Can docker install oracle?
docker can install oracle. Installation method: 1. Pull the official Oracle image and use "docker images" to view the image; 2. After starting the container, use "docker exec -it oracle11g bash" to enter the container and edit the environment variables; 3. Use "sqlplus /nolog" Just enter the oracle command line.

The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, docker version 19.03, Dell G3 computer.
Can docker install oracle?
You can use docker to deploy oracle, and it has many benefits. It can not only reduce the installation time, but also enable rapid deployment.
The benefits of using docker for deployment are as follows:
(1) Simplify the configuration, build it once and package it, and then it can be used as a test environment, production environment or pre-production environment. A lot of testing sessions can be saved. For example, one server can test multiple versions without waiting.
(2) can solve the difficulty of developers deploying the environment. For example, it may take half a day for a new colleague to install the environment, but it will be much more convenient to directly run an already configured container.
(3) Application isolation and server integration. One server can use docker to deploy multiple sets of services, and the isolation is very high (except for virtual machines).
(4) For development, after deployment, it can be run everywhere to facilitate development and debugging.
(5) It can reduce the utilization of resources. Compared with virtual machines, it saves a lot of unnecessary resources. The loss of isolation is more than compensated for by other advantages.
(6) For operation and maintenance, it can quickly expand the capacity and reduce the original utilization rate
(7) Each small service can be clustered, and docker’s resource utilization comparison It is small and can start multiple servers on one server. Compared with other products, it uses more I/O on the server.
(8) Can be deployed on multiple platforms
The examples are as follows:
It is very troublesome to install oracle in Linux, I believe everyone will encounter various problems. Plant pit. In order to install it once and make it easier to export the image for transplantation on various platforms in the future, I chose to install it with docker
Pull the image
Search for Oracle on DockerHub to find the official image of Oracle. Address: https://hub.docker.com/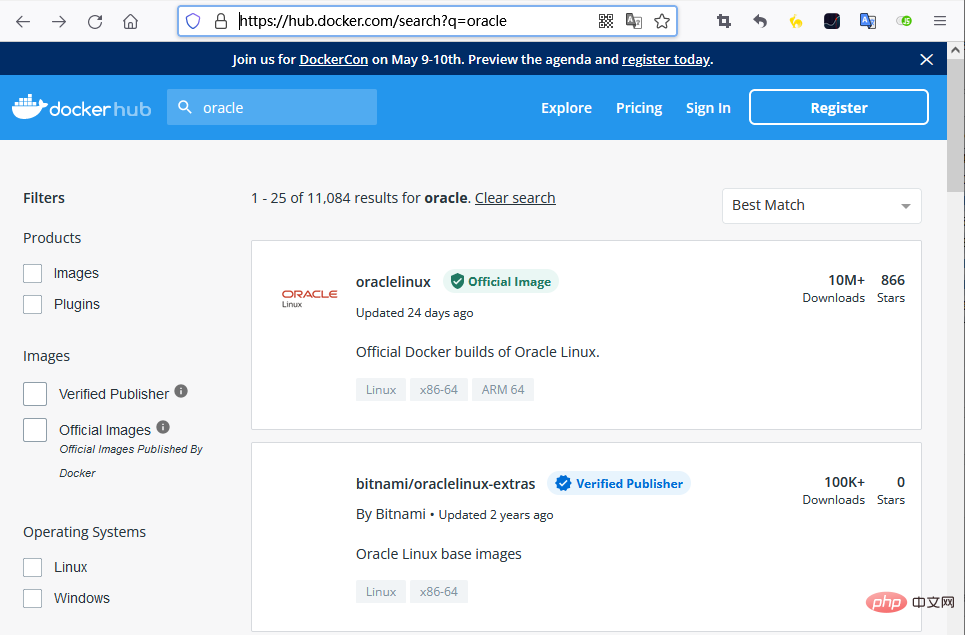
Note that if you use the docker pull oraclelinux command here, you cannot pull the image because it does not have latest tag. Therefore, you can only manually specify its version number
