nltkfrom nltk.corpus import treebank# 首次使用需要下载nltk.download('punkt')nltk.download('averaged_perceptron_tagger')nltk.download('maxent_ne_chunker')nltk.download('words')nltk.download('treebank')sentence = """At eight o'clock on Thursday morning Arthur didn't feel very good."""# Tokenizetokens = nltk.word_tokenize(sentence)tagged = nltk.pos_tag(tokens)# Identify named entitiesentities = nltk.chunk.ne_chunk(tagged)# Display a parse treet = treebank.parsed_sents('wsj_0001.mrg')[0]t.draw()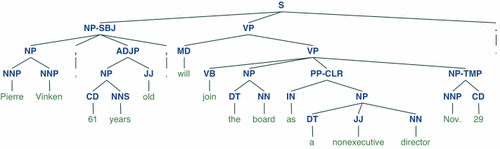
12、 spaCy
spaCy 是一个免费的开源库,用于 Python 中的高级 NLP。它可以用于构建处理大量文本的应用程序;也可以用来构建信息提取或自然语言理解系统,或者对文本进行预处理以进行深度学习。
import spacy
texts = [
"Net income was $9.4 million compared to the prior year of $2.7 million.",
"Revenue exceeded twelve billion dollars, with a loss of $1b.",
]
nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm")
for doc in nlp.pipe(texts, disable=["tok2vec", "tagger", "parser", "attribute_ruler", "lemmatizer"]):
# Do something with the doc here
print([(ent.text, ent.label_) for ent in doc.ents])nlp.pipe 生成 Doc 对象,因此我们可以对它们进行迭代并访问命名实体预测:
[('$9.4 million', 'MONEY'), ('the prior year', 'DATE'), ('$2.7 million', 'MONEY')][('twelve billion dollars', 'MONEY'), ('1b', 'MONEY')]13、 LibROSA
librosa 是一个用于音乐和音频分析的 Python 库,它提供了创建音乐信息检索系统所必需的功能和函数。
# Beat tracking exampleimport librosa# 1. Get the file path to an included audio examplefilename = librosa.example('nutcracker')# 2. Load the audio as a waveform `y`# Store the sampling rate as `sr`y, sr = librosa.load(filename)# 3. Run the default beat trackertempo, beat_frames = librosa.beat.beat_track(y=y, sr=sr)print('Estimated tempo: {:.2f} beats per minute'.format(tempo))# 4. Convert the frame indices of beat events into timestampsbeat_times = librosa.frames_to_time(beat_frames, sr=sr)14、 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)
Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 是一个快速、强大、灵活且易于使用的开源数据分析和操作工具, Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 可以从各种文件格式比如 CSV、JSON、SQL、Microsoft Excel 导入数据,可以对各种数据进行运算操作,比如归并、再成形、选择,还有数据清洗和数据加工特征。Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 广泛应用在学术、金融、统计学等各个数据分析领域。
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport pandas as pdimport numpy as np
ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(1000), index=pd.date_range("1/1/2000", periods=1000))ts = ts.cumsum()df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(1000, 4), index=ts.index, columns=list("ABCD"))df = df.cumsum()df.plot()plt.show()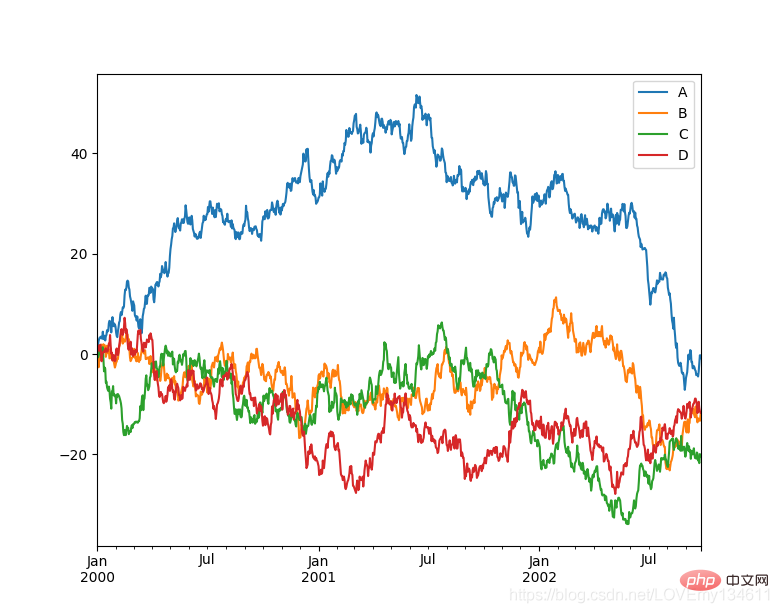
15、 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)
Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 是Python的绘图库,它提供了一整套和 matlab 相似的命令 API,可以生成出版质量级别的精美图形,Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 使绘图变得非常简单,在易用性和性能间取得了优异的平衡。
使用 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 绘制多曲线图:
# plot_multi_curve.pyimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = np.linspace(0.1, 2 * np.pi, 100)y_1 = x y_2 = np.square(x)y_3 = np.log(x)y_4 = np.sin(x)plt.plot(x,y_1)plt.plot(x,y_2)plt.plot(x,y_3)plt.plot(x,y_4)plt.show()
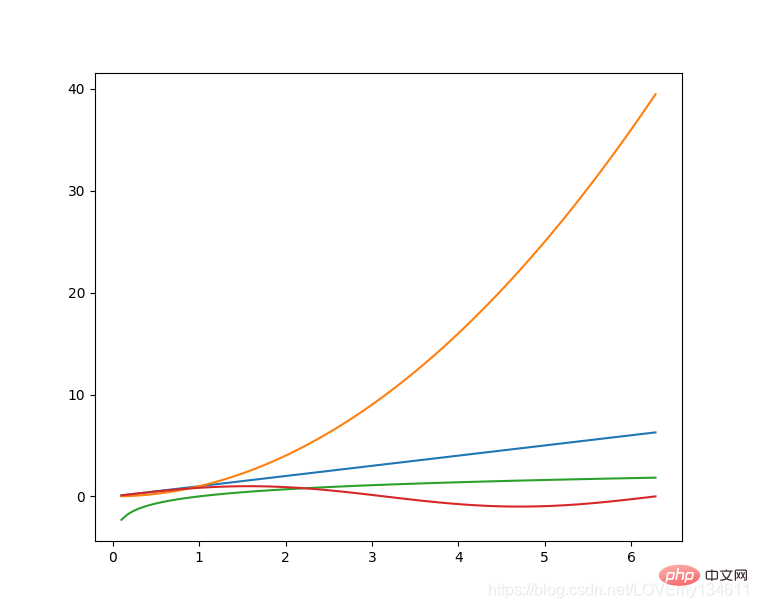 有关更多
有关更多Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)绘图的介绍可以参考此前博文———Python-Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)可视化。
16、 Seaborn
Seaborn 是在 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 的基础上进行了更高级的API封装的Python数据可视化库,从而使得作图更加容易,应该把 Seaborn 视为 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 的补充,而不是替代物。
import Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) as snsimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sns.set_theme(style="ticks")df = sns.load_dataset("penguins")sns.pairplot(df, hue="species")plt.show()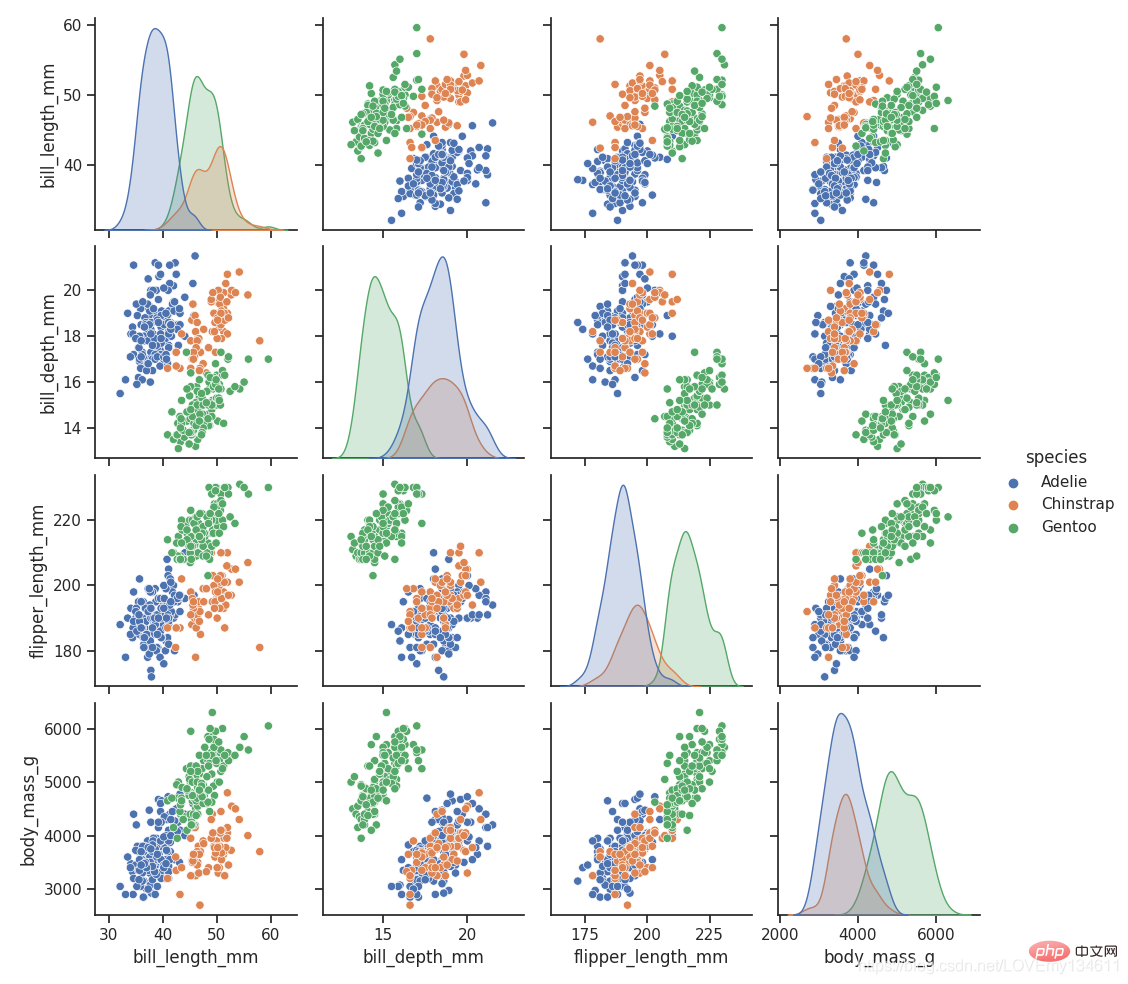
17、 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)
Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 是一个开源的数据挖掘和机器学习软件,提供了一系列的数据探索、可视化、预处理以及建模组件。Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 拥有漂亮直观的交互式用户界面,非常适合新手进行探索性数据分析和可视化展示;同时高级用户也可以将其作为 Python 的一个编程模块进行数据操作和组件开发。
使用 pip 即可安装 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing),好评~
$ pip install orange3
安装完成后,在命令行输入 orange-canvas 命令即可启动 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 图形界面:
$ orange-canvas
启动完成后,即可看到 Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) 图形界面,进行各种操作。
18、 PyBrain
PyBrain 是 Python 的模块化机器学习库。它的目标是为机器学习任务和各种预定义的环境提供灵活、易于使用且强大的算法来测试和比较算法。PyBrain 是 Python-Based Reinforcement Learning, Artificial Intelligence and Neural Network Library 的缩写。
我们将利用一个简单的例子来展示 PyBrain 的用法,构建一个多层感知器 (Multi Layer Perceptron, MLP)。
首先,我们创建一个新的前馈网络对象:
from pybrain.structure import FeedForwardNetwork n = FeedForwardNetwork()
接下来,构建输入、隐藏和输出层:
from pybrain.structure import LinearLayer, SigmoidLayer inLayer = LinearLayer(2)hiddenLayer = SigmoidLayer(3)outLayer = LinearLayer(1)
为了使用所构建的层,必须将它们添加到网络中:
n.addInputModule(inLayer)n.addModule(hiddenLayer)n.addOutputModule(outLayer)
可以添加多个输入和输出模块。为了向前计算和反向误差传播,网络必须知道哪些层是输入、哪些层是输出。
这就需要明确确定它们应该如何连接。为此,我们使用最常见的连接类型,全连接层,由 FullConnection 类实现:
from pybrain.structure import FullConnection in_to_hidden = FullConnection(inLayer, hiddenLayer)hidden_to_out = FullConnection(hiddenLayer, outLayer)
与层一样,我们必须明确地将它们添加到网络中:
