What is single sign-on? How to implement SSO using Nodejs
What is single sign-on? The following article will introduce you to the principle of single sign-on and talk about the method of using Node to implement single sign-on SSO. I hope it will be helpful to you!

What is single sign-on
As the company’s business increases, different systems will inevitably be generated. If each It would be very inconvenient if the system requires separate logins.
Therefore, a solution such as single sign-on was born. The full name of single sign-on is Single Sign On, or SSO for short. It means that if you log in to one system in multiple system application groups, you can be authorized in all other systems. No need to log in again.
For example, Xiao Ming logged into Taobao today. If he has not logged in, he will be asked to enter authentication information (user name, password, etc.). After logging in, when he visits Tmall's page, he can access it directly without logging in.
Single sign-on principle
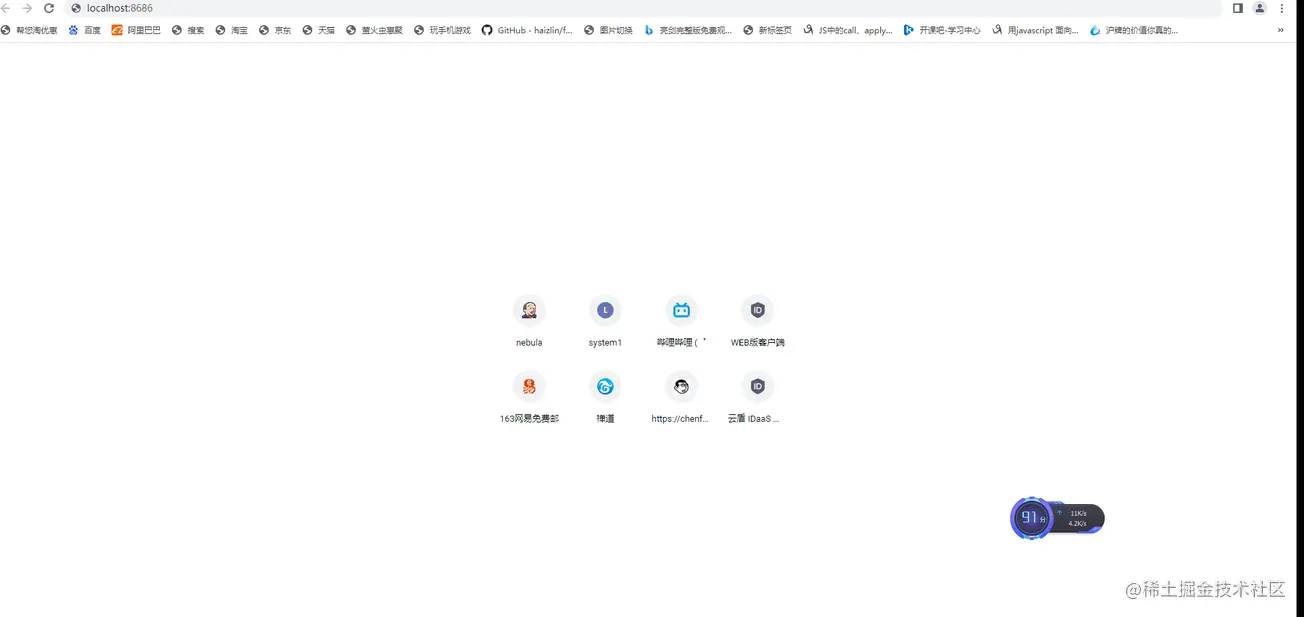
SSO requires an independent authentication center. Only the independent authentication center can accept users. For security information such as name and password, other systems do not provide login entrances and only accept indirect authorization from the certification center. The whole process can be simply described with the above picture:
When the user logs in to access application A, application A finds that the user is not logged in, jumps to the SSO authentication center, and uses its own address as The parameters are convenient for callback
The SSO certification center finds that the user has not logged in and guides the user to the login page; the user fills in the user name and password to submit the login application; the SSO certification center verifies the user information and creates the user Rain the session of the SSO authentication center (the information will be saved in the cookie at this time), and at the same time create the authorization token token
sso authentication center jumps to the original request address with the token (Application A)
Application A gets the token and goes to the SSO certification center to verify whether it is valid. If it returns a valid registration application A
Application A creates Conversation with the user, displaying resources and maintaining user login status
When the user accesses application B, it is found that the user is not logged in (the SSO authentication server and application A and application B are not in the same domain , unable to provide login status), jump to the SSO certification center, and bring your address and cookie information from the previous session with the SSO certification center
The SSO certification center finds that the user has logged in , jump back to the application B address, and attach the token token
-
The same application B gets the token and goes to the SSO certification center to verify whether it is valid. If it returns a valid registered application B
Application B creates a session with the user, displays resources and maintains the user's login status
NodeJS Demo
Three different services
Here we need to start three services to simulate application A, SSO authentication server and application B

The service with port number 8383 here is the SSO authentication server, and the rest: 8686 and :8787 represent application A and application B respectively.