For example docker pull oraclelinux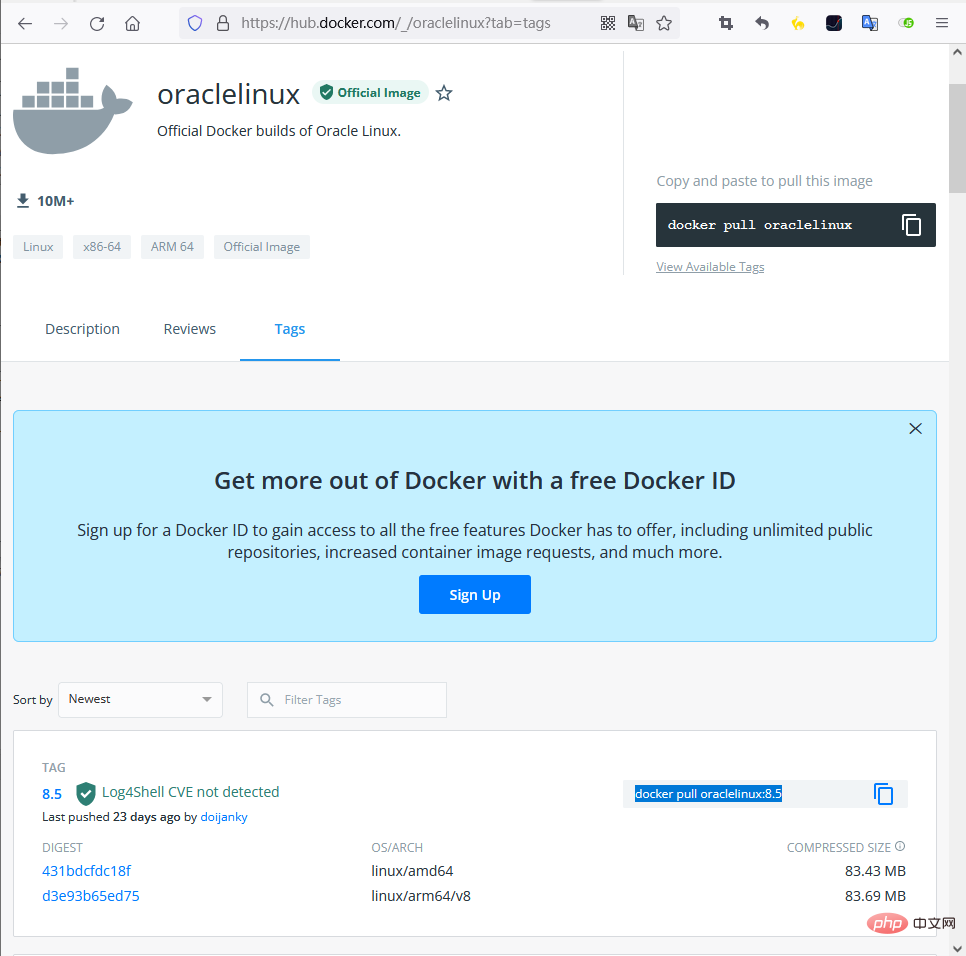
Using the official image download speed is very slow, therefore, we can use the Ali image docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/helowin/oracle_11g
can be found on dockerHub (the second one), you can refer to this configuration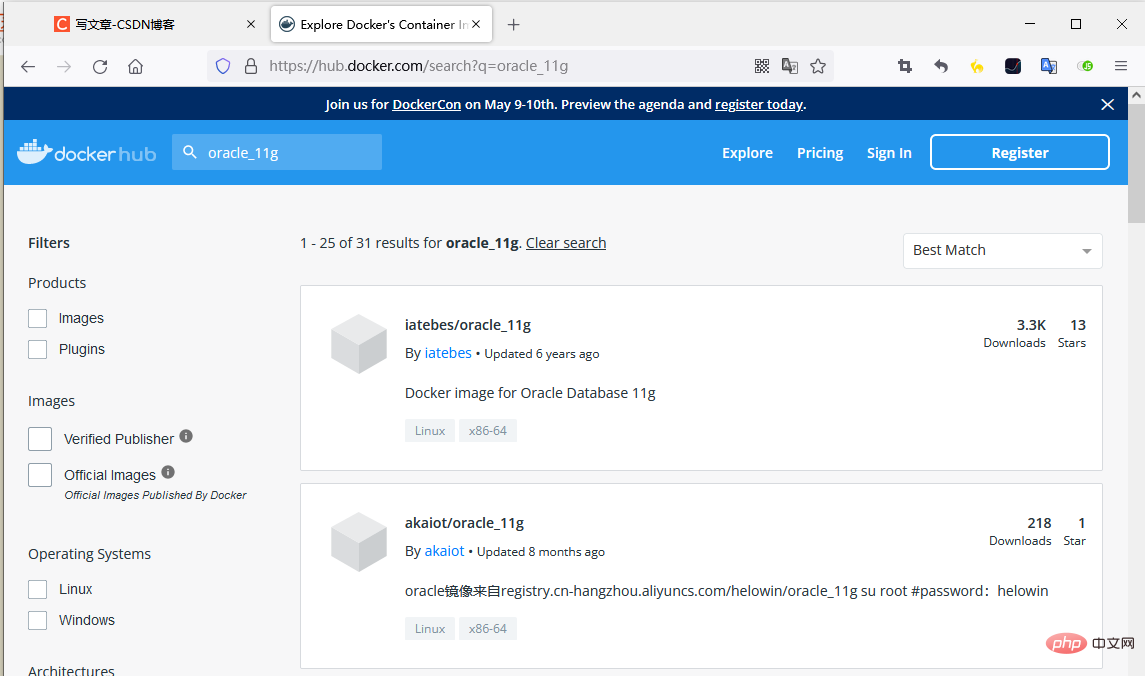
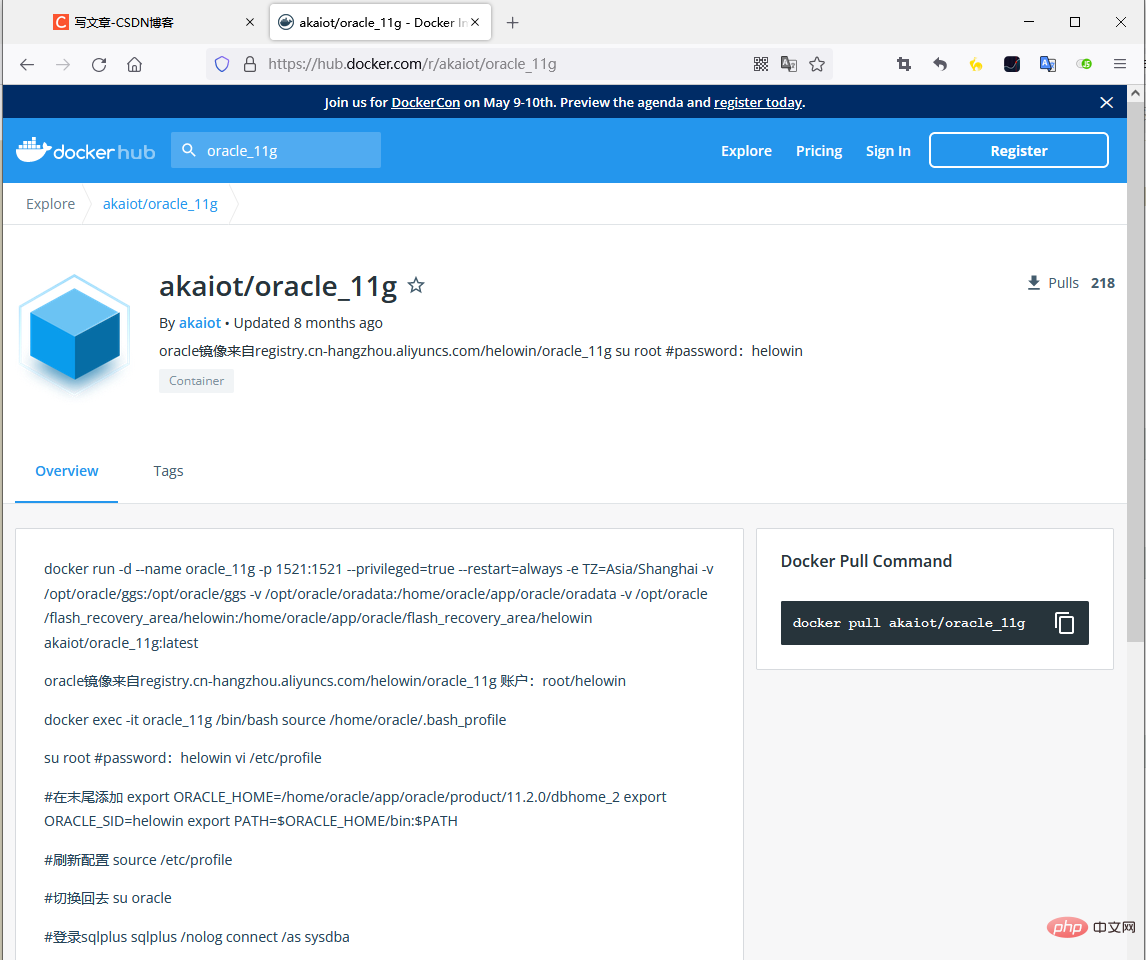 to use
to use docker images Check the image and confirm that it has been downloaded
Start the container
- The default way to start the container
docker run -d -it -p 1521:1521 --name oracle11g --restart=always registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/helowin/oracle_11g - How to start persistence
docker run -d -it -p 1521:1521 --name oracle --restart=always --mount source=oracle_vol,target=/home/oracle/app/oracle/oradata registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com /helowin/oracle_11g
View started threadsnetstat -tulnp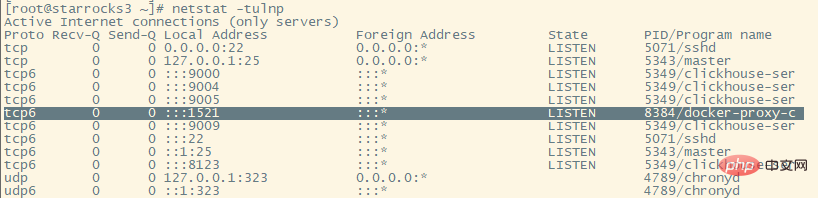
View running statusdocker ps -a 
Container environment configuration
Enter the containerdocker exec -it oracle11g bash
Switch to the root usersu root, password The environment variables configured for the helowin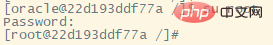
docker container are not in /etc/profile, and this file will not be used when the container is started.