n.addConnection(in_to_hidden)n.addConnection(hidden_to_out)
所有元素现在都已准备就位,最后,我们需要调用.sortModules()方法使MLP可用:
n.sortModules()
这个调用会执行一些内部初始化,这在使用网络之前是必要的。
19、 Milk
MILK(MACHINE LEARNING TOOLKIT) 是 Python 语言的机器学习工具包。它主要是包含许多分类器比如 SVMS、K-NN、随机森林以及决策树中使用监督分类法,它还可执行特征选择,可以形成不同的例如无监督学习、密切关系传播和由 MILK 支持的 K-means 聚类等分类系统。
使用 MILK 训练一个分类器:
import numpy as npimport milk features = np.random.rand(100,10)labels = np.zeros(100)features[50:] += .5labels[50:] = 1learner = milk.defaultclassifier()model = learner.train(features, labels)# Now you can use the model on new examples:example = np.random.rand(10)print(model.apply(example))example2 = np.random.rand(10)example2 += .5print(model.apply(example2))
20、 TensorFlow
TensorFlow 是一个端到端开源机器学习平台。它拥有一个全面而灵活的生态系统,一般可以将其分为 TensorFlow1.x 和 TensorFlow2.x,TensorFlow1.x 与 TensorFlow2.x 的主要区别在于 TF1.x 使用静态图而 TF2.x 使用Eager Mode动态图。
这里主要使用TensorFlow2.x作为示例,展示在 TensorFlow2.x 中构建卷积神经网络 (Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)。
import tensorflow as tffrom tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, models# 数据加载(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = datasets.cifar10.load_data()# 数据预处理train_images, test_images = train_images / 255.0, test_images / 255.0# 模型构建model = models.Sequential()model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(32, 32, 3)))model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))model.add(layers.Flatten())model.add(layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'))model.add(layers.Dense(10))# 模型编译与训练model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True), metrics=['accuracy'])history = model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=10, validation_data=(test_images, test_labels))
想要了解更多Tensorflow2.x的示例,可以参考专栏 Tensorflow.
