 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Learn Python characters and lists simply (detailed examples)
Learn Python characters and lists simply (detailed examples)
Learn Python characters and lists simply (detailed examples)
This article brings you relevant knowledge about python, which mainly introduces issues related to characters and lists, including string input and output, list loop traversal, and list addition. Let’s take a look at deletion, modification, nesting of lists, etc. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended learning: python video tutorial
1. String
String representation
a = "100"b = "hello world"c = 'hello world'd = '100'e = ‘18.20520'
1.1The len function returns the length or number of objects
Python len() method returns the length or number of items of an object (character, list, tuple, dictionary, etc.).
In [1]: a="abcdefg"In [2]: len(a)Out[2]: 7In [3]: b = [1,2,3,4,5,66,77,8888]In [4]: len(b)Out[4]: 8
1.2 Another way to form a string:
Strings will be spliced and numbers will be added
In [5]: a ="lao"In [6]: b="wang"In [7]: c=a+b In [8]: c Out[8]: 'laowang'In [9]: d= "===="+a+b+"===="In [10]: d Out[10]: '====laowang===='In [11]: f="===%s===="%(a+b)In [12]: f Out[12]: '===laowang===='
2. String Input and output
2.1 String input
Input information
name = input(“ 请输入你的姓名:”)position = input(“ 请输入你的职业:”)address = input(“ 请输入你的地址:”)
Output information
print("="*50)print(" 姓名:%s\n 职业:%s\n 地址:%s" % (name,position,address))print("="*50)2.2Format usage syntax :
Display data in a formatted manner, and can display data in a variety of ways. Such as through position, through keyword parameters, through mapping list.
1. By position
print("my name is {0},age is {1}".format('Liu Bei',20))
print("my name is {},age is {}".format('Liu Bei',20))
print("{1},{0},{1}".format('Liu Bei',20))
2. Through keyword parameters
print(“{age},{name}”.format(age=28,name=“Cao Cao”))
print(“{name},{name},{age }".format(age=28, name="Cao Cao"))
3. Through mapping list
alist = ["Sun Quan", 20, "China"]
blist = ["Diao Chan", 18,"China"]
print("my name is {1[0]}, from {0[2]}, age is {0[1]}".format(alist,blist))
The data obtained by input in python3 is saved in the form of a string. Even if the input is a number, it is saved in the form of a string.
# Determine whether the password is correct
user_name = input(“ 请输入用户名:”)password = input(“ 请输入密码:”)if user_name == “beijing” and password == “123” :print(“ 欢迎登录北京官网!")else :print(" 你的账户或者密码错误!")2.3 Subscript introduction
Subscript index index
The so-called "subscript" is the number, just like the storage cabinet in the supermarket Number, through which the corresponding storage space can be found.
Get some characters through subscripts
If there is a string: name = 'abcdef', the actual storage in the memory is as follows: 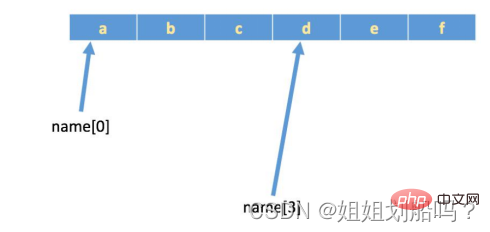
In [1] : len(name)
Out[1]: 7
In [2]: name[len(name)-1]
Out[2]: 'g'
In [3]: name[-1]
Out[3]: 'g' Positive numbers go from left to right, negative numbers go from right to left
2.4 Slice
Slicing refers to the operation of intercepting a part of the operation object. Strings, lists, and tuples all support slicing operations.
Syntax of slicing: [Start: End: Step]
Note: The selected interval is left-closed and right-open, that is, it starts from the "start" bit and ends at the previous bit of the "end" bit. (Does not include the end bit itself). Note that if the step size is not written, the default is 1.
The step size controls the direction. Positive numbers are taken from left to right, and negative numbers are taken from right to left.