You can set the environment variable configuration in the /home/oracle/.bashrc file, which can omit the creation of soft connections ln -s $ORACLE_HOME/bin/sqlplus /usr/ bin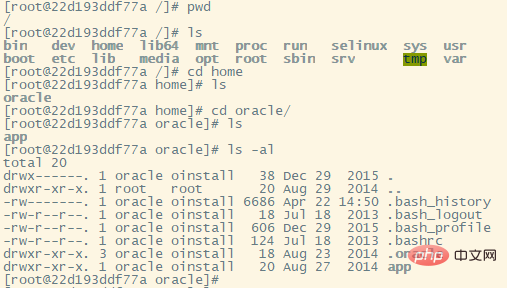
Edit environment variablesvi /home/oracle/.bashrc, add the following command at the end of the file
export ORACLE_HOME=/home/oracle/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_2 export ORACLE_SID=helowin export PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH
wq Save and exit. Then use source /home/oracle/.bashrc to refresh the environment variables and make them effective
Enter the oracle command line
Use sqlplus /nolog Enter the oracle command line 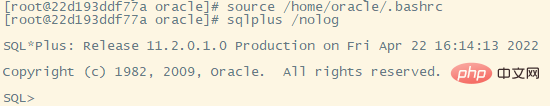
Use the "operating system authentication" method to log in to oracle conn / as sysdba
If you directly use the default root user to log in, a login failure will be reported . The su - oracle command must be used here to switch the current user to oracle, and then execute the login command 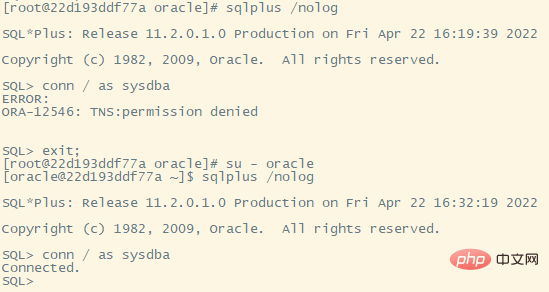
ORA-12514, TNS:listener does not currently know of service requested in connect descriptor
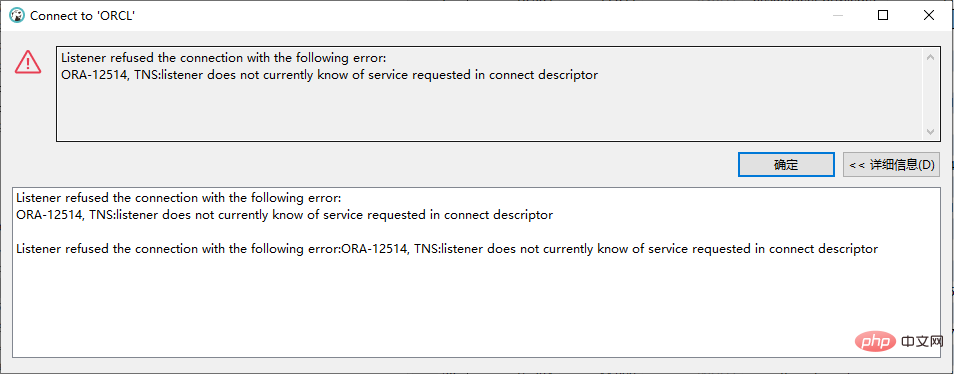 This error is due to the wrong database name
This error is due to the wrong database name
su - oracle sqlplus /nolog conn / as sysdba select instance_name from v$instance; show user;
Using the above command to find out, it is all available "database names" ” and “user name”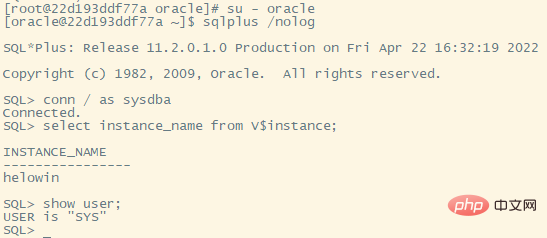
In this image of Ali, all passwords are unifiedhelowin
The system user has DBA authority, but No SYSDBA permissions. This account is usually used to manage the database.