21、 PyTorch
PyTorch 的前身是 Torch,其底层和 Torch 框架一样,但是使用 Python 重新写了很多内容,不仅更加灵活,支持动态图,而且提供了 Python 接口。
# 导入库import torchfrom torch import nnfrom torch.utils.data import DataLoaderfrom torchvision import datasetsfrom torchvision.transforms import ToTensor, Lambda, Composeimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 模型构建device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"print("Using {} device".format(device))# Define modelclass NeuralNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(NeuralNetwork, self).__init__()
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.linear_relu_stack = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(28*28, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 10),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.flatten(x)
logits = self.linear_relu_stack(x)
return logits
model = NeuralNetwork().to(device)# 损失函数和优化器loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)# 模型训练def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
for batch, (X, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# Compute prediction error
pred = model(X)
loss = loss_fn(pred, y)
# Backpropagation
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch % 100 == 0:
loss, current = loss.item(), batch * len(X)
print(f"loss: {loss:>7f} [{current:>5d}/{size:>5d}]")22、 Theano
Theano 是一个 Python 库,它允许定义、优化和有效地计算涉及多维数组的数学表达式,建在 NumPy 之上。
在 Theano 中实现计算雅可比矩阵:
import theanoimport theano.tensor as T
x = T.dvector('x')y = x ** 2J, updates = theano.scan(lambda i, y,x : T.grad(y[i], x), sequences=T.arange(y.shape[0]), non_sequences=[y,x])f = theano.function([x], J, updates=updates)f([4, 4])23、 Keras
Keras 是一个用 Python 编写的高级神经网络 API,它能够以 TensorFlow, CNTK, 或者 Theano 作为后端运行。Keras 的开发重点是支持快速的实验,能够以最小的时延把想法转换为实验结果。
from keras.models import Sequentialfrom keras.layers import Dense# 模型构建model = Sequential()model.add(Dense(units=64, activation='relu', input_dim=100))model.add(Dense(units=10, activation='softmax'))# 模型编译与训练model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='sgd', metrics=['accuracy'])model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5, batch_size=32)
24、 Caffe
在 Caffe2 官方网站上,这样说道:Caffe2 现在是 PyTorch 的一部分。虽然这些 api 将继续工作,但鼓励使用 PyTorch api。
25、 MXNet
MXNet 是一款设计为效率和灵活性的深度学习框架。它允许混合符号编程和命令式编程,从而最大限度提高效率和生产力。
使用 MXNet 构建手写数字识别模型:
import mxnet as mxfrom mxnet import gluonfrom mxnet.gluon import nnfrom mxnet import autograd as agimport mxnet.ndarray as F# 数据加载mnist = mx.test_utils.get_mnist()batch_size = 100train_data = mx.io.NDArrayIter(mnist['train_data'], mnist['train_label'], batch_size, shuffle=True)val_data = mx.io.NDArrayIter(mnist['test_data'], mnist['test_label'], batch_size)# CNN模型class Net(gluon.Block):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Net, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2D(20, kernel_size=(5,5))
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides = (2,2))
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2D(50, kernel_size=(5,5))
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides = (2,2))
self.fc1 = nn.Dense(500)
self.fc2 = nn.Dense(10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool1(F.tanh(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool2(F.tanh(self.conv2(x)))
# 0 means copy over size from corresponding dimension.
# -1 means infer size from the rest of dimensions.
x = x.reshape((0, -1))
x = F.tanh(self.fc1(x))
x = F.tanh(self.fc2(x))
return x
net = Net()# 初始化与优化器定义# set the context on GPU is available otherwise CPUctx = [mx.gpu() if mx.test_utils.list_gpus() else mx.cpu()]net.initialize(mx.init.Xavier(magnitude=2.24), ctx=ctx)trainer = gluon.Trainer(net.collect_params(), 'sgd', {'learning_rate': 0.03})# 模型训练# Use Accuracy as the evaluation metric.metric = mx.metric.Accuracy()softmax_cross_entropy_loss = gluon.loss.SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss()for i in range(epoch):
# Reset the train data iterator.
train_data.reset()
for batch in train_data:
data = gluon.utils.split_and_load(batch.data[0], ctx_list=ctx, batch_axis=0)
label = gluon.utils.split_and_load(batch.label[0], ctx_list=ctx, batch_axis=0)
outputs = []
# Inside training scope
with ag.record():
for x, y in zip(data, label):
z = net(x)
# Computes softmax cross entropy loss.
loss = softmax_cross_entropy_loss(z, y)
# Backpropogate the error for one iteration.
loss.backward()
outputs.append(z)
metric.update(label, outputs)
trainer.step(batch.data[0].shape[0])
# Gets the evaluation result.
name, acc = metric.get()
