Summary of Python multi-process knowledge points
This article brings you relevant knowledge about python, which mainly introduces the relevant content about multi-process, including what is multi-process, process creation, inter-process synchronization, and process Chi and so on, let’s take a look at it together, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended learning: python video tutorial
1. What is multi-process?
1. Process
Program: For example, xxx.py is a program, which is a static
Process: After a program is run, the resources used by the code are called processes. It is the basic unit for the operating system to allocate resources. Not only can multitasking be completed through threads, but also processes can be done
2. Process status
During work, the number of tasks is often greater than the number of CPU cores, that is, there must be some tasks being executed, and Some other tasks are waiting for the CPU to execute, resulting in different states 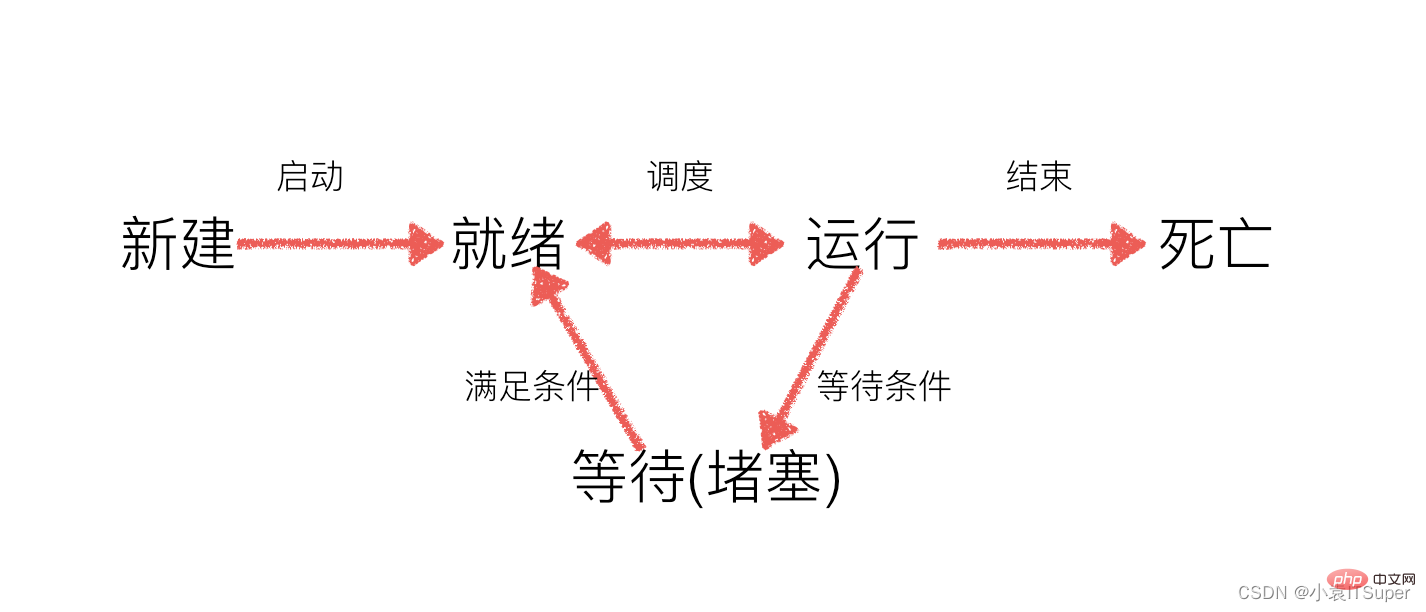
- Ready state: The running conditions have slowed down and are in progress Waiting for cpu execution
- Execution state: The CPU is executing its function
- Waiting state: Waiting for certain conditions to be met, such as a program sleeping , it is in the waiting state at this time
2. Creation of process-multiprocessing
1. Process class syntax description
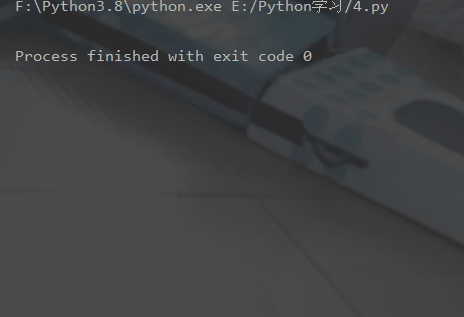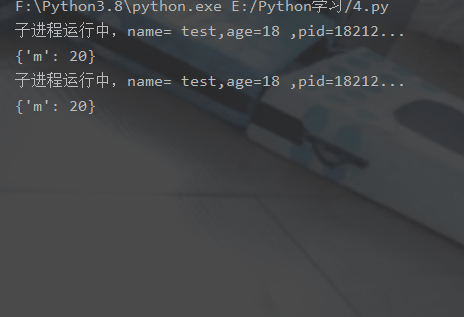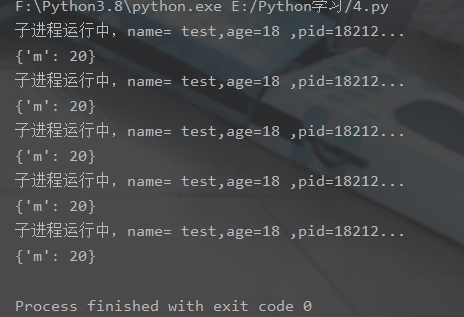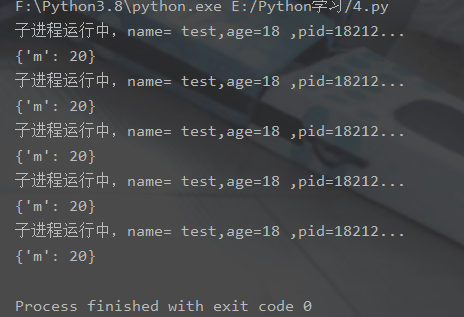
multiprocessingThe module generates a process by creating aProcessobject and then calling itsstart()method,Processis the same asthreading.Thread API.
Syntax format:multiprocessing.Process(group=None, target=None, name=None, args=(), kwargs={}, *, daemon =None)
Parameter description:
-
group: Specifies the process group, which is not used in most cases -
target: If a function reference is passed, the child process can be tasked to execute the code here -
name: Set a name for the process , you can not set -
args: The parameters passed to the function specified by the target are passed in the form of tuples -
kwargs: To the target The specified function passes named parameters