In fact, the codes of Application A and Application B are almost the same. As shown in the figure above, we can set different ports and application names by passing parameters.
Let’s take a look at the effect first

Jump to the login page for the first visit
Application A determines the login status and jumps to the SSO authentication server
Application A
const Koa=require('koa');
const Router=require('koa-router')
const views=require('koa-views')
const static=require('koa-static')
const path=require('path');
const app=new Koa();
const router=new Router();
const session=require('koa-session')
const koa2Req=require('koa2-request');
//模版引擎相关配置
app.use(views(path.join(__dirname,'./views')),{
extension:'ejs'
})
app.keys=['key']
const keyMap={
'8686':'koa:sess8686',
'8787':'koa:sess8787'
}
const CONFIG={
key:keyMap[process.env.PORT] || 'koa:sess',
maxAge:1000*60*60*24,
httpOnly:true
}
app.use(session(CONFIG,app))
const system=process.env.SERVER_NAME
router.get("/",async (ctx)=>{
//通过 session来判断 应用A的登录状态
let user=ctx.session.user
if(user){
//...
}
else //1、当用户登录访问应用A时,应用A发现用户未登录(应为服务器没有保存对应的session)
{
let token=ctx.query.token
//第一次登录url上也不会有令牌
if(!token)
{
//1、跳转到SSO认证服务器
ctx.redirect(`http://localhost:8383/login?redirectUrl=${ctx.host+ctx.originalUrl}`)
}
else
{
//...
}
}
})
app.use(router.routes())
const port=process.env.PORT||8888
app.listen(port,()=>{
console.log(`app ${system} running at ${port}`)
})The authentication server determines the login status and renders the login page
Authentication Server SSO
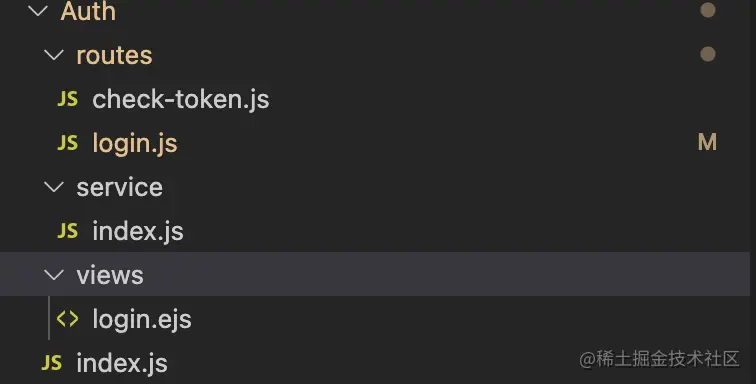
The directory structure of the authentication server is as follows It mainly handles two functions, one is the login logic, and the other is the subsequent verification of the validity of the token. There are routing login.js and check-token.js respectively to handle
Auth /index.js
const Koa=require('koa');
const Router=require('koa-router')
const views=require('koa-views')
const path=require('path');
const app=new Koa();
const router=new Router();
const login=require("./routes/login")
const checkToken=require('./routes/check-token')
const bodyparser=require('koa-bodyparser')
app.use(views(path.join(__dirname,'./views')),{
extension:'ejs'
})
app.use(bodyparser())
//处理登录相关的逻辑
router.use('/login',login.routes())
//处理令牌验证的逻辑
router.use('/check_token',checkToken.routes())
app.use(router.routes())
app.listen(8383,()=>{
console.log(`app listen at 8383`)
})Just now we jumped from application A tohttp://localhost:8383/login?redirectUrl=localhost:8686 to see the logic in login
Auth /routes/login.js
const service = require("../service");
const router=require("koa-router")()
router.get('/',async (ctx)=>{
const cookies=ctx.cookies;
const token=cookies.get('token');
//从cookie中判断应用A的登录态
if(token && service.isTokenVailid(token)){
//。。。如果有登录过
}else{
//2、SSO认证中心发现用户没有登录过,于是渲染登录页面登录页面;
await ctx.render('login.ejs',{
extension:'ejs'
})
}
})
//。。。
module.exports=routerLogin page
Auth/views/login.ejs
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>统一登录</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="统一登录">统一登录</h1>
<form method="post">
<div>用户名: <input type="text" name="name"/></div>
<div>密码 <input type="text" name="password" /></div>
<div><input type="submit" value='登录'></div>
</form>
</body>
</html>Verify user information and create token
Auth/routes/login.js
router.post('/',async (ctx)=>{
//2、用户填写用户名密码提交登录申请;
const body=ctx.request.body;
const {name,password}=body;
//2、SSO认证中心校验用户信息,
if(name==="admin" && password==="123456"){
//2、创建用户雨SSO认证中心的会话(这时会把信息保存到cookie中),同时创建授权令牌token
const token="passport";
await ctx.cookies.set('token',token,{
maxAge:1000*60*60*24*30,
httpOnly:true
})
if(ctx.query.redirectUrl){
//3、sso认证中心带着令牌跳转到最初的请求地址(应用A)
ctx.redirect(`${ctx.protocol}://${ctx.query.redirectUrl}?token=${token}`)
//回跳地址是 http://localhost:8686/?token=passport
}else{
ctx.body="<h1 id="登录成功">登录成功!</h1>"
}
}else{
ctx.response.body={
error:1,
msg:'用户名或密码错误'
}
}
})Carries the token from the authentication server to jump back to application A
Token verification returns resources
Application A
app.use(views(path.join(__dirname,'./views')),{
extension:'ejs'
})
//...
