Master the Oracle startup process in one article
This article brings you relevant knowledge about Oracle, which mainly sorts out the issues related to the startup process, including NOMOUNT status, MOUNT status, OPEN status, etc., as follows: Let's take a look, hope it helps everyone.

Oracle Video Tutorial"
In-depth understanding of the ORACLE startup processORACLE SERVER byInstance (Instance, Application) and Database (database, Database file) are composed of a set of background processes and a It consists of a shared memory area (sga), and the background process is the channel for interaction between the database and the operating system. The name of the background process is determined by ORACLE_SID. ORACLE looks for the parameter file to start the instance based on ORACLE_SID. A database refers to a set of physical files stored on disk.
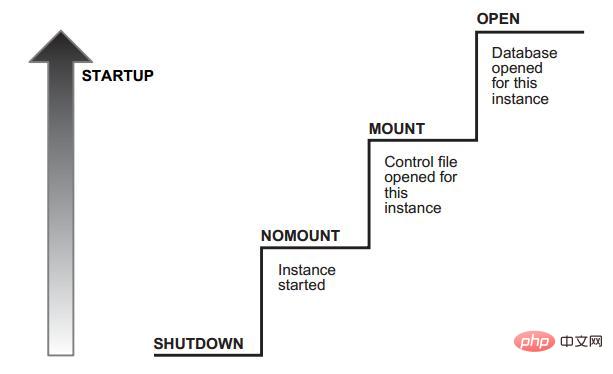
ORACLE startup is divided into 3 processes:NOMOUNT state: start the instance MOUNT state: open the control file OPEN state: open the control The file described in the file
NOMOUNT status:
ORACLE needs to find SPFILE(System Parameter File)(oracle 10g default, pfile (Parameter File)Also) file to create instances and allocate memory.
MOUNT state:
In this state, the control file needs to be opened, andthe control file contains the location information of log files, data files, and checkpoint information and other important information.
In ORACLE9i, an error will be reported if the password file is lost, and it can be rebuilt through the orapw tool. No error will be reported in Oracle 10g, query through v$pwfile_users view.lk_The file is created when the database is started and is used to lock the database by the operating system. (lock)
The password file exists in $ORACLE_HOME/dbs1 2 |
|
Rebuild the control file:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
|
OPEN status
First, check whether the checkpoint count in the data file header is consistent with the checkpoint count in the control file. Secondly, check whether the starting SCN of the data file header and the ending SCN of the file recorded in the control file are consistent. If the ending SCN in the control file is equal to the starting SCN in the data file header, it means no recovery is required. SQL>show parameter backgroud_dump_dest;If a file in the database is lost, the alarm log will not be displayed in the foreground during the MOUNT stage, but will be recorded in alter_.log. Oracle startup and shutdown1. sql*plus method:
Use sql*plus to connect to Oracle Sqlplus /nolog starts sql*plus without connecting to the databaseConnect /as sysdba connects to oracle as DBA . StartStartup to start . However, there are three Oracle startup modes: l Startup nomount (nomount mode) starts the instance without loading the database. l Startup mount (mount mode) starts the instance to load the database but does not open the database l Startup (open mode) starts the instance to load and open the database, which is the command we used aboveIn Nomount mode, Oracle only creates various memory structures and service processes for the instance, and does not open any database files.So:
1) Create a new database
2) Rebuild the control file
Both operations must be performed in this mode.
