An in-depth exploration of CSS mouse pointer interaction effects
Today, let’s implement such an interesting interactive effect. Let’s talk about front-end mouse pointer interaction through this exchange effect. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

Modify the original mouse pointer style to the effect you want, and add some special interactive effects. [Recommended learning: css video tutorial]
Modify mouse style
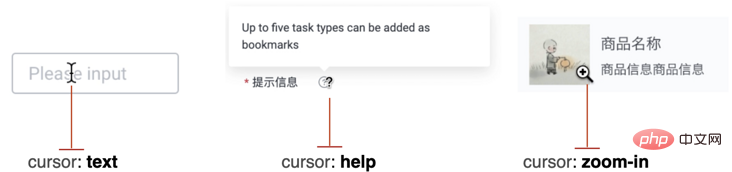
First of all, the first question, we can see that in the picture above , the style of the mouse pointer is modified to a dot:

Normally it should be like this:

Of course, this is relatively simple. In CSS, we can modify the mouse pointer shape through the cursor style.
Use cursor to modify the mouse style
cursor CSS property sets the type of the mouse pointer and displays the corresponding style when the mouse pointer hovers over the element .
cursor: auto; cursor: pointer; ... cursor: zoom-out; /* 使用图片 */ cursor: url(hand.cur) /* 使用图片,并且设置 fallback 兜底 */ cursor: url(hand.cur), pointer;
Everyone should know this. Generally speaking, choosing different mouse pointer styles in different scenarios is also a way to improve the user experience.