In [1]: name="abcdefABCDEF"In [2]: name[0:3]Out[2]: 'abc'In [3]: name[0:5:2]Out[3]: 'ace'In [4]: name[-1::-1] #逆序(倒叙)Out[4]: 'FEDCBAfedcba'
Summary of subscripts and slicing
[:] Extract the entire string from the beginning (default position 0) to the end
[start:] Extract from the start to the end
[:end] Extract from the beginning to the end - 1
[start:end] Extract from start to end - 1
[startstep] Extract from start to end - 1, extract one character per step
[::-1] Reverse order
3. Common string functions
find(), rfind (), index (), rindex (), replace (), split (), parttion (), rparttion (), splitlines () , startswith (), endswith (), lower (), upper (),…………
3.1find and rfind
In [1]: mystr="hello world yanzilu and yanziluPython"In [2]: mystr
Out[2]: 'hello world yanzilu and yanziluPython
In [3]: mystr.find("and")Out[3]: 20In [4]: mystr.find("world") #存在则返回该单词开始的下标Out[4]: 6In [5]: mystr.find("world1") #不存在则返回-1Out[5]: -1In [6]: mystr.find("yanzilu")Out[6]: 12In [7]: mystr.find("yanzilu",20,len(mystr)) #指定查找区域Out[7]: 24In [8]: mystr.rfind("yanzilu") #rfind,从右往左搜索Out[8]: 243.2index, rindex
has the same function as find, with one difference. If the content cannot be searched by index, an error will be reported
In [9]: mystr.index("and") Out[9]: 20In [10]: mystr.index("yanzilu")Out[10]: 12In [11]: mystr.index("yanzilu",20,len(mystr)) #指定查找区域Out[11]: 24In [12]: mystr.rindex("yanzilu") #从右往左搜索Out[12]: 24In [13]: mystr.rindex("zhangsan") #搜索不存在的会报错---------------------------------------------------------------------------ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)<ipython-input-67-6aff7ee60ad5> in <module>----> 1 mystr.rindex("zhangsan")ValueError: substring not found</module></ipython-input-67-6aff7ee60ad5>3.3 replace Replace
In [14]: mystr
Out[14]: 'hello world yanzilu and yanziluPython'In [15]: mystr.replace("world","WORLD")Out[15]: 'hello WORLD yanzilu and yanziluPython'In [16]: mystr
Out[16]: 'hello world yanzilu and yanziluPython'In [17]: mystr.replace("yan","zhang")Out[17]: 'hello world zhangzilu and zhangziluPython'In [18]: mystr.replace("yan","zhang",1) #指定替换次数Out[18]: 'hello world zhangzilu and yanziluPython'In [19]: mystr.replace("yan","xxx",1)Out19]: 'hello world xxxzilu and yanziluPython'In [20]: mystr.replace("yan","xxx",2)Out[20]: 'hello world xxxzilu and xxxziluPython'In [21]: mystr.replace("yan","xxx",33) #替换次数可以超过最大值Out[21]: 'hello world xxxzilu and xxxziluPython'3.4split, function to split, cut, syntax: split(str=' ',maxsplit)
In [22]: mystr
Out[22]: 'hello world yanzilu and yanziluPython'In [23]: mystr.split(" ")Out[23]: ['hello', 'world', 'yanzilu', 'and', 'yanziluPython']In [24]: mystr.split("and")Out[24]: ['hello world yanzilu ', ' yanziluPython']In [25]: mystr.split(" ",3)Out[25]: ['hello', 'world', 'yanzilu', 'and yanziluPython']In [26]: mystr.split()Out[26]: ['hello', 'world', 'yanzilu', 'and', 'yanziluPython']3.5 partition, split mystr into three parts with str, before str , str itself, after str
In [27]: mystr
Out[27]: 'hello world yanzilu and yanziluPython'In [28]: mystr.partition("and")Out[28]: ('hello world yanzilu ', 'and', ' yanziluPython')In [29]: mystr.partition("yanzilu")Out[29]: ('hello world ', 'yanzilu', ' and yanziluPython')In [30]: mystr.rpartition("yanzilu")Out[30]: ('hello world yanzilu and ', 'yanzilu', 'Python')3.6splitlines function, split according to rows, return a list containing each row as an element
In [31]: mystr1 Out[31]: 'hello\nworld\nyanzilu\nand\nyanziluPython'In [32]: mystr1.splitlines()Out[32]: ['hello', 'world', 'yanzilu', 'and', 'yanziluPython']
3.7 startswith () determines whether it begins with str; endswith () determines whether it ends with str.