In Mount mode, Oracle only loads the database but does not open the database, so: 1) Rename the data file 2) Add and delete and rename redo log files 3) Perform a full database recovery operation 4) Change the database archive mode These four operations must be performed in this mode Open mode (that is, our startup above does not take any parameters) starts normally. Of course, these three modes can be converted: Alter database mount (nomount mode) —> alter database open (mount mode) —> (open mode) Of course, there are other situations. In our open mode, the database can be set to unrestricted state and restricted stateIn the restricted state, only the DBA can access the database, so:1) 执行数据导入导出
2) 使用sql*loader提取外部数据
3) 需要暂时拒绝普通用户访问数据库
4) 进行数据库移植或者升级操作
这4种操作都必须在这个状态下进行
在打开数据库时使用startup restrict命令即进入受限状态。
使用alter system disable restricted session命令即可以将受限状态改变为非受限状态。
使用alter system enable restricted session命令可以将非受限状态变为受限状态
使用alter database open read only可以使数据库进入只读状态。
使用alter database open read write 可以使数据库进入读写状态。
当然在某些情况下可能是用上述各种启动方式都无法成功启动数据库,这个时候就要使用startup force命令来强行启动数据库。当然谁都不想碰到这种情况:)
c.关闭数据库
1)正常关闭 shutdown
2) 立即关闭 shutdown immediate
3) 关闭事务 shutdown transactional
4) 强行关闭 shutdown abort,当然谁都不想碰到这种情况。
二、OEM为例
Oracle Enterprise Management(OEM),
跟第一小节讲的Sqlplus /nolog ,Connect /as sysdba 这2个命令差不多的操作如图:
按照上面的一步步操作就能够连接到数据库。
下面是如何启动和关闭数据库:
点击我们前几章创建的ORADB01这个数据库树中的配置选项,这个里面的:
1)已启动 对应 Nomount模式
2)已转载 对应 mount模式
3)打开 对应 open模式
当你点击应有按钮之后就会进入如下对话框
1)正常 对应 正常关闭 shutdown
2) 立即 对应 立即关闭 shutdown immediate
3) 事务处理 对应 关闭事务 shutdown transactional
4) 中止 对应 强行关闭 shutdown abort
确定之后出现如下对话框
限制对数据库访问 对应 alter system disable restricted session
alter system enable restricted session
只读模式 对应 alter database open read only
alter database open read write
简单吧,sql*plus的一大堆命令到OEM中变成了几个按钮罢了。
3.windows控制台
这个熟悉吧:
oracle ***********Agent 用于OEM管理结构
oracle************HTTPSERVER oracle Web服务器
oracle ***********ManagementServer 用于OEM管理结构
oracle ***********TNSListener oracle网络结构的服务器端进程
oracle ***********OEMREP 资料档案库文件
oracle ***********ORADB001 用户创建的数据库
我一般都把所有的服务全部选成手动启动,如果全开,内存要用掉700M..............
提示:建议关闭数据库服务前先shutdown,否则可能会丢失数据。
如果是windows系统,关系不大,会自动提交未提交的DML。但是在unix或者linux系统的话,最好先shutdown immediate,在检查一下是否还有oracle进程,最后在关闭服务器。
Oracle启动的整个过程
1.启动选项
在发出startup命令启动数据库时,oracle将在默认位置$ORACLE_HOME/dbs(UNIX/Linux)中查找初始化参数文件。Oracle将以下面的顺序在其中寻找合适的初始化文件:
Spfile$ORACLE_SID.ora
Spfile.ora
Init$ORACLE_SID.ora
可以用几种方式启动oracle数据库。不同方式启动将影响启动数据库的程度。启动状态由nomount(数据库未装载)——>mount(数据库完成装载)——>open(数据库打开)
1.1 STARTUP NOMOUNT命令
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
--Oracle读参数文件(里面有控制文件目录),打开实例,启动Oracle后台进程,给Oracle分配SGA。此时数据库状态为未装载。
可以在SQL*Plus会话中使用STARTUP NOMOUNT命令启动实例,这样启动仅有实例运行。如果以这种方式启动,将不读控制文件,而且数据文件也不打开。操作系统启动Oracle后台进程,并且给oracle分配SGA。事实上,只有实例本身在运行。
1.2 STARTUP MOUNT命令
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
