How to use archiver in nodejs
In nodejs, archiver is used to compress and package some files into compressed packages in zip format or tar format; archiver is a module that can implement packaging functions across platforms. The packaging formats are zip and tar, which can be used The "npm install archiver" statement installs the module before use.

The operating environment of this article: Windows 10 system, nodejs version 12.19.0, Dell G3 computer.
How to use archiver in nodejs
Sometimes we need to compress and package some files into compressed packages in zip format or tar format, or we may also need to package the directory. In Node.js, you can use the third-party package archiver to perform operations.
archiver is a module that can realize cross-platform packaging function in nodejs. It can make zip and tar packages. It is a relatively easy-to-use third-party module.
Install the archive module before use.
The code is as follows:
npm install archiver
Introduction:
// 由于需要读取文件所以需要fs模块,也必须导入 const fs = require('fs'); const archiver = require('archiver');
Usage
The basic usage is as follows:
// 第一步,导入必要的模块
const fs = require('fs');
const archiver = require('archiver');
// 第二步,创建可写流来写入数据
const output = fs.createWriteStream(__dirname + "/hello.zip");// 将压缩包保存到当前项目的目录下,并且压缩包名为test.zip
const archive = archiver('zip', {zlib: {level: 9}});// 设置压缩等级
// 第三步,建立管道连接
archive.pipe(output);
// 第四步,压缩指定文件
var stream = fs.createReadStream(__dirname + "/hello.txt");// 读取当前目录下的hello.txt
archive.append(stream, {name: 'hello.txt'});
// 第五步,完成压缩
archive.finalize();After the code is successfully executed, it will Generate a compressed package named hello.zip in the directory where the project is located, and the compressed package contains the compressed file hello.txt. 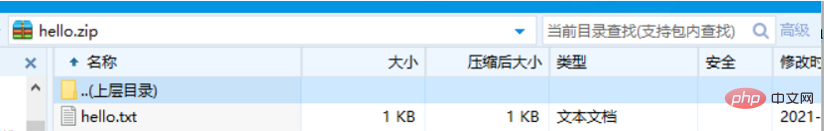
Example
Compress a single file
Compressed files can use archive.append() and archive.file () to perform operations.
The API for compressing a single file is as follows:
// 添加一个文件到压缩包,通过可写流的方式读取数据附加文件
const file1 = __dirname + '/file1.txt';
archive.append(fs.createReadStream(file1), { name: 'file1.txt' });
//添加一个文件到压缩包,通过将字符串写入到文件的方式附加文件
archive.append('string cheese!', { name: 'file2.txt' });
// 添加一个文件到压缩包,通过Buffer数据的方式附加文件
const buffer3 = Buffer.from('buff it!');
archive.append(buffer3, { name: 'file3.txt' });
// 添加一个文件到压缩包,直接传入文件路径
archive.file('file1.txt', { name: 'file4.txt' });The complete example is as follows:
// 第一步,导入必要的模块
const fs = require('fs');
const archiver = require('archiver');
// 第二步,创建可写流来写入数据
const output = fs.createWriteStream(__dirname + "/hello.zip");// 将压缩包保存到当前项目的目录下,并且压缩包名为test.zip
const archive = archiver('zip', {zlib: {level: 9}});// 设置压缩等级
// 第三步,建立管道连接
archive.pipe(output);
// 第四步,压缩指定文件
archive.append(fs.createReadStream(__dirname + '/hello.txt'), {name: 'hello.txt'});// 文件流
archive.append('index.html', {name: 'index.html'});// 文件路径
archive.append(Buffer.from("这是Buffer格式的数据"), {name: 'buffer.txt'});// Buffer对象
archive.append("直接传入字符串", {name: 'string.txt'});// 字符串
// 第五步,完成压缩
archive.finalize();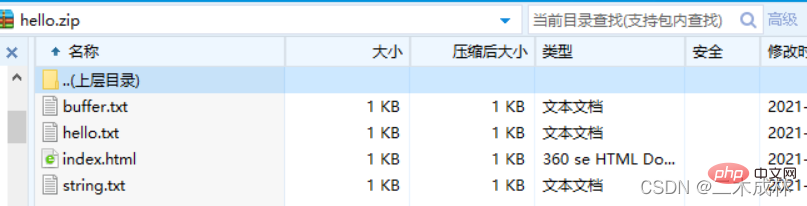
Note: archive.append()The second parameter{name: 'hello.txt'} is to rename the corresponding file in the compressed package.