In [33]: mystr
Out[33]: 'hello world yanzilu and yanziluPython'In [34]: mystr.startswith("hello")Out[34]: TrueIn [35]: mystr.startswith("Hello")Out[35]: FalseIn [36]: mystr.startswith("h")Out[36]: TrueIn [37]: mystr.endswith("Pthon")Out[37]: FalseIn [38]: mystr.endswith("Python")Out[38]: True3.8upper converts all letters to uppercase; lower converts all letters to lowercase.
In [39]: mystr.upper()。 Out[39]: 'HELLO WORLD YANZILU AND YANZILUPYTHON'In [40]: mystr.lower() Out[40]: 'hello world yanzilu and yanzilupython'
3.9center adds spaces on both sides of the string and displays it in the center
In [41]: mystr = "那一夜我伤害了你"In [42]: mystr = mystr.center(30) In [43]: mystr Out[43]: ' 那一夜我伤害了你
In [44]: mystr.lstrip()Out[44]: '那一夜我伤害了你
3.11rstrip删除字符串右边的空格
In [45]: mystr.rstrip()Out[45]: ' 那一夜我伤害了你'
3.12 strip删除字符串两边的空格
In [46]: mystr.strip()Out[46]: '那一夜我伤害了你'
3.13isspace判断是否只包含空格
In [47]: mystr.isspace()Out[47]: FalseIn [48]: mystr = " "In [49]: mystr.isspace()Out[49]: True
3.14salpha判断字符串中是否只包含字母
In [50]: mystr = "abc" In [51]: mystr.isalpha()Out[51]: TrueIn [52]: mystr = "abc1"In [53]: mystr.isalpha()Out[53]: False
3.15isdigit判断是否只包含数字。
In [54]: mystr = "123123"In [55]: mystr.isdigit()Out[55]: TrueIn [56]: mystr = "123123aa"In [57]: mystr.isdigit()Out[57]: False
3.16isalnum判断是否只包含数字和字母。
In [58]: mystr.isalnum()Out[58]: TrueIn [59]: mystr = "123123 aa"In [60]: mystr.isalnum()Out[60]: False
3.17title将每个单词的首字母大写,其余小写
In [61]: mystr = 'hello world yanzilu and yanziluPython'In [62]: mystr.title()Out[63]: 'Hello World Yanzilu And Yanzilupython'
3.18capitalize将字符串的第一个字符大写,其余小写
In [64]: mystr.capitalize()Out[64]: 'Hello world yanzilu and yanzilupython'
3.19count统计单词出现的次数
In [65]: mystr.count("hello")Out[65]: 1In [66]: mystr.count("yan")Out[66]: 23.20join在每个字符后面插入str,构造出一个新的字符串。
In [67]: mystr = " "In [68]: name Out[68]: ['hello', 'world', 'yanzilu', 'and', 'yanziluPython']In [69]: mystr.join(name)Out[69]: 'hello world yanzilu and yanziluPython'In [70]: mystr = "_"In [71]: mystr.join(name)Out[71]: 'hello_world_yanzilu_and_yanziluPython'
4.列表及循环遍历
4.1列表的格式
#变量names_list的类型为列表names_list = [' 刘备',' 曹操',' 孙权']
#打印多个姓名names_list = [' 刘备',' 曹操',' 孙权']print(names_list[0])print(names_list[1])print(names_list[2]) names = [' 刘备',' 曹操',' 孙权'] for x in names print(x)i=1while i<len><h2 id="列表的增删改查">5.列表的增删改查:</h2>
<p>列表中存放的数据是可以进行修改的,比如"增"、“删”、“改”</p>
<h3 id="strong-列表的添加元素-增-append-extend-insert-strong"><strong>5.1列表的添加元素("增"append, extend, insert)</strong></h3>
