
Arrays can be placed in php arrays. PHP arrays can store all types of data, including the array itself; if the elements in an array are another array, it forms an array containing the array, that is, a multi-dimensional array. Different dimensions of the array indicate that several subscripts (indexes) are needed to obtain the corresponding array elements. For example, a two-dimensional array requires two subscripts.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, PHP7.1 version, DELL G3 computer
Arrays can be placed in php arrays.
Array is one of the most important data types in PHP and is widely used in PHP. Because PHP is a programming language with weak data types, array variables in PHP can store any number of data of any type, and can implement the functions of data structures such as heaps, stacks, and queues in other strong data types.
Arrays in PHP can store all types of data, including the array itself. If the elements in one array are another array, an array containing the array is formed, that is, a multi-dimensional array:
Two-dimensional array
Three-dimensional array
Four-dimensional array
...
But the array exceeds three dimensions Then the readability will be greatly reduced, and it will also be inconvenient to manage.
Let’s take a look at how to define a multi-dimensional array:
1. Define a two-dimensional array
Two-dimensional array and One-dimensional arrays are declared in the same way, except that one or more elements in the array are also declared as an array. There are also two methods of declaring a two-dimensional array, directly assigning values to the array elements and using the array() function.
1), directly assign values to array elements
We can pass the format of "$array variable name[row subscript][column subscript]= Value;" format to create and initialize the two-dimensional array
<?php
header("Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
$array[0]['姓名'] = '张三';
$array[0]['年龄'] = '25';
$array[0]['性别'] = '男';
$array[1]['姓名'] = '李四';
$array[1]['年龄'] = '21';
$array[1]['性别'] = '男';
$array[2]['姓名'] = '娜娜';
$array[2]['年龄'] = '22';
$array[2]['性别'] = '女';
var_dump($array);
?>Output result:
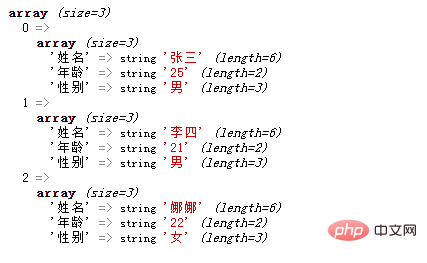
The row subscript of the two-dimensional array The and column subscripts can be empty (that is, no specific index value is specified), then the default is a numeric index, and the index value increases sequentially starting from 0 by default.
Example 1: "Column subscript" is empty
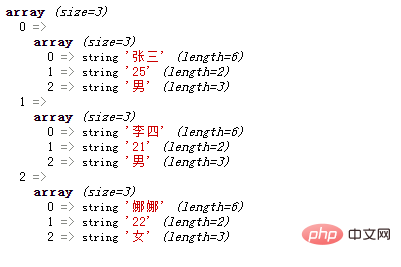
<?php
header("Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
$array[0][] = '张三';
$array[0][] = '25';
$array[0][] = '男';
$array[1][] = '李四';
$array[1][] = '21';
$array[1][] = '男';
$array[2][] = '娜娜';
$array[2][] = '22';
$array[2][] = '女';
var_dump($array);
?>Output result:
Example 2: "Row subscript" is Empty
<?php
header("Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
$array[]['姓名'] = '张三';
$array[]['年龄'] = '25';
$array[]['性别'] = '男';
$array[]['姓名'] = '李四';
$array[]['年龄'] = '21';
$array[]['性别'] = '男';
$array[]['姓名'] = '娜娜';
$array[]['年龄'] = '22';
$array[]['性别'] = '女';
var_dump($array);
?>Output result:

Example 3: "Row subscript" and "Column subscript" are both empty
<?php
header("Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
$array[][] = '张三';
$array[][] = '25';
$array[][] = '男';
$array[][] = '李四';
$array[][] = '21';
$array[][] = '男';
$array[][] = '娜娜';
$array[][] = '22';
$array[][] = '女';
var_dump($array);
?>Output result:

2), use the array() function
Using the array() function to declare a two-dimensional array is the same as declaring one Dimensional arrays are similar.
Index array
<?php
header("Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
$array = array
(
array("张三",25,"男"),
array("李四",21,"男"),
array("娜娜",22,"女")
);
var_dump($array);
?>Output result:

Associative array
Example 1:
<?php
header("Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
$array = array
(
"学生1"=>array("张三",25,"男"),
"学生2"=>array("李四",21,"男"),
"学生3"=>array("娜娜",22,"女")
);
var_dump($array);
?>Output result:

Example 2:
<?php
header("Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
$array = array
(
"学生1"=>array("姓名"=>"张三","年龄"=>25,"性别"=>"男"),
"学生2"=>array("姓名"=>"李四","年龄"=>21,"性别"=>"男"),
"学生3"=>array("姓名"=>"娜娜","年龄"=>22,"性别"=>"女")
);
var_dump($array);
?>Output result:

Extension: Get the elements in the two-dimensional array
Just need to indicate each The subscript of a dimension can
<?php
header("Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
$array = array
(
array("姓名"=>"张三","年龄"=>25,"性别"=>"男"),
array("姓名"=>"李四","年龄"=>21,"性别"=>"男"),
array("姓名"=>"娜娜","年龄"=>22,"性别"=>"女")
);
echo $array[0]['姓名'].'同学的年龄为'.$array[0]['年龄'].'岁';
?>Output result:

Note:The different dimensions of the array mark our Several subscripts (indexes) need to be used to obtain the corresponding array elements. For example, a two-dimensional array requires two subscripts to obtain the corresponding array elements, a three-dimensional array requires three, and so on.
2. Creation of multi-dimensional arrays
Refer to the two-dimensional array and draw inferences, you can easily create three-dimensional arrays and four-dimensional arrays Or other higher dimensional arrays. An example of defining a three-dimensional array is as follows:
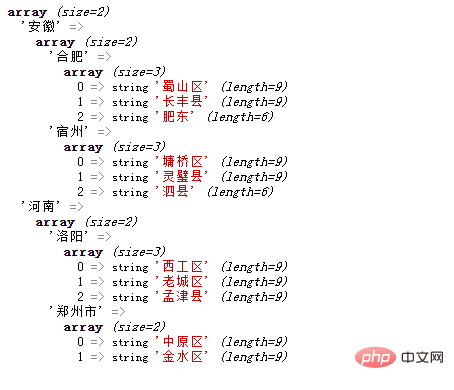
<?php
header("Content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8");
$array = array(
'安徽' => array(
'合肥'=>array('蜀山区','长丰县','肥东'),
'宿州'=>array('墉桥区','灵璧县','泗县')
),
'河南' => array(
'洛阳'=>array('西工区','老城区','孟津县'),
'郑州市'=>array('中原区','金水区')
)
);
var_dump($array);
?>Output result:
Recommended learning: "PHP Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of Can arrays be placed in php arrays?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!