How redis implements queue blocking, delay, publishing and subscription
This article brings you relevant knowledge about Redis, which mainly introduces related issues about how to implement queue blocking, delay, publishing and subscription. Let's take a look at it together. I hope everyone has to help.

Recommended learning: Redis video tutorial
Redis can not only be used as a cache server, but also as a message queue. Its list type inherently supports use as a message queue. As shown in the figure below: 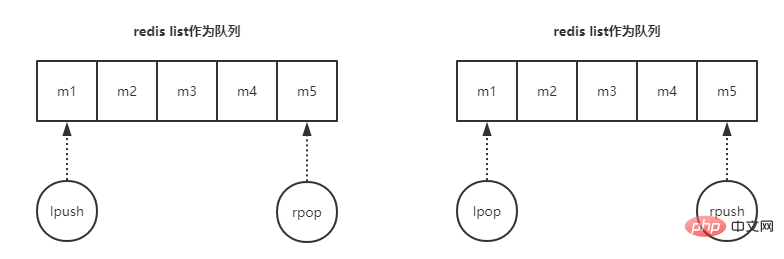
Since the Redis list is implemented using a doubly linked list, the head node and the tail node are saved, so inserting or obtaining elements on both sides of the head and tail of the list is It is very fast and the time complexity is O(1).
Ordinary Queue
You can directly use the Redis list data type to implement the message queue, with just two simple instructions: lpush and rpop or rpush and lpop.
- lpush rpop: left-in and right-out queue
- rpush lpop: left-out and right-in queue
The following uses the redis command to simulate ordinary queue.
Use the lpush command to produce messages:
>lpush queue:single 1"1">lpush queue:single 2"2">lpush queue:single 3"3"
Use the rpop command to consume messages:
>rpop queue:single"1">rpop queue:single"2">rpop queue:single"3"
The following uses Java code to implement a common queue.
Producer SingleProducer
package com.morris.redis.demo.queue.single;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;/**
* 生产者
*/public class SingleProducer {
public static final String SINGLE_QUEUE_NAME = "queue:single";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis();
for (int i = 0; i <p>Consumer SingleConsumer: </p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">package com.morris.redis.demo.queue.single;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;import java.util.Objects;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/**
* 消费者
*/public class SingleConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis();
while (true) {
String message = jedis.rpop(SingleProducer.SINGLE_QUEUE_NAME);
if(Objects.nonNull(message)) {
System.out.println(message);
} else {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
}
}
}}The above code has basically realized the production and consumption of ordinary queues, but the consumer of the message in the above example There are two problems:
- Consumers need to constantly call the rpop method to check whether there is data (message) to be processed in the redis list. A connection will be initiated every time it is called. There may be no data in the list, resulting in a large number of empty polls and unnecessary waste. Maybe you can use Thread.sleep() and other methods to allow the consumer thread to consume again after a period of time. If the sleep time is too long, some time-sensitive messages cannot be processed. If the sleep time is too short, it will also cause comparisons on the connection. Big overhead.
- If the producer speed is greater than the consumer consumption speed, the length of the message queue will continue to increase, which will occupy a lot of memory space over time.
Blocking queue
Consumers can use the brpop instruction to obtain data from the redis list. This instruction will only return if there are elements. If not, it will block until timeout and return null. Therefore, the consumer does not need to sleep to obtain data, which is equivalent to implementing a blocking queue.
Use the brpop command of redis to simulate the blocking queue.
>brpop queue:single 30
You can see that the command line is blocked here in brpop, and will return after 30 seconds without data.
The Java code is implemented as follows:
The producer is the same as the producer of the ordinary queue.
Consumer BlockConsumer:
package com.morris.redis.demo.queue.block;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;import java.util.List;/**
* 消费者
*/public class BlockConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis();
while (true) {
// 超时时间为1s
List<string> messageList = jedis.brpop(1, BlockProducer.BLOCK_QUEUE_NAME);
if (null != messageList && !messageList.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(messageList);
}
}
}}</string>Disadvantages: One production and multiple consumption cannot be achieved.
Publish and subscribe mode
In addition to providing support for message queues, Redis also provides a set of commands to support the publish/subscribe mode. Using the pub/sub mode of Redis, you can implement a queue that produces once and consumes multiple times.
Publish: The PUBLISH instruction can be used to publish a message, format:
PUBLISH channel message
The return value indicates the number of subscribers to the message.
Subscription: The SUBSCRIBE instruction is used to receive a message, format:
SUBSCRIBE channel
After using the SUBSCRIBE instruction, you enter the subscription mode, but you will not receive the message sent by publish before subscribing. This is because only Subscriptions will not receive the message until it is sent. For other commands in this mode, only replies can be seen.
Replies are divided into three types:
- If it is subscribe, the second value indicates the subscribed channel, and the third value indicates the number of subscribed channels
- If it is message (message), the second value is the channel that generated the message, and the third value is the message.
- If it is unsubscribe, the second value represents the channel to unsubscribe from, and the third value is the channel that generated the message. The value represents the current client's subscription number.
The following uses the redis command to simulate the publish-subscribe mode.
