 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 What are asynchronous resources? A brief analysis of Node's method of realizing asynchronous resource context sharing
What are asynchronous resources? A brief analysis of Node's method of realizing asynchronous resource context sharing
What are asynchronous resources? A brief analysis of Node's method of realizing asynchronous resource context sharing
How does Node.js implement asynchronous resource context sharing? The following article will introduce to you how Node implements asynchronous resource context sharing. Let’s talk about the use of asynchronous resource context sharing for us. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

Asynchronous resource context sharing means sharing context data within a network request life cycle or asynchronous resource call chain.
Before answering this question, we must first understand what asynchronous resources are.
Asynchronous resources
Asynchronous resources can be understood as objects with callbacks, such as but not limited to Promises, Timeouts, TCPWrap, UDP, etc. See Asynchronous resource type list for details.
The official definition is as follows:
An asynchronous resource represents an object with an associated callback. This callback may be called multiple times, such as the 'connection' event in net.createServer( ), or just a single time like in fs.open(). A resource can also be closed before the callback is called.
AsyncLocalStorage
here Introducing Node.js AsyncLocalStorage, the officially provided asynchronous context sharing solution. This feature was still an experimental feature before 16.4.0 and has been stable since 16.4.0.
AsyncLocalStorage can share data in asynchronous operation chains.
AsyncLocalStorage instance asyncLocalStorage has the following main methods:
- disable() disables asyncLocalStorage;
- getStore() returns the current context store, which must pass asyncLocalStorage .run() or asyncLocalStorage.enterWith() to perform asynchronous context initialization;
- enterWith(store) passes the context store through this method, and the store can be obtained in all subsequent asynchronous calls;
Example:
const store = { id: 1 };
// Replaces previous store with the given store object
asyncLocalStorage.enterWith(store);
asyncLocalStorage.getStore(); // Returns the store object
someAsyncOperation(() => {
asyncLocalStorage.getStore(); // Returns the same object
});- run(store, callback[, ...args]) Use run to specify the context store and its effective callback function. The store will only be in is obtained from the callback function.
- exit(callback[, ...args])
asyncLocalStorage.run() The first parameter of the function is to store the shared data we need to access in the asynchronous call. The second parameter is an asynchronous function.
The following is an example to demonstrate how to use AsyncLocalStorage to implement asynchronous resource context sharing:
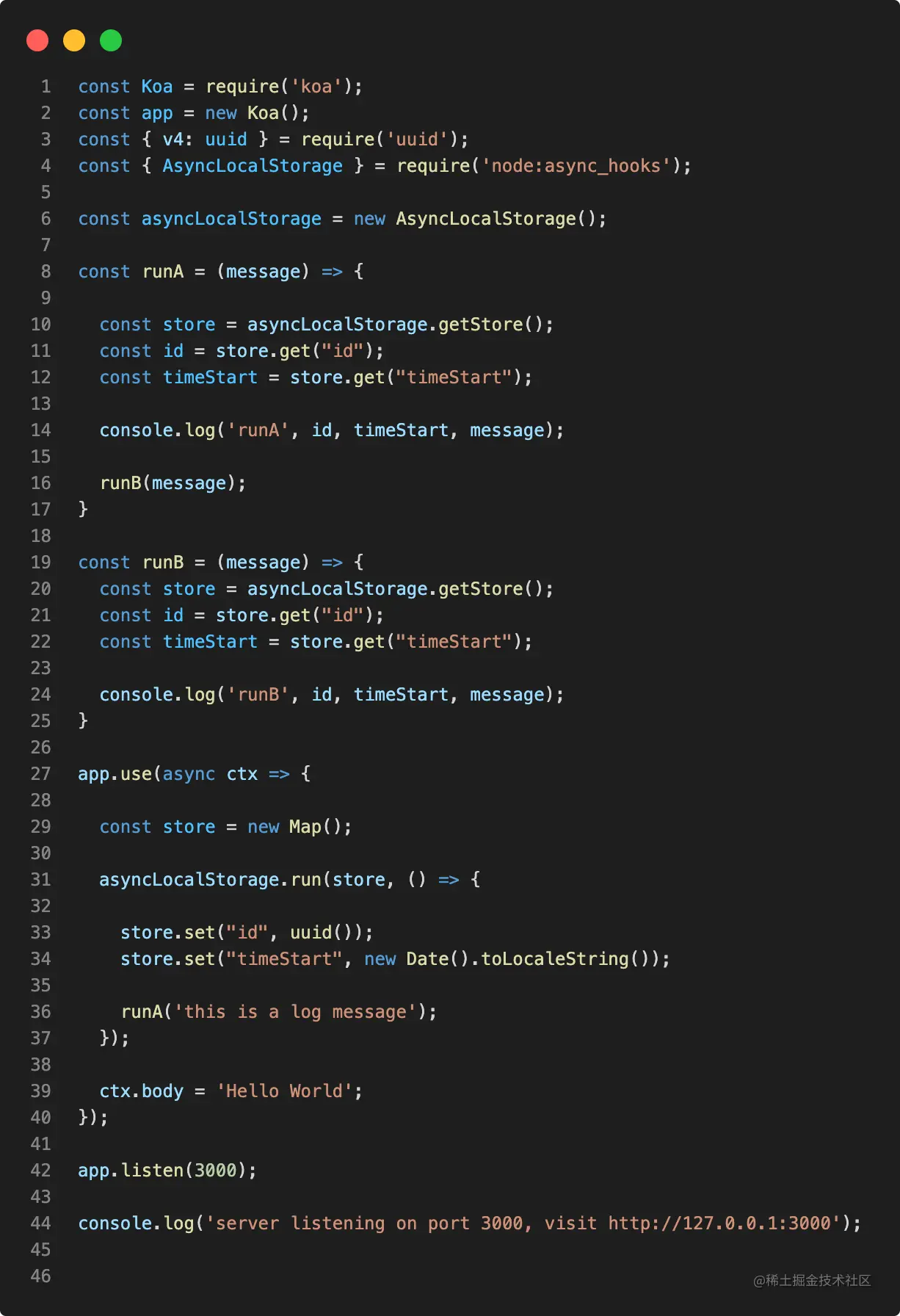
Output:
runA 8f19ebef-58d7-4b1a-8b9b-46d158beb5d2 2022/5/24 20:26:17 this is a log message runB 8f19ebef-58d7-4b1a-8b9b-46d158beb5d2 2022/5/24 20:26:17 this is a log message
Through asyncLocalStorage.run In the same asynchronous function running, function runA and function runB will be run, and runA and runB can access the same context data.