The sys user is the account with the highest authority in the Oracle database. It has "SYSDBA" and "SYSOPER" permissions and is generally not allowed to log in from the outside.
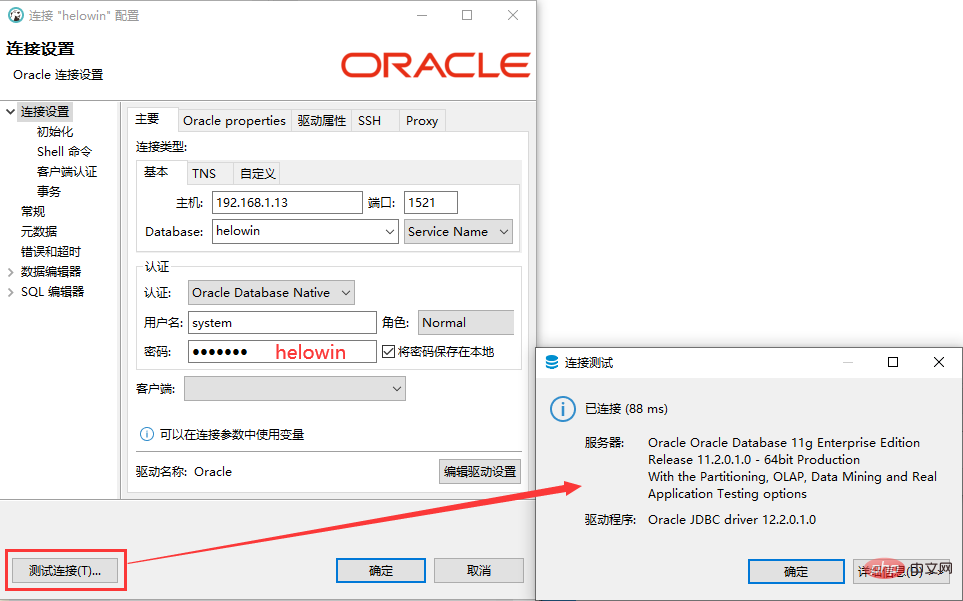
Configuring the firewall
The firewall must allow port 1521 so that external database management tools can connect
# 打开防火墙 systemctl start firewalld # 查询端口状态 firewall-cmd --query-port=1521/tcp # 永久性开放端口 firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=1521/tcp # 重启防火墙 firewall-cmd --reload firewall-cmd --query-port=1521/tcp
Recommended study: "docker video tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of Can docker install oracle?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Steps to create a Docker image: Write a Dockerfile that contains the build instructions. Build the image in the terminal, using the docker build command. Tag the image and assign names and tags using the docker tag command.
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Troubleshooting steps for failed Docker image build: Check Dockerfile syntax and dependency version. Check if the build context contains the required source code and dependencies. View the build log for error details. Use the --target option to build a hierarchical phase to identify failure points. Make sure to use the latest version of Docker engine. Build the image with --t [image-name]:debug mode to debug the problem. Check disk space and make sure it is sufficient. Disable SELinux to prevent interference with the build process. Ask community platforms for help, provide Dockerfiles and build log descriptions for more specific suggestions.
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to save docker image
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:54 AM
How to save docker image
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:54 AM
To save the image in Docker, you can use the docker commit command to create a new image, containing the current state of the specified container, syntax: docker commit [Options] Container ID Image name. To save the image to the repository, you can use the docker push command, syntax: docker push image name [: tag]. To import saved images, you can use the docker pull command, syntax: docker pull image name [: tag].




