What does the linux command ls mean?
In Linux, the full name of ls is "list", which means "list" in Chinese. Its main function is to display the contents of the specified working directory (list the files and subdirectories contained in the working directory), or it can View file permissions, syntax "ls [options] directory_name". When the ls command does not use any options, by default only the names of non-hidden files will be displayed and sorted by file name. At the same time, the file names will be colored according to the specific type of the file (blue displays directories, white displays general files).

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
ls command, the abbreviation of list, Chinese means "list"
ls is the most common directory operation command, its main function is to display the specified work The contents of the directory (list the files and subdirectories contained in the current working directory).
Through the ls command, you can not only view the files contained in the Linux folder, but also view file permissions (including directory, folder, file permissions), view directory information, etc.
# ls [选项] 目录名称
Table 1 lists the commonly used options of the ls command and their respective functions.
| Options | Function |
|---|---|
| -a | Show all files, including hidden files (files starting with .) are also listed together, this is one of the most commonly used options. |
| -A | Display all files, including hidden files, excluding the . and .. directories. |
| -d | Only the directory itself is listed, not the file data within the directory. |
| -f | ls sorts by file name by default. Using the -f option will list the results directly without sorting. |
| -F | Add the file type indicator after the file or directory name, for example, * represents a executable file, / represents a directory, = represents a socket file, | represents a FIFO file. |
| -h | Display file or directory size in a human-readable format, such as 1KB, 234MB, 2GB, etc. |
| -i | Display inode node information. |
| -l | List file and directory information using long format. |
| -n | The UID and GID are displayed instead of the file user name and group name respectively. |
| -r | Output the sorting results in reverse order. For example, if the original file names are from small to large, the reverse order is from large to small. |
| -R | Listing together with the contents of the subdirectory is equivalent to displaying all files in the directory. |
| -S | Sort by file size, not by file name. |
| -t | Sort by time, not by file name. |
|
--color=never --color=always --color=auto |
never means not to give color display based on file characteristics. always means displaying color, ls adopts this method by default. auto means to let the system determine whether to give color based on the configuration. |
| --full-time | Output in complete time mode (including year, month, day, hour, minute) |
| --time={atime,ctime} | Output access time or change permission attribute time (ctime), not content change time. |
注意,当 ls 命令不使用任何选项时,默认只会显示非隐藏文件的名称,并以文件名进行排序,同时会根据文件的具体类型给文件名配色(蓝色显示目录,白色显示一般文件)。除此之外,如果想使用 ls 命令显示更多内容,就需要使用表 1 相应的选项。
地方
ls命令示例
示例1:列出所有文件(注意和-A参数的区别,结果里面包括表示当前目录.和上级目录..这两个文件)。
[root@localhost ~]# ls -a #列出所有文件

示例2:列出所有的文件,但不包括表示当前目录.和上级目录..这两个文件。
[root@localhost ~]# ls -A

示例3:显示列表并且以ctime排序
[root@localhost /]# ls -clt #和 -lt参数一起使用,以时间排序

[root@localhost /]# ls -cl #和-l参数一起使用,以文件名排序并显示时间

[root@localhost /]# ls -c #单独使用,以时间排序,但不显示时间 tmp dev etc net misc selinux sys proc sbin bin lib64 root home lib mnt var boot usr media srv lost+found opt
示例4:仅仅列出目录本身,不需要列出目录里的内容
[root@localhost /]# ls -d /home #仅列出/home目录本身 /home [root@localhost /]# ls /home #列出/home目录里的内容 sgl software # 加上-l参数,比较的更清楚一些: [root@localhost /]# ls -ld /home drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Nov 18 22:05 /home [root@localhost /]# ls -l /home total 16 drwx------ 16 sgl sgl 4096 Oct 17 2015 sgl drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Nov 14 05:13 software
示例5:显示完整时间
[root@localhost ~]# ls --full-time /

示例6:以易读方式显示列表
[root@localhost ~]# ls -lh / #注意列表容量大小列的单位

[root@localhost ~]# ls -l / #默认方式,以字节为单位显示

示例7:显示inode
[root@localhost ~]# ls -li /

示例8:列出文件夹内容,并显示出文件所属用户和组的id
[root@localhost ~]# ls -ln /

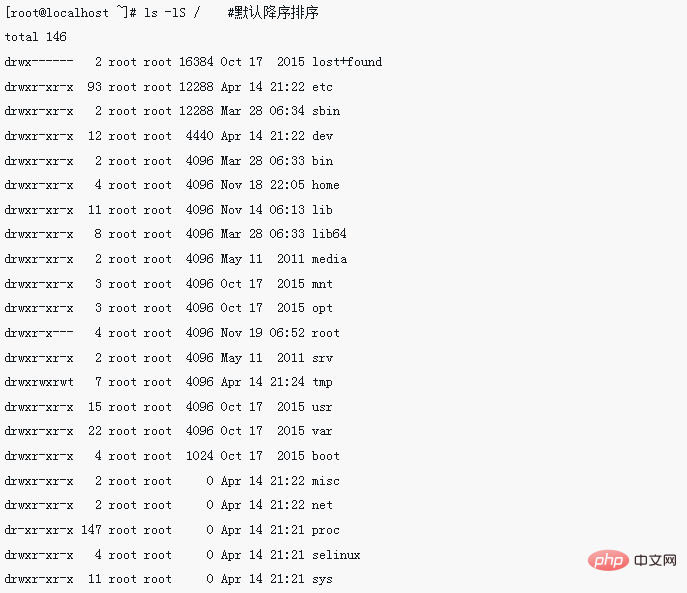
示例9:以文件大小排序(升序和降序)
[root@localhost ~]# ls -lS / #默认降序排序

[root@localhost ~]# ls -lSr / #通过-r参数实现升序排列
相关推荐:《Linux视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of What does the linux command ls mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
Steps to start Nginx in Linux: Check whether Nginx is installed. Use systemctl start nginx to start the Nginx service. Use systemctl enable nginx to enable automatic startup of Nginx at system startup. Use systemctl status nginx to verify that the startup is successful. Visit http://localhost in a web browser to view the default welcome page.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
In Linux, use the following command to check whether Nginx is started: systemctl status nginx judges based on the command output: If "Active: active (running)" is displayed, Nginx is started. If "Active: inactive (dead)" is displayed, Nginx is stopped.
 How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
The server does not have permission to access the requested resource, resulting in a nginx 403 error. Solutions include: Check file permissions. Check the .htaccess configuration. Check nginx configuration. Configure SELinux permissions. Check the firewall rules. Troubleshoot other causes such as browser problems, server failures, or other possible errors.
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
CentOS will be shut down in 2024 because its upstream distribution, RHEL 8, has been shut down. This shutdown will affect the CentOS 8 system, preventing it from continuing to receive updates. Users should plan for migration, and recommended options include CentOS Stream, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux to keep the system safe and stable.
 How to start nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
How to start nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
Question: How to start Nginx? Answer: Install Nginx Startup Nginx Verification Nginx Is Nginx Started Explore other startup options Automatically start Nginx