--Oracle 打开并读取控制文件(里面有数据文件和日志文件的目录),获取数据文件和重做日志文件的名称和位置。此时数据库完成装载。
在启动过程中,oracle把实例与数据库关联。Oracle打开并读取控制文件,获取数据文件和重做日志文件的名称和位置。在进行诸如全数据库恢复、更改数据库的归档日志模式或重命名数据文件这一类的活动时,通常需要以安装模式启动数据库。请注意,这三种操作都要求oracle访问数据文件,但不提供对文件的用户操作。
1.3 STARTUP [OPEN]命令
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
--Oracle打开数据文件和重做日志文件,才能对外(所有有效用户)提供数据库服务。
启动过程的最后一步是打开数据库。当数据库以打开模式启动时,所有有效用户可以连接到数据库,执行数据库操作。在此步骤之前,一般用户根本就不能连接到数据库。通过发布下面的命令让数据库出于打开模式。
Oracle 的启动需要经历四个状态,SHUTDOWN 、NOMOUNT 、MOUNT 、OPEN。
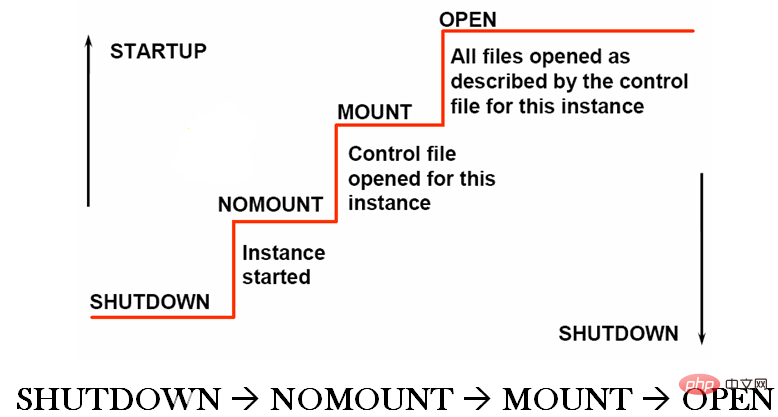
SHUTDOWN状态
第一状态没什么好解释的,oracle的所有文件都静静的躺在磁盘里,一切都还未开始,属于关机状态
NOMOUNT状态
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
|
查找参数文件的顺序如上面列表的,读取优先级
spfilechongshi.ora > spfile.ora>initchongshi.ora
如果三个文件都找不到的话,那么将启动失败。
* 启动算法,分配内存
* 启动后台进程
* 开放alertSID.log文件和跟踪文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
|
现在就处在一个nomount状态。
mount状态
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
* 把一个数据库和启动的实例关联起来
* 在参数文件(spfile/pfile)中找到控制文件进行读取
查看参数文件:
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
控制文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
* 读取控制文件,获得的数据文件和联机重做日志文件,然而,在这个时候没有进行检查以验证存在的数据文件和联机重做日志文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
|
现在进入了数据库的mount状态,我们通过mount启动的时候,下面会多一句提示“Database mounted.” 数据库准备就绪。
open状态
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
打开数据库包括下列任务:
打开在线数据日志文件
打开联机重做日志文件
如果任何数据文件或非线性重做日志文件不存在,当您试图打开的数据库,服务器返回错误。
在这最后阶段,该服务器验证所有数据文件和联机重做日志文件可以打开并检查数据库的一致性。如果需要,该系统监控进程开始实例恢复。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
|
在上面的命令中,startup后面不加其它信息的话,系统会为我们直接启动到第4个状态。
数据库关闭的三种方式
1、shutdown normal
正常方式关闭数据库。
发出该命令后,任何新的连接都将再不允许连接到数据库。在数据库关闭之前,Oracle将等待目前连接的所有用户都从数据库中退出后才开始关闭数据库。采 用这种方式关闭数据库,在下一次启动时不需要进行任何的实例恢复。但需要注意一点的是,采用这种方式,也许关闭一个数据库需要几天时间,也许更长。
2. shutdown immediate
Close the database immediately.
When shutdown immediate is executed in SVRMGRL, the database is not closed immediately.
Instead, it is closed after Oracle performs certain cleanup work (terminating the session and releasing session resources).
When shutdown cannot be used to close the database , shutdown immediate can complete the database shutdown operation.
This is a commonly used way to close the database. If you want to close the database quickly, but also want the database to be closed cleanly, this method is often used.
The SQL statement currently being processed by Oracle is immediately interrupted, and any uncommitted transactions in the system are rolled back. If there is a long uncommitted transaction in the system, shutting down the database in this way will also take some time (the transaction rollback time). The system does not wait for all users connected to the database to exit the system, forcibly rolls back all currently active transactions, and then disconnects all connected users.
