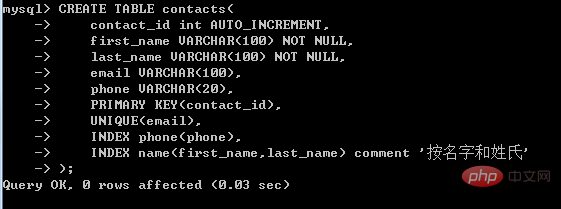
What is the query statement of mysql index
The query statement of mysql index is "SHOW INDEX", which can return the index information associated with the table in the current database or the specified database. The complete syntax is "SHOW INDEX FROM table name [FROM database name];"; where , the "FROM database name" option is optional. If it is omitted, the index information associated with the table in the current database will be returned. If it is not omitted, the index information of the table in the specified database will be returned.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, mysql8 version, Dell G3 computer.
After the index creation is completed, you can use SQL statements to view the existing indexes. In MySQL, you can use the SHOW INDEX statement to view the indexes created in a table.
MySQL SHOW INDEX statement
The SHOW INDEX statement can return index information associated with a table in the current database or a specified database.
The syntax format for viewing the index is as follows:
SHOW INDEX FROM 表名 [ FROM 数据库名];
The syntax description is as follows:
Table name: Specify the index to be viewed Data table name.
Database name: Specify the database where the data table where the index needs to be viewed is located, which can be omitted. For example,
SHOW INDEX FROM student FROM test;statement means to view the index of the student data table in the test database.If you are not connected to any database, or you want to obtain index information for tables in other databases, you can specify the database name.
Return SHOW INDEXES to the following information:
| illustrate | |
|---|---|
| Indicates the name of the data table where the index is created, here is the tb_stu_info2 data table. | |
| Indicates whether the index is a unique index. If it is not a unique index, the value of this column is 1; if it is a unique index, the value of this column is 0. | |
| Represents the name of the index. | |
| Indicates the position of the column in the index. If the index is a single column, the value of this column is 1; if the index is a combined index, the value of this column is the order of each column in the index definition. | |
| Represents the column field that defines the index. | |
| Indicates the order in which columns are stored in the index. In MySQL, ascending order displays the value "A" (ascending order), if displayed as NULL, it means no classification. | |
| An estimate of the number of unique values in the index. Cardinality counts against statistics that are stored as integers, so even for small tables, the value does not need to be exact. The larger the cardinality, the greater the chance that MySQL will use the index when doing joins. | |
| Represents the number of indexed characters in the column. If the column is only partially indexed, the value of the column is the number of characters indexed; if the entire column is indexed, the value of the column is NULL. | |
| Indicates how keywords are compressed. If not compressed, the value is NULL. | |
| Used to display whether the index column contains NULL. If a column contains NULL, the value of the column is YES. If not, the value of this column is NO. | |
| Shows the type and method used by the index (BTREE, FULLTEXT, HASH, RTREE). | |
| Show comments. |