const system=process.env.SERVER_NAME
router.get("/",async (ctx)=>{
let user=ctx.session.user
if(user){
//...
}
else
//这时应用A依旧没有登录态 但url上有了令牌 http://localhost:8686/?token=passport
{
let token=ctx.query.token
if(!token)
{
//...跳转去SSO登录页面
}
else
//跳回应用A时走这里的逻辑
{
//ajax请求 4. 应用A拿到令牌去SSO认证中心认证是否有效,如果返回有效注册应用A
const url=`://localhost:8383/check_token?token=${token}&t=${new Date().getTime()}`
let data = await koa2Req(ctx.protocol + url);
if(data && data.body){
try {
const body=JSON.parse(data.body)
const {error,userId}=body;
// console.log(error,userId) 0,admin
if(error==0){
if(!userId){
ctx.redirect(`http://localhost:8383/login?redirectUrl=${ctx.host+ctx.originalUrl}`)
return
}
//验证通过后注册session,渲染页面
//5. 应用A创建与用户之间的会话,展示资源并维持用户登录态
ctx.session.user=userId;
await ctx.render('index.ejs',{
user:userId,
system
})
}else{
ctx.redirect(`http://localhost:8383/login?redirectUrl=${ctx.host+ctx.originalUrl}`)
}
} catch (error) {console.log(error)}
}
}
}
})
app.use(router.routes())
const port=process.env.PORT||8888
app.listen(port,()=>{
console.log(`app ${system} running at ${port}`)
})The corresponding logic for processing verification tokens in SSO
Auth/routes/check-token
const router=require("koa-router")()
const service=require("../service")
router.get('/',async (ctx)=>{
const token=ctx.query.token;
const result={
error:1
}
//当token 是 password时
if(service.isTokenVailid(token)){
result.error=0;
result.userId='admin'
}
ctx.body=result
})
module.exports=routerAuth/service/index.js
module.exports={
isTokenVailid: function(token){
if(token && token==='passport'){
return true
}
return false
}
}Now the user can access application A normally, and the user’s login information is available on the SSO server and application A server.
Access application B
Jump to SSO authentication server with cookie
Application B
//...
router.get("/",async (ctx)=>{
let user=ctx.session.user
if(user){
//...
}else{
let token=ctx.query.token
//...
if(!token)
{
//同样既没有session也没有令牌,跳转到SSO认证服务器
//6、当用户访问应用B时,发现用户未登录(SSO认证服务器与应用A应用B不是同一个域,不能提供登录态),跳转到SSO认证中心,并将自己的地址和之前和SSO认证中心会话的cookie信息带入
ctx.redirect(`http://localhost:8383/login?redirectUrl=${ctx.host+ctx.originalUrl}`)
}
else
{
//。。。验证令牌的部分
}
}
})
app.use(router.routes())
const port=process.env.PORT||8888
app.listen(port,()=>{
console.log(`app ${system} running at ${port}`)
})从认证服务器携带令牌跳转回应用B
SSO认证服务器 ,再次登录时携带了cookie,因此不会再请求登录页面 Auth/routes/login
//...
router.get('/',async (ctx)=>{
const cookies=ctx.cookies;
const token=cookies.get('token');
//7. SSO认证中心发现用户已登录,跳转回应用B地址,并附上令牌token
if(token && service.isTokenVailid(token)){
const redirectUrl=ctx.query.redirectUrl;
if(redirectUrl){
//带着令牌跳转回应用B
ctx.redirect(`${ctx.protocol}://${redirectUrl}?token=${token}`)
}else{
ctx.body="<h1 id="登录成功">登录成功!</h1>"
}
}else{
//...渲染登录页面
}
})
//..令牌校验 返回资源
这里的逻辑和5,6两步一样,因为token容易伪造,所以要检验真伪。 应用B
app.use(views(path.join(__dirname,'./views')),{
extension:'ejs'
})
//...
const system=process.env.SERVER_NAME
router.get("/",async (ctx)=>{
let user=ctx.session.user
if(user){
//...
