How to modify the directory directory in Oracle
In Oracle, you can use the "create or replace directory dumpdir as 'directory directory path';" statement to modify the directory directory. This statement can not only be used to modify the directory directory, but also to create the directory.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 10 system, Oracle 11g version, Dell G3 computer.
How to modify the directory in Oracle
1. Query the directory
1 |
|
2. Create or modify the directory
1 |
|
3 , empower directory directory
1 |
|
4, delete directory directory
1 |
|
Expand knowledge:
Oracle Directory (directory) allows users to log in to the Oracle database Flexibly read and write files, greatly improving Oracle's ease of use and scalability. The syntax is as follows:
1 |
|
The permissions to create and delete Directory are: CREATE ANY DIRECTORY, DROP ANY DIRECTORY. The permissions given to ordinary users to use Directory include READ, WRITE, and EXECUTE. They can also directly write ALL, as shown below:
1 2 |
|
It should be noted that when creating a Directory database object, the corresponding path does not exist and will not When reporting an error, the Oracle database will not verify the existence of the path on the operating system. It will only verify the existence of the path when it is used. Therefore, when creating the Directory, remember the true existence of the corresponding path, otherwise ORA-29913 or ORA may be reported. -29400 error.
The following is an example of creating Oracle Directory:
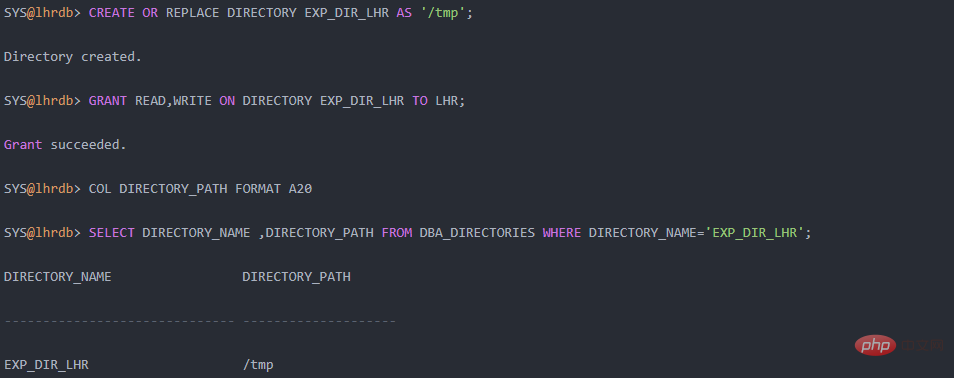
Recommended tutorial: "Oracle Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to modify the directory directory in Oracle. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 37
37
 110
110
 What to do if the oracle can't be opened
Apr 11, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
What to do if the oracle can't be opened
Apr 11, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Solutions to Oracle cannot be opened include: 1. Start the database service; 2. Start the listener; 3. Check port conflicts; 4. Set environment variables correctly; 5. Make sure the firewall or antivirus software does not block the connection; 6. Check whether the server is closed; 7. Use RMAN to recover corrupt files; 8. Check whether the TNS service name is correct; 9. Check network connection; 10. Reinstall Oracle software.
 How to delete all data from oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:36 PM
How to delete all data from oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:36 PM
Deleting all data in Oracle requires the following steps: 1. Establish a connection; 2. Disable foreign key constraints; 3. Delete table data; 4. Submit transactions; 5. Enable foreign key constraints (optional). Be sure to back up the database before execution to prevent data loss.
 How to solve the problem of closing oracle cursor
Apr 11, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to solve the problem of closing oracle cursor
Apr 11, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
The method to solve the Oracle cursor closure problem includes: explicitly closing the cursor using the CLOSE statement. Declare the cursor in the FOR UPDATE clause so that it automatically closes after the scope is ended. Declare the cursor in the USING clause so that it automatically closes when the associated PL/SQL variable is closed. Use exception handling to ensure that the cursor is closed in any exception situation. Use the connection pool to automatically close the cursor. Disable automatic submission and delay cursor closing.
 How to paginate oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
How to paginate oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
Oracle database paging uses ROWNUM pseudo-columns or FETCH statements to implement: ROWNUM pseudo-columns are used to filter results by row numbers and are suitable for complex queries. The FETCH statement is used to get the specified number of first rows and is suitable for simple queries.
 How to create cursors in oracle loop
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:18 AM
How to create cursors in oracle loop
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:18 AM
In Oracle, the FOR LOOP loop can create cursors dynamically. The steps are: 1. Define the cursor type; 2. Create the loop; 3. Create the cursor dynamically; 4. Execute the cursor; 5. Close the cursor. Example: A cursor can be created cycle-by-circuit to display the names and salaries of the top 10 employees.
 How to stop oracle database
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:12 AM
How to stop oracle database
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:12 AM
To stop an Oracle database, perform the following steps: 1. Connect to the database; 2. Shutdown immediately; 3. Shutdown abort completely.
 How to create oracle dynamic sql
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:06 AM
How to create oracle dynamic sql
Apr 12, 2025 am 06:06 AM
SQL statements can be created and executed based on runtime input by using Oracle's dynamic SQL. The steps include: preparing an empty string variable to store dynamically generated SQL statements. Use the EXECUTE IMMEDIATE or PREPARE statement to compile and execute dynamic SQL statements. Use bind variable to pass user input or other dynamic values to dynamic SQL. Use EXECUTE IMMEDIATE or EXECUTE to execute dynamic SQL statements.
 How to open a database in oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open a database in oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
The steps to open an Oracle database are as follows: Open the Oracle database client and connect to the database server: connect username/password@servername Use the SQLPLUS command to open the database: SQLPLUS