Compress multiple files
If you want to compress multiple files, just call the archive.append() method to append the files. These additional files will be added to in compressed package. For example:
// 第一步,导入必要的模块
const fs = require('fs');
const archiver = require('archiver');
// 第二步,创建可写流来写入数据
const output = fs.createWriteStream(__dirname + "/hello.zip");// 将压缩包保存到当前项目的目录下,并且压缩包名为test.zip
const archive = archiver('zip', {zlib: {level: 9}});// 设置压缩等级
// 第三步,建立管道连接
archive.pipe(output);
// 第四步,压缩多个文件到压缩包中
archive.append('index.html', {name: 'index.html'});
archive.append('hello.js', {name: 'hello.js'});
archive.append('hello.html', {name: 'hello.html'});
archive.append('db.json', {name: 'db.json'});
// 第五步,完成压缩
archive.finalize();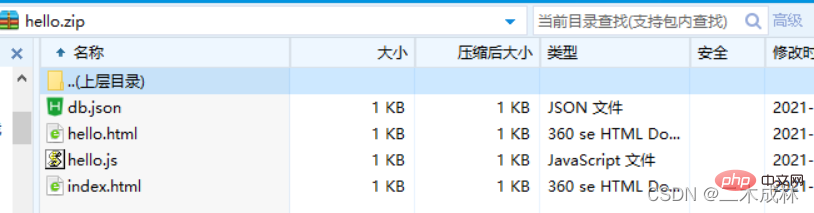
Compress directory
If you want to compress the directory, you need to use archive.directory() to complete it. The API is as follows:
// 将指定目录打包压缩到压缩包中,并且重命名为new-subdir,并且subdir目录下的所有文件仍然在new-subdir目录下,而不是在压缩包的根目录下 archive.directory('subdir/', 'new-subdir'); // 将指定目录下的所有文件打包压缩到压缩包中,而这些文件在压缩包的根目录,而非子目录中 archive.directory('subdir/', false);
The complete example is as follows:
// 第一步,导入必要的模块
const fs = require('fs');
const archiver = require('archiver');
// 第二步,创建可写流来写入数据
const output = fs.createWriteStream(__dirname + "/hello.zip");// 将压缩包保存到当前项目的目录下,并且压缩包名为test.zip
const archive = archiver('zip', {zlib: {level: 9}});// 设置压缩等级
// 第三步,建立管道连接
archive.pipe(output);
// 第四步,压缩目录到压缩包中
archive.directory('public/', 'new-public');
archive.directory('demo/', false);
// 第五步,完成压缩
archive.finalize();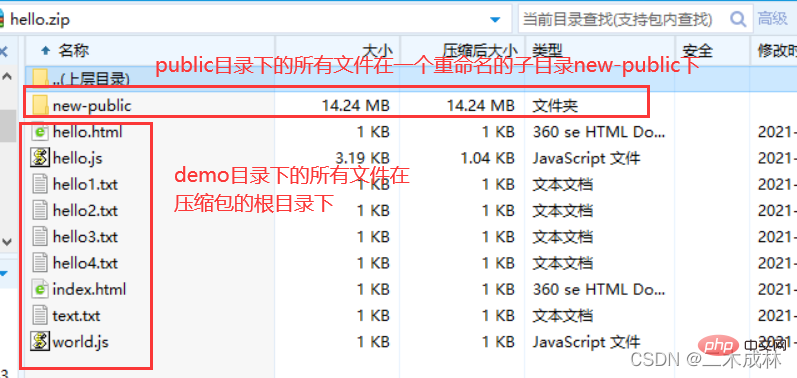
Recommended learning: "nodejs video tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to use archiver in nodejs. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
Node.js is a server-side JavaScript runtime, while Vue.js is a client-side JavaScript framework for creating interactive user interfaces. Node.js is used for server-side development, such as back-end service API development and data processing, while Vue.js is used for client-side development, such as single-page applications and responsive user interfaces.
 Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Node.js can be used as a backend framework as it offers features such as high performance, scalability, cross-platform support, rich ecosystem, and ease of development.
 How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
To connect to a MySQL database, you need to follow these steps: Install the mysql2 driver. Use mysql2.createConnection() to create a connection object that contains the host address, port, username, password, and database name. Use connection.query() to perform queries. Finally use connection.end() to end the connection.
 What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
There are two npm-related files in the Node.js installation directory: npm and npm.cmd. The differences are as follows: different extensions: npm is an executable file, and npm.cmd is a command window shortcut. Windows users: npm.cmd can be used from the command prompt, npm can only be run from the command line. Compatibility: npm.cmd is specific to Windows systems, npm is available cross-platform. Usage recommendations: Windows users use npm.cmd, other operating systems use npm.
 What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
The following global variables exist in Node.js: Global object: global Core module: process, console, require Runtime environment variables: __dirname, __filename, __line, __column Constants: undefined, null, NaN, Infinity, -Infinity
 Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
The main differences between Node.js and Java are design and features: Event-driven vs. thread-driven: Node.js is event-driven and Java is thread-driven. Single-threaded vs. multi-threaded: Node.js uses a single-threaded event loop, and Java uses a multi-threaded architecture. Runtime environment: Node.js runs on the V8 JavaScript engine, while Java runs on the JVM. Syntax: Node.js uses JavaScript syntax, while Java uses Java syntax. Purpose: Node.js is suitable for I/O-intensive tasks, while Java is suitable for large enterprise applications.
 Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Yes, Node.js is a backend development language. It is used for back-end development, including handling server-side business logic, managing database connections, and providing APIs.
 How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Server deployment steps for a Node.js project: Prepare the deployment environment: obtain server access, install Node.js, set up a Git repository. Build the application: Use npm run build to generate deployable code and dependencies. Upload code to the server: via Git or File Transfer Protocol. Install dependencies: SSH into the server and use npm install to install application dependencies. Start the application: Use a command such as node index.js to start the application, or use a process manager such as pm2. Configure a reverse proxy (optional): Use a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to route traffic to your application