Performance issues
AsyncLocalStorage provides a large traversal for us to easily implement asynchronous resource context sharing in Node.js, but every asynchronous resource operation will trigger Async Hooks , will inevitably have a certain impact on the performance of our Node application. So how big is the impact?
According to an actual measurement by Kuzzle, using AsyncLocalStorage will cause about 8% additional performance loss. Of course, different business scenarios may have different performance. If you are concerned about this part of performance, you can also add comparative testing to your business to test the specific performance impact.
| ---- | Log with AsyncLocalStorage | Log classic | difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| req/s | 2613 | 2842 | ~8% |
Application Scenario
In other multi-threaded languages, each HTTP creates a new thread, and each thread has its own memory. You can store global state in thread memory and retrieve global state from anywhere in your code.
In Node.js, because Node.js is single-threaded and shares memory among all HTTP requests, each HTTP request cannot hold mutually isolated global state.
AsyncLocalStorage can effectively isolate the status between different asynchronous operations, and plays a very important role in scenarios such as HTTP request tracking, APM tools, context log tracking, and request-based full-link log tracking.
For more node-related knowledge, please visit: nodejs tutorial!
The above is the detailed content of What are asynchronous resources? A brief analysis of Node's method of realizing asynchronous resource context sharing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 An article about memory control in Node
Apr 26, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
An article about memory control in Node
Apr 26, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
The Node service built based on non-blocking and event-driven has the advantage of low memory consumption and is very suitable for handling massive network requests. Under the premise of massive requests, issues related to "memory control" need to be considered. 1. V8’s garbage collection mechanism and memory limitations Js is controlled by the garbage collection machine
 Detailed graphic explanation of the memory and GC of the Node V8 engine
Mar 29, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
Detailed graphic explanation of the memory and GC of the Node V8 engine
Mar 29, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
This article will give you an in-depth understanding of the memory and garbage collector (GC) of the NodeJS V8 engine. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 How to use express to handle file upload in node project
Mar 28, 2023 pm 07:28 PM
How to use express to handle file upload in node project
Mar 28, 2023 pm 07:28 PM
How to handle file upload? The following article will introduce to you how to use express to handle file uploads in the node project. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Let's talk in depth about the File module in Node
Apr 24, 2023 pm 05:49 PM
Let's talk in depth about the File module in Node
Apr 24, 2023 pm 05:49 PM
The file module is an encapsulation of underlying file operations, such as file reading/writing/opening/closing/delete adding, etc. The biggest feature of the file module is that all methods provide two versions of **synchronous** and **asynchronous**, with Methods with the sync suffix are all synchronization methods, and those without are all heterogeneous methods.
 An in-depth analysis of Node's process management tool 'pm2”
Apr 03, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
An in-depth analysis of Node's process management tool 'pm2”
Apr 03, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
This article will share with you Node's process management tool "pm2", and talk about why pm2 is needed, how to install and use pm2, I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Detailed explanation and installation guide for PiNetwork nodes This article will introduce the PiNetwork ecosystem in detail - Pi nodes, a key role in the PiNetwork ecosystem, and provide complete steps for installation and configuration. After the launch of the PiNetwork blockchain test network, Pi nodes have become an important part of many pioneers actively participating in the testing, preparing for the upcoming main network release. If you don’t know PiNetwork yet, please refer to what is Picoin? What is the price for listing? Pi usage, mining and security analysis. What is PiNetwork? The PiNetwork project started in 2019 and owns its exclusive cryptocurrency Pi Coin. The project aims to create a one that everyone can participate
 Let's talk about the event loop in Node
Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:08 PM
Let's talk about the event loop in Node
Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:08 PM
The event loop is a fundamental part of Node.js and enables asynchronous programming by ensuring that the main thread is not blocked. Understanding the event loop is crucial to building efficient applications. The following article will give you an in-depth understanding of the event loop in Node. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 What should I do if node cannot use npm command?
Feb 08, 2023 am 10:09 AM
What should I do if node cannot use npm command?
Feb 08, 2023 am 10:09 AM
The reason why node cannot use the npm command is because the environment variables are not configured correctly. The solution is: 1. Open "System Properties"; 2. Find "Environment Variables" -> "System Variables", and then edit the environment variables; 3. Find the location of nodejs folder; 4. Click "OK".



