What is Oracle's interval query statement?
Oracle's interval query statement: 1. "select * from table name where rownum

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 10 system, Oracle version 12c, Dell G3 computer.
What is Oracle’s interval query statement?
Oracle uses the rownum keyword to implement this query:
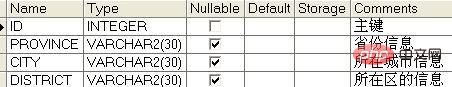
First we Suppose there is a regional information table area, and its table structure is as shown in the figure below:
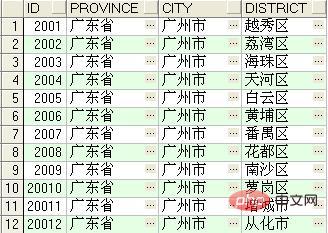
The data in the table is as shown in the figure below (the result of the select * from area statement) :
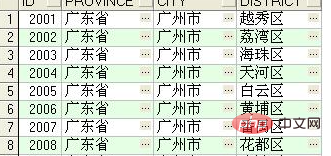
1) Query the first 8 records in the table
select * from area where rownum <= 8
The query results are as follows:
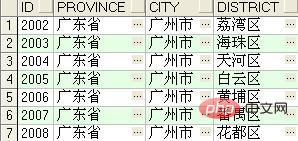
2) Query the 2nd to 8th records
For this form of query, Oracle is not as convenient as mysql. It must be implemented using subqueries or set operations. We can use the following three methods to achieve this:
A: select id,province,city,district from (select id,province,city,district,rownum as num from area) where num between 2 and 8;
First get a temporary table based on select id, province, city, district, rownum as num from area. There is a rownum in this temporary table. Column (a pseudo column, similar to
rowid, but different from rowid, because rowid is a physically existing column, that is to say, any table in Oracle has a rowid column, and rownum does not exist physically),
Then query in the temporary table.
B: select * from area where rownum <= 8 minus select * from area where rownum < 2;
Use the set minus operator minus, which returns records that appear in the first select but not in the second select.
C: select id,province,city,district from (select id,province,city,district,rownum as num from area) where num >=2 intersect
select * from area where rownum
Using the set intersection operator intersect, there is a twist here (but this twist realizes that rownum is greater than a certain Number query), it first uses A's method to query to obtain all records with
rownum greater than 2, and then performs an intersection operation with the record set with rownum less than or equal to 8. The results obtained by the three operations are the same, as shown in the figure below:
Recommended tutorial: "Oracle Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What is Oracle's interval query statement?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to check tablespace size of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
How to check tablespace size of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
To query the Oracle tablespace size, follow the following steps: Determine the tablespace name by running the query: SELECT tablespace_name FROM dba_tablespaces; Query the tablespace size by running the query: SELECT sum(bytes) AS total_size, sum(bytes_free) AS available_space, sum(bytes) - sum(bytes_free) AS used_space FROM dba_data_files WHERE tablespace_
 How to view instance name of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to view instance name of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
There are three ways to view instance names in Oracle: use the "sqlplus" and "select instance_name from v$instance;" commands on the command line. Use the "show instance_name;" command in SQL*Plus. Check environment variables (ORACLE_SID on Linux) through the operating system's Task Manager, Oracle Enterprise Manager, or through the operating system.
 How to encrypt oracle view
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to encrypt oracle view
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
Oracle View Encryption allows you to encrypt data in the view, thereby enhancing the security of sensitive information. The steps include: 1) creating the master encryption key (MEk); 2) creating an encrypted view, specifying the view and MEk to be encrypted; 3) authorizing users to access the encrypted view. How encrypted views work: When a user querys for an encrypted view, Oracle uses MEk to decrypt data, ensuring that only authorized users can access readable data.
 How to uninstall Oracle installation failed
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to uninstall Oracle installation failed
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Uninstall method for Oracle installation failure: Close Oracle service, delete Oracle program files and registry keys, uninstall Oracle environment variables, and restart the computer. If the uninstall fails, you can uninstall manually using the Oracle Universal Uninstall Tool.
 How to delete all data from oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:36 PM
How to delete all data from oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:36 PM
Deleting all data in Oracle requires the following steps: 1. Establish a connection; 2. Disable foreign key constraints; 3. Delete table data; 4. Submit transactions; 5. Enable foreign key constraints (optional). Be sure to back up the database before execution to prevent data loss.
 How to set up users of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
How to set up users of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
To create a user in Oracle, follow these steps: Create a new user using the CREATE USER statement. Grant the necessary permissions using the GRANT statement. Optional: Use the RESOURCE statement to set the quota. Configure other options such as default roles and temporary tablespaces.
 How to check invalid numbers of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to check invalid numbers of oracle
Apr 11, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
Oracle Invalid numeric errors may be caused by data type mismatch, numeric overflow, data conversion errors, or data corruption. Troubleshooting steps include checking data types, detecting digital overflows, checking data conversions, checking data corruption, and exploring other possible solutions such as configuring the NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS parameter and enabling data verification logging.
 What to do if the oracle can't be opened
Apr 11, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
What to do if the oracle can't be opened
Apr 11, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Solutions to Oracle cannot be opened include: 1. Start the database service; 2. Start the listener; 3. Check port conflicts; 4. Set environment variables correctly; 5. Make sure the firewall or antivirus software does not block the connection; 6. Check whether the server is closed; 7. Use RMAN to recover corrupt files; 8. Check whether the TNS service name is correct; 9. Check network connection; 10. Reinstall Oracle software.