<p>append可以向列表添加元素<br> extend将另一个集合中的元素逐一添加到列表中<br> insert在指定位置index前插入元素</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">name=[“刘备” , ”曹操” , ”孙权”]print(“增加之前:”,name)info=[“黄忠” , ”魏延”]append追加
names.append("吕布")names.append("貂蝉")names.append(info)
#append把中括号也增加上了print("增加之后:",names)这里是引用
使用extend合并列表
info = ["黄忠","魏延"]names.extend(info)print("增加之后:",names)这里是引用
insert在指定位置前插入元素
names.insert(0,"刘禅")print("增加之后:",names)5.2删除元素 (" 删 "del, pop, remove)
del根据下标进行删除
pop删除最后一个元素
remove根据元素的值进行删除
names = ['刘备', '曹操', '孙权', '吕布', '貂蝉', '黄忠', '魏延']print("删除前:",names)5.3del指定下标删除
del names[1]print("del删除后:",names)5.4使用pop删除最后一个元素
names.pop()names.pop()print("pop删除后:",names)5.5使用remove根据元素值进行删除
name = input("请输入您要删除的历史人物:")names.remove(name)print("remove删除后:",names)5.6列表的修改
通过下标修改元素 (" 改 ")
names = ["刘备","曹操","孙权"]names[0] = "刘禅"print(names)
5.7查找元素("查"in, not in, index, count)
python中查找的常用方法为:
in (存在), 如果存在那么结果为True ,否则为False
not in (不存在),如果不存在那么结果为True ,否则False
index和count与字符串中的用法相同
names = ['刘备', '曹操', '孙权', '吕布', '貂蝉', '黄忠', '魏延',"曹操"]findName = input("请输入您要查找的姓名:")if findName in names:
print("已经找到:%s"%findName)else:
print("没有找到:%s"%findName)In [1]: names = ['刘备', '曹操', '孙权', '吕布', '貂蝉', '黄忠', '魏延',’曹操’]In [2]: name.index(“曹操”)Out[2]:1In [3]: name.index(“曹操”,2,leb(names))Out[3]:7In [4]: name.count(“曹操”)Out[4]:2
6.排序(sort, reverse)
sort方法是将list按特定顺序重新排列,默认为由小到大(True:从小到大;False从大到小)
reverse=True可改为倒序,由大到小。
reverse方法是将list逆置。需要先排序再降序
7.列表嵌套
类似while循环的嵌套,列表也是支持嵌套的一个列表中的元素又是一个列表,那么这就是列表的嵌套
示例:
school_names = [[' 北京大学',' 清华大学'],[' 南开大学',' 天津大学'],[' 贵州大学',' 青海大学']]print(school_names)
#print(school_names)#print(len(school_names))#print(school_names[2][1])for school in school_names:
print("="*30)
print(school)
for name in school:
print(name)8.列表嵌套的应用- - 随机安排老师工位
一个学校,有3个办公室,现在有8位老师等待工位的分配,请编写程序,完成随机的分配
import random
offices = [[ ],[ ],[ ]]names = ['刘备', '曹操', '孙权', '吕布', '貂蝉', '黄忠', '魏延','大乔']for office in offices:
#得到一个教师的下标
index = random.randint(0,len(names)-1)
#分配老师
name = names[index]
office.append(name)
#要移除已经完成分配的老师
names.remove(name)for name in names:
#得到办公室编号
index = random.randint(0,2)
offices[index].append(name)#print(offices)#打印出来哪些办公室有哪些老师i= 1for office in offices:
#office = ["刘备","曹操"]
print("办公室%s : 共%s人"%(i,len(office)))
i+=1
for name in office:
print("%s"%name,end="\t\t")
print()
print("="*30)推荐学习:python视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Learn Python characters and lists simply (detailed examples). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.