3. shutdown abort
Close the database directly, and the session accessing the database will be terminated suddenly (equivalent to directly closing the background instance service process)
If there are a large number of operations being executed in the database, execute shutdown at this time After abort, restarting the database takes a long time.
4. After shutdown in Windows, you need to restart the background instance service process, otherwise the ora-12514 error will be reported. After restarting the instance service, the database automatically executed startup to the open state.
Recommended tutorial: "Oracle Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of Master the Oracle startup process in one article. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 How long will Oracle database logs be kept?
May 10, 2024 am 03:27 AM
How long will Oracle database logs be kept?
May 10, 2024 am 03:27 AM
The retention period of Oracle database logs depends on the log type and configuration, including: Redo logs: determined by the maximum size configured with the "LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST" parameter. Archived redo logs: Determined by the maximum size configured by the "DB_RECOVERY_FILE_DEST_SIZE" parameter. Online redo logs: not archived, lost when the database is restarted, and the retention period is consistent with the instance running time. Audit log: Configured by the "AUDIT_TRAIL" parameter, retained for 30 days by default.
 The order of the oracle database startup steps is
May 10, 2024 am 01:48 AM
The order of the oracle database startup steps is
May 10, 2024 am 01:48 AM
The Oracle database startup sequence is: 1. Check the preconditions; 2. Start the listener; 3. Start the database instance; 4. Wait for the database to open; 5. Connect to the database; 6. Verify the database status; 7. Enable the service (if necessary ); 8. Test the connection.
 How much memory does oracle require?
May 10, 2024 am 04:12 AM
How much memory does oracle require?
May 10, 2024 am 04:12 AM
The amount of memory required by Oracle depends on database size, activity level, and required performance level: for storing data buffers, index buffers, executing SQL statements, and managing the data dictionary cache. The exact amount is affected by database size, activity level, and required performance level. Best practices include setting the appropriate SGA size, sizing SGA components, using AMM, and monitoring memory usage.
 How to see the number of occurrences of a certain character in Oracle
May 09, 2024 pm 09:33 PM
How to see the number of occurrences of a certain character in Oracle
May 09, 2024 pm 09:33 PM
To find the number of occurrences of a character in Oracle, perform the following steps: Get the total length of a string; Get the length of the substring in which a character occurs; Count the number of occurrences of a character by subtracting the substring length from the total length.
 Oracle database server hardware configuration requirements
May 10, 2024 am 04:00 AM
Oracle database server hardware configuration requirements
May 10, 2024 am 04:00 AM
Oracle database server hardware configuration requirements: Processor: multi-core, with a main frequency of at least 2.5 GHz. For large databases, 32 cores or more are recommended. Memory: At least 8GB for small databases, 16-64GB for medium sizes, up to 512GB or more for large databases or heavy workloads. Storage: SSD or NVMe disks, RAID arrays for redundancy and performance. Network: High-speed network (10GbE or higher), dedicated network card, low-latency network. Others: Stable power supply, redundant components, compatible operating system and software, heat dissipation and cooling system.
 How to read dbf file in oracle
May 10, 2024 am 01:27 AM
How to read dbf file in oracle
May 10, 2024 am 01:27 AM
Oracle can read dbf files through the following steps: create an external table and reference the dbf file; query the external table to retrieve data; import the data into the Oracle table.
 How much memory is needed to use oracle database
May 10, 2024 am 03:42 AM
How much memory is needed to use oracle database
May 10, 2024 am 03:42 AM
The amount of memory required for an Oracle database depends on the database size, workload type, and number of concurrent users. General recommendations: Small databases: 16-32 GB, Medium databases: 32-64 GB, Large databases: 64 GB or more. Other factors to consider include database version, memory optimization options, virtualization, and best practices (monitor memory usage, adjust allocations).
 Oracle scheduled tasks execute the creation step once a day
May 10, 2024 am 03:03 AM
Oracle scheduled tasks execute the creation step once a day
May 10, 2024 am 03:03 AM
To create a scheduled task in Oracle that executes once a day, you need to perform the following three steps: Create a job. Add a subjob to the job and set its schedule expression to "INTERVAL 1 DAY". Enable the job.