# Reset evaluation result to initial state.
metric.reset()
print('training acc at epoch %d: %s=%f'%(i, name, acc))26、 PaddlePaddle
飞桨 (PaddlePaddle) 以百度多年的深度学习技术研究和业务应用为基础,集深度学习核心训练和推理框架、基础模型库、端到端开发套件、丰富的工具组件于一体。是中国首个自主研发、功能完备、开源开放的产业级深度学习平台。
使用 PaddlePaddle 实现 LeNtet5:
# 导入需要的包import paddleimport numpy as npfrom paddle.nn import Conv2D, MaxPool2D, Linear## 组网import paddle.nn.functional as F# 定义 LeNet 网络结构class LeNet(paddle.nn.Layer): def __init__(self, num_classes=1): super(LeNet, self).__init__() # 创建卷积和池化层 # 创建第1个卷积层 self.conv1 = Conv2D(in_channels=1, out_channels=6, kernel_size=5) self.max_pool1 = MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2, stride=2) # 尺寸的逻辑:池化层未改变通道数;当前通道数为6 # 创建第2个卷积层 self.conv2 = Conv2D(in_channels=6, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5) self.max_pool2 = MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2, stride=2) # 创建第3个卷积层 self.conv3 = Conv2D(in_channels=16, out_channels=120, kernel_size=4) # 尺寸的逻辑:输入层将数据拉平[B,C,H,W] -> [B,C*H*W] # 输入size是[28,28],经过三次卷积和两次池化之后,C*H*W等于120 self.fc1 = Linear(in_features=120, out_features=64) # 创建全连接层,第一个全连接层的输出神经元个数为64, 第二个全连接层输出神经元个数为分类标签的类别数 self.fc2 = Linear(in_features=64, out_features=num_classes) # 网络的前向计算过程 def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) # 每个卷积层使用Sigmoid激活函数,后面跟着一个2x2的池化 x = F.sigmoid(x) x = self.max_pool1(x) x = F.sigmoid(x) x = self.conv2(x) x = self.max_pool2(x) x = self.conv3(x) # 尺寸的逻辑:输入层将数据拉平[B,C,H,W] -> [B,C*H*W] x = paddle.reshape(x, [x.shape[0], -1]) x = self.fc1(x) x = F.sigmoid(x) x = self.fc2(x) return x
27、 CNTK
CNTK(Cognitive Toolkit) 是一个深度学习工具包,通过有向图将神经网络描述为一系列计算步骤。在这个有向图中,叶节点表示输入值或网络参数,而其他节点表示对其输入的矩阵运算。CNTK 可以轻松地实现和组合流行的模型类型,如 CNN 等。CNTK 用网络描述语言 (network description language, NDL) 描述一个神经网络。 简单的说,要描述输入的 feature,输入的 label,一些参数,参数和输入之间的计算关系,以及目标节点是什么。
NDLNetworkBuilder=[ run=ndlLR ndlLR=[ # sample and label dimensions SDim=$dimension$ LDim=1 features=Input(SDim, 1) labels=Input(LDim, 1) # parameters to learn B0 = Parameter(4) W0 = Parameter(4, SDim) B = Parameter(LDim) W = Parameter(LDim, 4) # operations t0 = Times(W0, features) z0 = Plus(t0, B0) s0 = Sigmoid(z0) t = Times(W, s0) z = Plus(t, B) s = Sigmoid(z) LR = Logistic(labels, s) EP = SquareError(labels, s) # root nodes FeatureNodes=(features) LabelNodes=(labels) CriteriaNodes=(LR) EvalNodes=(EP) OutputNodes=(s,t,z,s0,W0) ] ]
总结与分类
python 常用机器学习及深度学习库总结
| 库名 | 官方网站 | 简介 |
|---|---|---|
| NumPy | http://www.numpy.org/ | 提供对大型多维阵列的支持,NumPy是计算机视觉中的一个关键库,因为图像可以表示为多维数组,将图像表示为NumPy数组有许多优点 |
| Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) | https://opencv.org/ | 开源的计算机视觉库 |
| Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) | https:// scikit-image.org/ | 图像处理算法的集合,由scikit-image操作的图像只能是NumPy数组 |
| Python Imaging Library(PIL) | http://www.pythonware.com/products/pil/ | 图像处理库,提供强大的图像处理和图形功能 |
| Pillow | https://pillow.readthedocs.io/ | PIL的一个分支 |
| SimpleCV | http://simplecv.org/ | 计算机视觉框架,提供了处理图像处理的关键功能 |
| Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) | https://mahotas.readthedocs.io/ | 提供了用于图像处理和计算机视觉的一组函数,它最初是为生物图像信息学而设计的;但是,现在它在其他领域也发挥了重要作用,它完全基于numpy数组作为其数据类型 |
| Ilastik | http://ilastik.org/ | 用户友好且简单的交互式图像分割、分类和分析工具 |
| Scikit-learn | http://scikit-learn.org/ | 机器学习库,具有各种分类、回归和聚类算法 |
| Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) | https://www.scipy.org/ | 科学和技术计算库 |
| Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) | https://www.nltk.org/ | 处理自然语言数据的库和程序 |
| spaCy | https://spacy.io/ | 开源软件库,用于Python中的高级自然语言处理 |
| LibROSA | https://librosa.github.io/librosa/ | 用于音乐和音频处理的库 |
| Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) | https://pandas.pydata.org/ | 构建在NumPy之上的库,提供高级数据计算工具和易于使用的数据结构 |
| Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) | https://matplotlib.org | 绘图库,它提供了一整套和 matlab 相似的命令 API,可以生成所需的出版质量级别的图形 |
| Seaborn | https://Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing).pydata.org/ | 是建立在Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing)之上的绘图库 |
| Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) | https://orange.biolab.si/ | 面向新手和专家的开源机器学习和数据可视化工具包 |
| PyBrain | http://pybrain.org/ | 机器学习库,为机器学习提供易于使用的最新算法 |
| Milk | http://luispedro.org/software/milk/ | 机器学习工具箱,主要用于监督学习中的多分类问题 |
| TensorFlow | https://www.tensorflow.org/ | 开源的机器学习和深度学习库 |
| PyTorch | https://pytorch.org/ | 开源的机器学习和深度学习库 |
| Theano | http://deeplearning.net/software/theano/ | 用于快速数学表达式、求值和计算的库,已编译为可在CPU和GPU架构上运行 |
| Keras | https://keras.io/ | 高级深度学习库,可以在 TensorFlow、CNTK、Theano 或 Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit 之上运行 |
| Caffe2 | https://caffe2.ai/ | Caffe2 是一个兼具表现力、速度和模块性的深度学习框架,是 Caffe 的实验性重构,能以更灵活的方式组织计算 |
| MXNet | https://mxnet.apache.org/ | 设计为效率和灵活性的深度学习框架,允许混合符号编程和命令式编程 |
| PaddlePaddle | https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn | 以百度多年的深度学习技术研究和业务应用为基础,集深度学习核心训练和推理框架、基础模型库、端到端开发套件、丰富的工具组件于一体 |
| CNTK | https://cntk.ai/ | 深度学习工具包,通过有向图将神经网络描述为一系列计算步骤。在这个有向图中,叶节点表示输入值或网络参数,而其他节点表示对其输入的矩阵运算 |
Classification
These libraries can be classified according to their primary purpose:
| Category | Library |
|---|---|
| Image processing | NumPy, Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing), scikit image, PIL, Pillow, SimpleCV, Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing), ilastik |
| Text processing | Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing), spaCy, NumPy, scikit learn, PyTorch |
| Audio processing | LibROSA |
| Machine Learning | pandas, scikit-learn, Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing), PyBrain, Milk |
| Data viewing | Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing), Seaborn, scikit-learn, Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) |
| Deep Learning | TensorFlow, Pytorch, Theano, Keras, Caffe2, MXNet, PaddlePaddle, CNTK |
| Scientific Computing | Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing) |
Recommended learning: python video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to commonly used machine learning and deep learning libraries in python (summary sharing). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
The key to running Jupyter Notebook in VS Code is to ensure that the Python environment is properly configured, understand that the code execution order is consistent with the cell order, and be aware of large files or external libraries that may affect performance. The code completion and debugging functions provided by VS Code can greatly improve coding efficiency and reduce errors.