The multiprocessing.Process object has the following methods and properties:
| Method name/property | Explanation |
|---|---|
run() |
The specific execution method of the process |
start() |
Start a child process instance (create a child process) |
join([timeout ]) |
If the optional parameter timeout is the default value None, it will block until the process calling the join() method terminates; if timeout is a positive number, it will block for up to timeout seconds |
name |
The alias of the current process, the default is Process-N, N is an integer increasing from 1 |
pid |
The pid (process number) of the current process |
is_alive() |
Determine whether the child process of the process is still alive |
##exitcode | The exit code of the child process|
daemon | The daemon flag of the process is a Boolean value. |
authkey | The authentication key for the process. |
sentinel | Numeric handle to the system object that will become ready when the process ends. |
terminate() | Immediately terminate the child process regardless of whether the task is completed|
kill() | Same as terminate(), but uses the SIGKILL signal on Unix. |
close() | Close the Process object and release all resources associated with it
| Method name | Description |
|---|---|
q=Queue() |
Initialize the Queue() object. If the maximum number of messages that can be received is not specified in the brackets, or the number is a negative value, then Represents that there is no upper limit on the number of messages that can be accepted (until the end of memory) |
Queue.qsize() |
Returns the number of messages contained in the current queue |
Queue.empty() |
If the queue is empty, return True, otherwise False |
Queue.full() |
If the queue is full, return True, otherwise False |
Queue.get([block[ , timeout]]) |
Get a message in the queue and then remove it from the queue. The default value of block is True. 1. If the block uses the default value and no timeout (in seconds) is set, and the message queue is empty, the program will be blocked (stopped in the reading state) until the message is read from the message queue. If timeout is set , it will wait for timeout seconds, and if no message has been read, a "Queue.Empty" exception will be thrown. 2. If the block value is False and the message queue is empty, the "Queue.Empty" exception will be thrown immediately |