Producer:
127.0.0.1:6379> publish queue hello(integer) 1127.0.0.1:6379> publish queue hi(integer) 1
Consumer:
127.0.0.1:6379> subscribe queue Reading messages... (press Ctrl-C to quit)1) "subscribe"2) "queue"3) (integer) 11) "message"2) "queue"3) "hello"1) "message"2) "queue"3) "hi"
The Java code is implemented as follows:
Producer PubsubProducer:
package com.morris.redis.demo.queue.pubsub;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;/**
* 生产者
*/public class PubsubProducer {
public static final String PUBSUB_QUEUE_NAME = "queue:pubsub";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis();
for (int i = 0; i <p>Consumer PubsubConsumer: </p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">package com.morris.redis.demo.queue.pubsub;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPubSub;/**
* 消费者
*/public class PubsubConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis();
JedisPubSub jedisPubSub = new JedisPubSub() {
@Override
public void onMessage(String channel, String message) {
System.out.println("receive message: " + message);
if(message.indexOf("99") > -1) {
this.unsubscribe();
}
}
@Override
public void onSubscribe(String channel, int subscribedChannels) {
System.out.println("subscribe channel: " + channel);
}
@Override
public void onUnsubscribe(String channel, int subscribedChannels) {
System.out.println("unsubscribe channel " + channel);
}
};
jedis.subscribe(jedisPubSub, PubsubProducer.PUBSUB_QUEUE_NAME);
}}Consumers can start multiple consumers, and each consumer can receive all messages.
You can use the command UNSUBSCRIBE to unsubscribe. If no parameters are added, all channels subscribed to by the SUBSCRIBE command will be unsubscribed.
Redis also supports message subscription based on wildcards, using the command PSUBSCRIBE (pattern subscribe), for example:
psubscribe channel.*
Channels subscribed with the PSUBSCRIBE command must also use the command PUNSUBSCRIBE command to unsubscribe. This command cannot Unsubscribe from the channel subscribed by SUBSCRIBE. Similarly, UNSUBSCRIBE cannot unsubscribe from the channel subscribed by PSUBSCRIBE command.
At the same time, the PUNSUBSCRIBE instruction wildcard will not be expanded. For example: PUNSUBSCRIBE \* will not match channel.\*, so to unsubscribe from channel.\*, you must write PUBSUBSCRIBE channel. \*.
Redis' pub/sub also has its shortcomings, that is, if the consumer goes offline, the producer's messages will be lost.
延时队列和优先级队列
Redis中有个数据类型叫Zset,其本质就是在数据类型Set的基础上加了个排序的功能而已,除了保存原始的数据value之外,还提供另一个属性score,这一属性在添加修改元素时候可以进行指定,每次指定后,Zset会自动重新按新的score值进行排序。
如果score字段设置为消息的优先级,优先级最高的消息排在第一位,这样就能实现一个优先级队列。
如果score字段代表的是消息想要执行时间的时间戳,将它插入Zset集合中,便会按照时间戳大小进行排序,也就是对执行时间先后进行排序,集合中最先要执行的消息就会排在第一位,这样的话,只需要起一个死循环线程不断获取集合中的第一个元素,如果当前时间戳大于等于该元素的score就将它取出来进行消费删除,就可以达到延时执行的目的,注意不需要遍历整个Zset集合,以免造成性能浪费。
下面使用redis的zset来模拟延时队列。
生产者:
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd queue:delay 1 order1 2 order2 3 order3(integer) 0
消费者:
127.0.0.1:6379> zrange queue:delay 0 0 withscores1) "order1"2) "1"127.0.0.1:6379> zrem queue:delay order1(integer) 1
Java代码如下:
生产者DelayProducer:
package com.morris.redis.demo.queue.delay;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;import java.util.Date;import java.util.Random;/**
* 生产者
*/public class DelayProducer {
public static final String DELAY_QUEUE_NAME = "queue:delay";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis();
long now = new Date().getTime();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i <p>消费者:</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">package com.morris.redis.demo.queue.delay;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;import redis.clients.jedis.Tuple;import java.util.Date;import java.util.List;import java.util.Set;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/**
* 消费者
*/public class DelayConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis();
while (true) {
long now = new Date().getTime();
Set<tuple> tupleSet = jedis.zrangeWithScores(DelayProducer.DELAY_QUEUE_NAME, 0, 0);
if(tupleSet.isEmpty()) {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} else {
for (Tuple tuple : tupleSet) {
Double score = tuple.getScore();
long time = score.longValue();
if(time <h2 id="应用场景">应用场景</h2>
<ul>
<li>延时队列可用于订单超时失效的场景</li>
<li>二级缓存(local+redis)中,当有缓存需要更新时,可以使用发布订阅模式通知其他服务器使得本地缓存失效。</li>
</ul>
<p>推荐学习:<a href="https://www.php.cn/course/list/54.html" target="_blank">Redis视频教程</a></p></tuple>The above is the detailed content of How redis implements queue blocking, delay, publishing and subscription. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
How to make message middleware for redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Redis, as a message middleware, supports production-consumption models, can persist messages and ensure reliable delivery. Using Redis as the message middleware enables low latency, reliable and scalable messaging.




