Summarize Oracle view knowledge points
This article brings you relevant knowledge about Oracle, which mainly introduces related issues about views. A view is a database object, which is obtained from one or more data tables or views. Let’s take a look at the virtual table exported from . I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Oracle Video Tutorial"
- View is a database object that is a virtual table derived from one or more data tables or views.
The- data corresponding to the view is not actually stored in the view, but is stored in the referenced data table.
The structure and data of the view are the results of querying the data table.
#According to the conditions given when creating the view, the view can be part of a data table or a union of multiple base tables.
- It stores the definition of the
- query statement to be retrieved for use when referencing the view.
Advantages of using views:
- Simplified data operations: Views can Simplify how users work with data.
- Focus on specific data: Unnecessary data or sensitive data may not appear in the view.
View provides a simple and effective security mechanism that can customize different users' access rights to data.- Provide backward compatibility: Views enable users to create backward-compatible interfaces for tables when their schema changes.
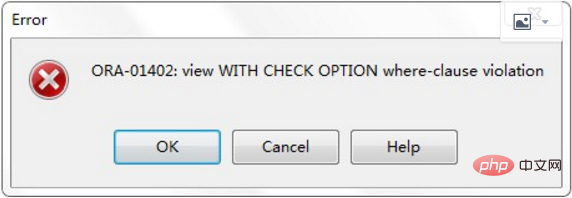
1. Create a modified viewCREATE [OR REPLACE] [FORCE] VIEW 'view_name'AS 'sub_query'[WITH CHECK OPTION]-- 只读[WITH READ ONLY]
Copy after login
CREATE [OR REPLACE] [FORCE] VIEW 'view_name'AS 'sub_query'[WITH CHECK OPTION]-- 只读[WITH READ ONLY]
| Description | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| If the created view already exists, | Oracle will automatically rebuild the view |
||||||||||
| This view will be automatically created regardless of whether the base table exists | Oracle |
||||||||||
| A complete | SELECT statement, in which an alias can be defined | ##WITH CHECK OPTION||||||||||
| WITH READ ONLY | |||||||||||
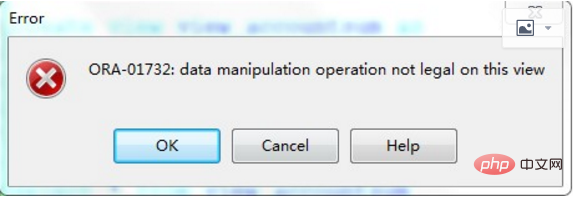
| DML | operations can be performed on this view |
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SNAPTIME$$ | 用于表示刷新时间。 |
| DMLTYPE$$ | 用于表示 DML 操作类型(I 表示 INSERT,D 表示 DELETE,U 表示 UPDATE)。 |
| OLD_NEW$$ | 用于表示这个值是新值还是旧值(N(EW)表示新值,O(LD)表示旧值,U 表示 UPDATE 操作)。 |
| CHANGE_VECTOR$$ | 表示修改矢量,用来表示被修改的是哪个或哪几个字段(此列是 RAW 类型)。其实 Oracle 采用的方式就是用每个 BIT 位去映射一个列。插入操作显示为: FE,删除显示为:OO,更新操作则根据更新字段的位置而显示不同的值。 |
- 当手动刷新物化视图后,物化视图日志被清空,物化视图更新。
begin
DBMS_MVIEW.refresh('MV_ADDRESS4', 'C');end;推荐教程:《Oracle视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of Summarize Oracle view knowledge points. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How long will Oracle database logs be kept?
May 10, 2024 am 03:27 AM
How long will Oracle database logs be kept?
May 10, 2024 am 03:27 AM
The retention period of Oracle database logs depends on the log type and configuration, including: Redo logs: determined by the maximum size configured with the "LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST" parameter. Archived redo logs: Determined by the maximum size configured by the "DB_RECOVERY_FILE_DEST_SIZE" parameter. Online redo logs: not archived, lost when the database is restarted, and the retention period is consistent with the instance running time. Audit log: Configured by the "AUDIT_TRAIL" parameter, retained for 30 days by default.
 Function to calculate the number of days between two dates in oracle
May 08, 2024 pm 07:45 PM
Function to calculate the number of days between two dates in oracle
May 08, 2024 pm 07:45 PM
The function in Oracle to calculate the number of days between two dates is DATEDIFF(). The specific usage is as follows: Specify the time interval unit: interval (such as day, month, year) Specify two date values: date1 and date2DATEDIFF(interval, date1, date2) Return the difference in days
 The order of the oracle database startup steps is
May 10, 2024 am 01:48 AM
The order of the oracle database startup steps is
May 10, 2024 am 01:48 AM
The Oracle database startup sequence is: 1. Check the preconditions; 2. Start the listener; 3. Start the database instance; 4. Wait for the database to open; 5. Connect to the database; 6. Verify the database status; 7. Enable the service (if necessary ); 8. Test the connection.
 How much memory does oracle require?
May 10, 2024 am 04:12 AM
How much memory does oracle require?
May 10, 2024 am 04:12 AM
The amount of memory required by Oracle depends on database size, activity level, and required performance level: for storing data buffers, index buffers, executing SQL statements, and managing the data dictionary cache. The exact amount is affected by database size, activity level, and required performance level. Best practices include setting the appropriate SGA size, sizing SGA components, using AMM, and monitoring memory usage.
 How to use interval in oracle
May 08, 2024 pm 07:54 PM
How to use interval in oracle
May 08, 2024 pm 07:54 PM
The INTERVAL data type in Oracle is used to represent time intervals. The syntax is INTERVAL <precision> <unit>. You can use addition, subtraction, multiplication and division operations to operate INTERVAL, which is suitable for scenarios such as storing time data and calculating date differences.
 How to see the number of occurrences of a certain character in Oracle
May 09, 2024 pm 09:33 PM
How to see the number of occurrences of a certain character in Oracle
May 09, 2024 pm 09:33 PM
To find the number of occurrences of a character in Oracle, perform the following steps: Get the total length of a string; Get the length of the substring in which a character occurs; Count the number of occurrences of a character by subtracting the substring length from the total length.
 How to replace string in oracle
May 08, 2024 pm 07:24 PM
How to replace string in oracle
May 08, 2024 pm 07:24 PM
The method of replacing strings in Oracle is to use the REPLACE function. The syntax of this function is: REPLACE(string, search_string, replace_string). Usage steps: 1. Identify the substring to be replaced; 2. Determine the new string to replace the substring; 3. Use the REPLACE function to replace. Advanced usage includes: multiple replacements, case sensitivity, special character replacement, etc.
 Oracle database server hardware configuration requirements
May 10, 2024 am 04:00 AM
Oracle database server hardware configuration requirements
May 10, 2024 am 04:00 AM
Oracle database server hardware configuration requirements: Processor: multi-core, with a main frequency of at least 2.5 GHz. For large databases, 32 cores or more are recommended. Memory: At least 8GB for small databases, 16-64GB for medium sizes, up to 512GB or more for large databases or heavy workloads. Storage: SSD or NVMe disks, RAID arrays for redundancy and performance. Network: High-speed network (10GbE or higher), dedicated network card, low-latency network. Others: Stable power supply, redundant components, compatible operating system and software, heat dissipation and cooling system.