## Queue.get_nowait() | Quite Queue.get(False)|
Queue.put(item,[block[, timeout]]) |
Write item messages to the queue, the default value of block is True. 1. If the block uses the default value and no timeout (in seconds) is set, if there is no space for writing in the message queue, the program will be blocked (stopped in the writing state) until space is made available in the message queue. If timeout is set, it will wait for timeout seconds. If there is no space, a "Queue.Full" exception will be thrown. 2. If the block value is False, if there is no space to write in the message queue, the "Queue.Full" exception will be thrown immediately |
|
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
close() |
关闭Pool,使其不再接受新的任务 |
terminate() |
不管任务是否完成,立即终止 |
join() |
主进程阻塞,等待子进程的退出, 必须在close或terminate之后使用 |
2. Pool实例
初始化Pool时,可以指定一个最大进程数,当有新的请求提交到Pool中时,如果池还没有满,那么就会创建一个新的进程用来执行该请求;但如果池中的进程数已经达到指定的最大值,那么该请求就会等待,直到池中有进程结束,才会用之前的进程来执行新的任务,请看下面的实例:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-from multiprocessing import Poolimport os, time, randomdef worker(msg):
t_start = time.time()
print("%s开始执行,进程号为%d" % (msg,os.getpid()))
# random.random()随机生成0~1之间的浮点数
time.sleep(random.random()*2)
t_stop = time.time()
print(msg,"执行完毕,耗时%0.2f" % (t_stop-t_start))po = Pool(3) # 定义一个进程池,最大进程数3for i in range(0,10):
# Pool().apply_async(要调用的目标,(传递给目标的参数元祖,))
# 每次循环将会用空闲出来的子进程去调用目标
po.apply_async(worker,(i,))print("----start----")po.close()
# 关闭进程池,关闭后po不再接收新的请求po.join()
# 等待po中所有子进程执行完成,必须放在close语句之后print("-----end-----")运行结果:
----start---- 0开始执行,进程号为21466 1开始执行,进程号为21468 2开始执行,进程号为21467 0 执行完毕,耗时1.01 3开始执行,进程号为21466 2 执行完毕,耗时1.24 4开始执行,进程号为21467 3 执行完毕,耗时0.56 5开始执行,进程号为21466 1 执行完毕,耗时1.68 6开始执行,进程号为21468 4 执行完毕,耗时0.67 7开始执行,进程号为21467 5 执行完毕,耗时0.83 8开始执行,进程号为21466 6 执行完毕,耗时0.75 9开始执行,进程号为21468 7 执行完毕,耗时1.03 8 执行完毕,耗时1.05 9 执行完毕,耗时1.69 -----end-----
3. 进程池中的Queue
如果要使用Pool创建进程,就需要使用multiprocessing.Manager()中的Queue()
而不是multiprocessing.Queue(),否则会得到一条如下的错误信息:RuntimeError: Queue objects should only be shared between processes through inheritance.