}
else
//这时应用B依旧没有登录态 但url上有了令牌 http://localhost:8787/?token=passport
{
let token=ctx.query.token
if(!token)
{
//...跳转去SSO登录页面
}
else
//跳回应用B时走这里的逻辑
{
//ajax请求 8. 同样的应用B拿到令牌去SSO认证中心认证是否有效,如果返回有效注册应用B
const url=`://localhost:8383/check_token?token=${token}&t=${new Date().getTime()}`
let data = await koa2Req(ctx.protocol + url);
if(data && data.body){
try {
const body=JSON.parse(data.body)
const {error,userId}=body;
// console.log(error,userId) 0,admin
if(error==0){
if(!userId){
ctx.redirect(`http://localhost:8383/login?redirectUrl=${ctx.host+ctx.originalUrl}`)
return
}
//验证通过后注册session,渲染页面
//9. 应用B创建与用户之间的会话,展示资源并维持用户登录态
ctx.session.user=userId;
await ctx.render('index.ejs',{
user:userId,
system
})
}else{
ctx.redirect(`http://localhost:8383/login?redirectUrl=${ctx.host+ctx.originalUrl}`)
}
} catch (error) {console.log(error)}
}
}
}
})
app.use(router.routes())
const port=process.env.PORT||8888
app.listen(port,()=>{
console.log(`app ${system} running at ${port}`)
})至此单点登录的大部分逻辑都已经完成,之后再session有效期内再访问页面,就不需要再登录,直接返回资源
router.get("/",async (ctx)=>{
//如果session中有用户信息,说明已经登录过,直接返回请求资源
let user=ctx.session.user
if(user){
await ctx.render('index.ejs',{
user,
system
})
}
//...
})原文地址:https://juejin.cn/post/7088343138905325582
作者:YoYo君
更多node相关知识,请访问:nodejs 教程!
The above is the detailed content of What is single sign-on? How to implement SSO using Nodejs. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1384
1384
 52
52
 The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
Node.js is a server-side JavaScript runtime, while Vue.js is a client-side JavaScript framework for creating interactive user interfaces. Node.js is used for server-side development, such as back-end service API development and data processing, while Vue.js is used for client-side development, such as single-page applications and responsive user interfaces.
 Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Node.js can be used as a backend framework as it offers features such as high performance, scalability, cross-platform support, rich ecosystem, and ease of development.
 How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
To connect to a MySQL database, you need to follow these steps: Install the mysql2 driver. Use mysql2.createConnection() to create a connection object that contains the host address, port, username, password, and database name. Use connection.query() to perform queries. Finally use connection.end() to end the connection.
 What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
There are two npm-related files in the Node.js installation directory: npm and npm.cmd. The differences are as follows: different extensions: npm is an executable file, and npm.cmd is a command window shortcut. Windows users: npm.cmd can be used from the command prompt, npm can only be run from the command line. Compatibility: npm.cmd is specific to Windows systems, npm is available cross-platform. Usage recommendations: Windows users use npm.cmd, other operating systems use npm.
 What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
The following global variables exist in Node.js: Global object: global Core module: process, console, require Runtime environment variables: __dirname, __filename, __line, __column Constants: undefined, null, NaN, Infinity, -Infinity
 Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
The main differences between Node.js and Java are design and features: Event-driven vs. thread-driven: Node.js is event-driven and Java is thread-driven. Single-threaded vs. multi-threaded: Node.js uses a single-threaded event loop, and Java uses a multi-threaded architecture. Runtime environment: Node.js runs on the V8 JavaScript engine, while Java runs on the JVM. Syntax: Node.js uses JavaScript syntax, while Java uses Java syntax. Purpose: Node.js is suitable for I/O-intensive tasks, while Java is suitable for large enterprise applications.
 Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Yes, Node.js is a backend development language. It is used for back-end development, including handling server-side business logic, managing database connections, and providing APIs.
 How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Server deployment steps for a Node.js project: Prepare the deployment environment: obtain server access, install Node.js, set up a Git repository. Build the application: Use npm run build to generate deployable code and dependencies. Upload code to the server: via Git or File Transfer Protocol. Install dependencies: SSH into the server and use npm install to install application dependencies. Start the application: Use a command such as node index.js to start the application, or use a process manager such as pm2. Configure a reverse proxy (optional): Use a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to route traffic to your application




