 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 Vue.js
Vue.js
 What is Key in vue? What is the difference between setting the key and not setting it?
What is Key in vue? What is the difference between setting the key and not setting it?
What is Key in vue? What is the difference between setting the key and not setting it?
What is Key in vue? The following article will introduce to you the principle of key in vue, and talk about the difference between setting the key and not setting the key. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

1. What is Key
Before we begin, let’s restore two actual work scenarios
When we use
v-for, we need to addkey
<ul>
<li v-for="item in items" :key="item.id">...</li>
</ul>- ## to the unit #Use the timestamp generated by
new Date()
askey, and manually force a re-rendering
<Comp :key="+new Date()" />
key?
key is the unique ID given to each vnode, and it is also an optimization strategy for diff. It can find the corresponding one more accurately and faster based on the key. vnode node. (Learning video sharing: vue video tutorial)
The logic behind the scene
When we are usingv-for When , you need to add key
- If no key is used, Vue will adopt the in-place restoration principle: minimize the movement of the element, and will try to do its best To a certain extent, patch or reuse elements of the same type in the same appropriate place. If key is used, Vue will record the elements according to the order of keys. If the element that once owned the key no longer appears, it will be directly removed or destroyed
new Date()The generated timestamp is used as key, manually forced to trigger re-rendering
- When the rerender with the new value is used as the key, the new key is Comp appears, then the old key Comp will be removed, and the new key Comp will trigger rendering
2. The difference between setting the key and not setting the key
For example Example:Create an instance and insert data into the
items array after 2 seconds
<body>
<div id="demo">
<p v-for="item in items" :key="item">{{item}}</p>
</div>
<script src="../../dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 创建实例
const app = new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: { items: ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'] },
mounted () {
setTimeout(() => {
this.items.splice(2, 0, 'f') //
}, 2000);
},
});
</script>
</body>key, vue This operation will be performed:
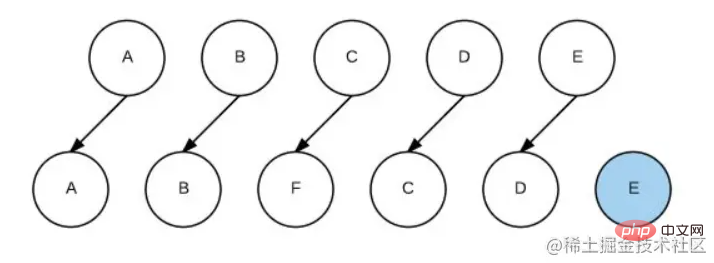
- Compare A, A, nodes of the same type, and perform
- patch
, but the data is the same, the operation does not occurdom Compare B, B, nodes of the same type, perform - patch
, but the data is the same, does not occurdomOperationCompare C, F, nodes of the same type, perform - patch
, the data is different,domoperation occurs Compare D, C, nodes of the same type, perform - patch
, the data is different,domoperation occursCompare E, D, nodes of the same type, perform - patch
, the data is different,domoperation occurs The loop ends, insert E into - DOM
key: vue will perform the following operation:
- Compare A, A, nodes of the same type, perform
- patch
, but the data is the same, nodomoperation occursCompare B, B, nodes of the same type, perform - patch
, but the data is the same, nodomoperation occursCompare C, F, nodes of different types - Compare E, E, the same type Node, perform
- patch
, but the data is the same, nodomoperation will occur
Compare D, D, nodes of the same type, perform- patch
- patch
, but the data is the same, nodomoperation occursCompare C and C, nodes of the same type, perform - patch
, but the data is the same, Nodomoperation occursThe loop ends, before F is inserted into C
key can greatly reduce the DOM operations on the page and improve the diff efficiency
Can setting the key value definitely improve diff efficiency?
In fact, this is not the case. The document also clearly states that When Vue.js uses v-for to update the rendered element list, it defaults to "in-place reuse" Strategy. If the order of the data items is changed, Vue will not move the DOM elements to match the order of the data items, but will simply reuse each element here and ensure that it displays each element that has been rendered at a specific index This default mode is efficient, but it is only suitable for list rendering output that does not rely on subcomponent state or temporary DOM state (for example: form input values) It is recommended to use it whenever possible ## Providekey when #v-for, unless traversing the output DOM content is very simple, or deliberately relying on the default behavior to obtain performance improvements<h2 id="strong-三-原理分析-strong"><strong>三、原理分析</strong></h2><p>源码位置:core/vdom/patch.js </p><p>里判断是否为同一个<code>key,首先判断的是key值是否相等如果没有设置key,那么key为undefined,这时候undefined是恒等于undefined
function sameVnode (a, b) {
return (
a.key === b.key && (
(
a.tag === b.tag &&
a.isComment === b.isComment &&
isDef(a.data) === isDef(b.data) &&
sameInputType(a, b)
) || (
isTrue(a.isAsyncPlaceholder) &&
a.asyncFactory === b.asyncFactory &&
isUndef(b.asyncFactory.error)
)
)
)
}updateChildren方法中会对新旧vnode进行diff,然后将比对出的结果用来更新真实的DOM
function updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
...
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
if (isUndef(oldStartVnode)) {
...
} else if (isUndef(oldEndVnode)) {
...
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
...
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) {
...
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) { // Vnode moved right
...
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) { // Vnode moved left
...
} else {
if (isUndef(oldKeyToIdx)) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
idxInOld = isDef(newStartVnode.key)
? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key]
: findIdxInOld(newStartVnode, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
if (isUndef(idxInOld)) { // New element
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx)
} else {
vnodeToMove = oldCh[idxInOld]
if (sameVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx)
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, vnodeToMove.elm, oldStartVnode.elm)
} else {
// same key but different element. treat as new element
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx)
}
}
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
}
}
...
}The above is the detailed content of What is Key in vue? What is the difference between setting the key and not setting it?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1375
1375
 52
52
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 What does it mean to lazy load vue?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
What does it mean to lazy load vue?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
In Vue.js, lazy loading allows components or resources to be loaded dynamically as needed, reducing initial page loading time and improving performance. The specific implementation method includes using <keep-alive> and <component is> components. It should be noted that lazy loading can cause FOUC (splash screen) issues and should be used only for components that need lazy loading to avoid unnecessary performance overhead.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
You can query the Vue version by using Vue Devtools to view the Vue tab in the browser's console. Use npm to run the "npm list -g vue" command. Find the Vue item in the "dependencies" object of the package.json file. For Vue CLI projects, run the "vue --version" command. Check the version information in the <script> tag in the HTML file that refers to the Vue file.
 Vue realizes marquee/text scrolling effect
Apr 07, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
Vue realizes marquee/text scrolling effect
Apr 07, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
Implement marquee/text scrolling effects in Vue, using CSS animations or third-party libraries. This article introduces how to use CSS animation: create scroll text and wrap text with <div>. Define CSS animations and set overflow: hidden, width, and animation. Define keyframes, set transform: translateX() at the beginning and end of the animation. Adjust animation properties such as duration, scroll speed, and direction.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.