下面的实例演示了进程池中的进程如何通信:
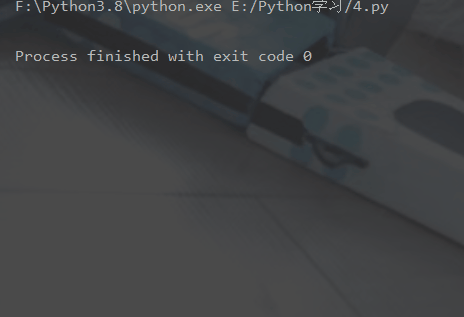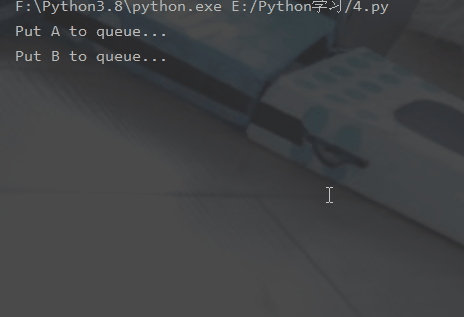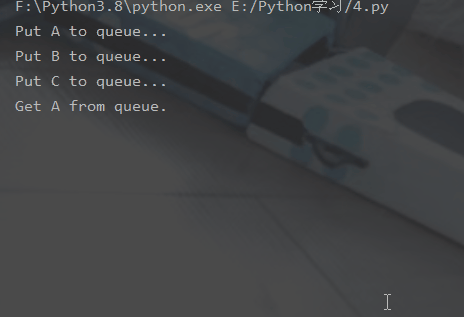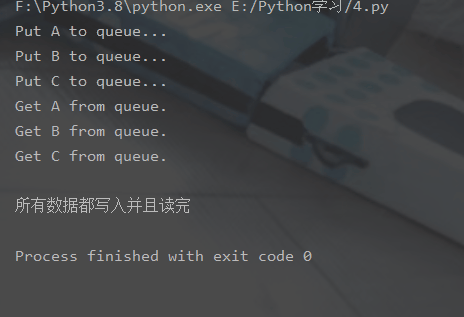
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# 修改import中的Queue为Managerfrom multiprocessing import Manager,Poolimport os,time,randomdef reader(q):
print("reader启动(%s),父进程为(%s)" % (os.getpid(), os.getppid()))
for i in range(q.qsize()):
print("reader从Queue获取到消息:%s" % q.get(True))def writer(q):
print("writer启动(%s),父进程为(%s)" % (os.getpid(), os.getppid()))
for i in "itcast":
q.put(i)if __name__=="__main__":
print("(%s) start" % os.getpid())
q = Manager().Queue() # 使用Manager中的Queue
po = Pool()
po.apply_async(writer, (q,))
time.sleep(1) # 先让上面的任务向Queue存入数据,然后再让下面的任务开始从中取数据
po.apply_async(reader, (q,))
po.close()
po.join()
print("(%s) End" % os.getpid())运行结果:
(11095) start writer启动(11097),父进程为(11095)reader启动(11098),父进程为(11095)reader从Queue获取到消息:i reader从Queue获取到消息:t reader从Queue获取到消息:c reader从Queue获取到消息:a reader从Queue获取到消息:s reader从Queue获取到消息:t(11095) End
六、进程、线程对比
1. 功能
进程:能够完成多任务,比如 在一台电脑上能够同时运行多个QQ
线程:能够完成多任务,比如 一个QQ中的多个聊天窗口
定义的不同
进程是系统进行资源分配和调度的一个独立单位.
线程是进程的一个实体,是CPU调度和分派的基本单位,它是比进程更小的能独立运行的基本单位.线程自己基本上不拥有系统资源,只拥有一点在运行中必不可少的资源(如程序计数器,一组寄存器和栈),但是它可与同属一个进程的其他的线程共享进程所拥有的全部资源.
2. 区别
- 一个程序至少有一个进程,一个进程至少有一个线程.
-线程的划分尺度小于进程(资源比进程少),使得多线程程序的并发性高。
-进程在执行过程中拥有独立的内存单元,而多个线程共享内存,从而极大地提高了程序的运行效率
- 线线程不能够独立执行,必须依存在进程中
- 可以将进程理解为工厂中的一条流水线,而其中的线程就是这个流水线上的工人
3. 优缺点
- 线程:线程执行开销小,但不利于资源的管理和保护
- 进程:进程执行开销大,但利于资源的管理和保护
推荐学习:python视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Summary of Python multi-process knowledge points. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
Can vscode run ipynb
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
The key to running Jupyter Notebook in VS Code is to ensure that the Python environment is properly configured, understand that the code execution order is consistent with the cell order, and be aware of large files or external libraries that may affect performance. The code completion and debugging functions provided by VS Code can greatly improve coding efficiency and reduce errors.
 Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang is more suitable for high concurrency tasks, while Python has more advantages in flexibility. 1.Golang efficiently handles concurrency through goroutine and channel. 2. Python relies on threading and asyncio, which is affected by GIL, but provides multiple concurrency methods. The choice should be based on specific needs.