We are not trying to set the cursor In any way, just the opposite, we need to hide it.
Hide the cursor via cursor: none
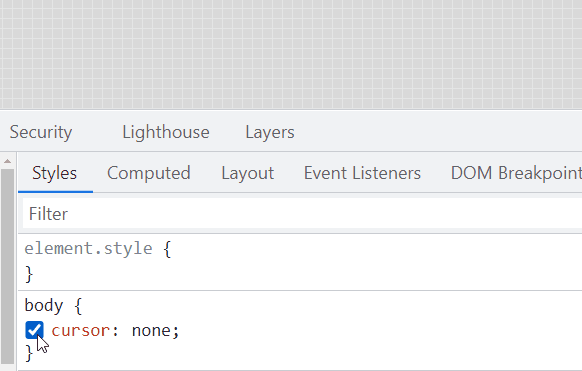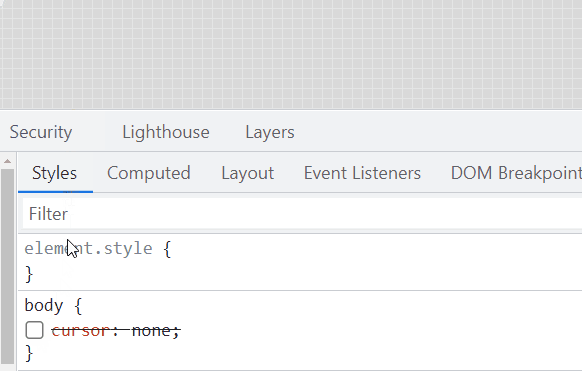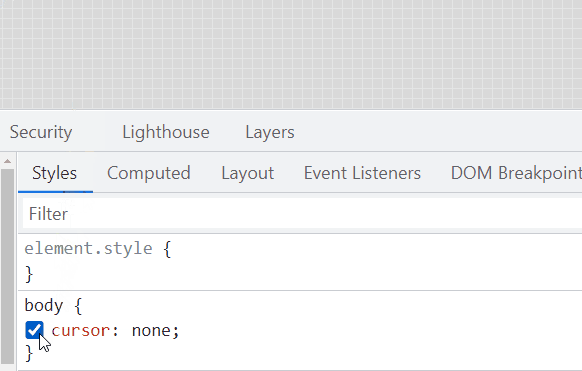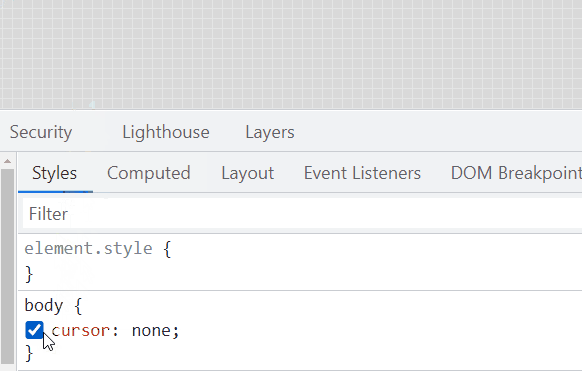
Here, we hide the mouse pointer of the page via cursor: none:
{
cursor: none;
}
Simulate through global event listening Since the mouse pointer
has disappeared, we simply simulate a mouse pointer. We first implement a10px x 10px circular div, set to absolute positioning based on
: <div></div>
#g-pointer {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 10px;
height: 10px;
background: #000;
border-radius: 50%;
}
mousemove## on the body. #, coincide the position of the small circle with the real-time mouse pointer position: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">const element = document.getElementById("g-pointer");
const body = document.querySelector("body");
function setPosition(x, y) {
element.style.transform = `translate(${x}px, ${y}px)`;
}
body.addEventListener('mousemove', (e) => {
window.requestAnimationFrame(function(){
setPosition(e.clientX - 5, e.clientY - 5);
});
});</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div> In this way, if
is not set, the effect will be like this:
 Add
Add
to the body, which is equivalent to simulating a mouse pointer:
 On this basis, since the current mouse pointer is actually a
On this basis, since the current mouse pointer is actually a
, so we can add any interactive effect to it. Taking the example at the beginning of the article as an example, we only need to use the mix mode
to enable the simulated mouse pointer to intelligently move between different background colors. Next change your color.
https:// github.com/chokcoco/iCSS/issues/169
Complete code:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
<div></div> <div></div>
body {
cursor: none;
background-color: #fff;
}
#g-pointer-1,
#g-pointer-2
{
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 12px;
height: 12px;
background: #999;
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: #fff;
mix-blend-mode: exclusion;
z-index: 1;
}
#g-pointer-2 {
width: 42px;
height: 42px;
background: #222;
transition: .2s ease-out;
}const body = document.querySelector("body");
const element = document.getElementById("g-pointer-1");
const element2 = document.getElementById("g-pointer-2");
const halfAlementWidth = element.offsetWidth / 2;
const halfAlementWidth2 = element2.offsetWidth / 2;
function setPosition(x, y) {
element.style.transform = `translate(${x - halfAlementWidth}px, ${y - halfAlementWidth}px)`;
element2.style.transform = `translate(${x - halfAlementWidth2}px, ${y - halfAlementWidth2}px)`;
}
body.addEventListener('mousemove', (e) => {
window.requestAnimationFrame(function(){
setPosition(e.clientX, e.clientY);
});
});We can perfectly restore the effect of the question picture:
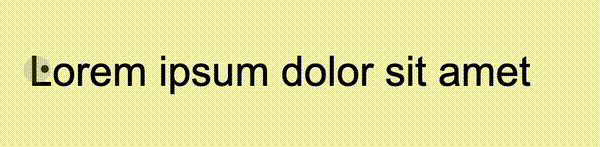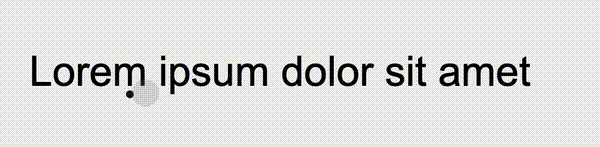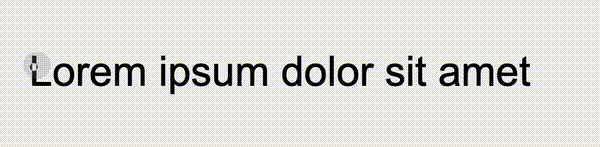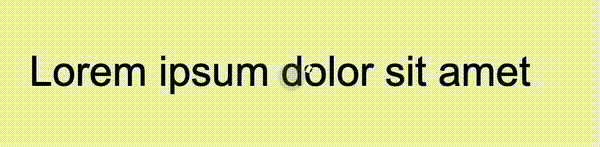
https://codepen.io/Chokcoco/pen/rNJQXXV
伪类事件触发
有一点需要注意的是,利用模拟的鼠标指针去 Hover 元素,Click 元素的时候,会发现这些事件都无法触发。
这是由于,此时被隐藏的指针下面,其实悬浮的我们模拟鼠标指针,因此,所有的 Hover、Click 事件都触发在了这个元素之上。
当然,这个也非常好解决,我们只需要给模拟指针的元素,添加上 pointer-events: none,阻止默认的鼠标事件,让事件透传即可:
{
pointer-events: none;
}鼠标跟随,不仅于此
当然,这里核心就是一个鼠标跟随动画,配合上 cursor: none。
而且,鼠标跟随,我们不一定一定要使用 JavaScript。
我在 不可思议的纯 CSS 实现鼠标跟随 一文中,介绍了一种纯 CSS 实现的鼠标跟随效果,感兴趣的也可以看看。
https://github.com/chokcoco/iCSS/issues/46
基于纯 CSS 的鼠标跟随,配合 cursor: none,也可以制作出一些有意思的动画效果。像是这样:

CodePen Demo -- Cancle transition & cursor none
https://codepen.io/Chokcoco/pen/gOvZoVv
(学习视频分享:web前端)
The above is the detailed content of An in-depth exploration of CSS mouse pointer interaction effects. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
There are two ways to create a Bootstrap split line: using the tag, which creates a horizontal split line. Use the CSS border property to create custom style split lines.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use the Bootstrap button? Introduce Bootstrap CSS to create button elements and add Bootstrap button class to add button text
 How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
To adjust the size of elements in Bootstrap, you can use the dimension class, which includes: adjusting width: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust height: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-
 How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
To set up the Bootstrap framework, you need to follow these steps: 1. Reference the Bootstrap file via CDN; 2. Download and host the file on your own server; 3. Include the Bootstrap file in HTML; 4. Compile Sass/Less as needed; 5. Import a custom file (optional). Once setup is complete, you can use Bootstrap's grid systems, components, and styles to create responsive websites and applications.
 How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
There are several ways to insert images in Bootstrap: insert images directly, using the HTML img tag. With the Bootstrap image component, you can provide responsive images and more styles. Set the image size, use the img-fluid class to make the image adaptable. Set the border, using the img-bordered class. Set the rounded corners and use the img-rounded class. Set the shadow, use the shadow class. Resize and position the image, using CSS style. Using the background image, use the background-image CSS property.




