Let's talk about how to obtain data in advance in Angular Route
How to get data in advance in Angular Route? The following article will introduce to you how to obtain data in advance from Angular Route. I hope it will be helpful to you!

Getting ahead of time means getting the data before it is presented on the screen. In this article, you will learn how to obtain data before routing changes. Through this article, you will learn to use resolver, apply resolver in Angular App, and apply it to a public preloaded navigation. [Related tutorial recommendations: "angular tutorial"]
Why should you use Resolver
Resolver Plays the role of middleware service between routing and components. Suppose you have a form with no data, and you want to present an empty form to the user, display a loader when the user data is loaded, and then when the data is returned, fill the form and hide the loader.
Usually, we will get the data in the ngOnInit() hook function of the component. In other words, after the component is loaded, we initiate a data request.
Operation in ngOnInit(), we need to add loader display in its routing page after each required component is loaded. Resolver can simplify the addition and use of loader. Instead of adding loader to every route, you can just add one loader that applies to each route.
This article will use examples to analyze the knowledge points of resolver. So that you can remember it and use it in your projects.
Using Resolver in an application
In order to use resolver in an application, you need to prepare some interfaces. You can simulate it through JSONPlaceholder without developing it yourself.
JSONPlaceholder is a great interface resource. You can use it to better learn related concepts of the front end without being constrained by the interface.
Now that the interface problem is solved, we can start the application of resolver. A resolver is a middleware service, so we will create a service.
$ ng g s resolvers/demo-resolver --skipTests=true
--skipTests=true Skip generating test files A service is created in the
src/app/resolvers folder. resolver There is a resolve() method in the interface, which has two parameters: route (an instance of ActivatedRouteSnapshot) and state (an instance of RouterStateSnapshot).
loader Normally all AJAX requests are written in ngOnInit(), but the logic will be in resolver Implemented in, replacing ngOnInit().
Next, create a service to obtain the list data in JSONPlaceholder. Then call it in resolver, and then configure resolve information in the route, (the page will wait) until resolver is processed. After resolver is processed, we can obtain data through routing and display it in the component.
Create the service and write the logic to get the list data
$ ng g s services/posts --skipTests=true
Now that we have successfully created the service, it is time to write the logic for an AJAX request . The use of
model can help us reduce errors.
$ ng g class models/post --skipTests=true
post.ts
export class Post { id: number;
title: string;
body: string;
userId: string;
}model Ready, it’s time to get the data for post post.
post.service.ts
import { Injectable } from "@angular/core";
import { HttpClient } from "@angular/common/http";
import { Post } from "../models/post";
@Injectable({
providedIn: "root"
})
export class PostsService {
constructor(private _http: HttpClient) {}
getPostList() {
let URL = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts";
return this._http.get<Post[]>(URL);
}
}Now, this service can be called at any time.
demo-resolver.service.ts
import { Injectable } from "@angular/core";
import {
Resolve,
ActivatedRouteSnapshot,
RouterStateSnapshot
} from "@angular/router";
import { PostsService } from "../services/posts.service";
@Injectable({
providedIn: "root"
})
export class DemoResolverService implements Resolve<any> {
constructor(private _postsService: PostsService) {}
resolve(route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot, state: RouterStateSnapshot) {
return this._postsService.getPostList();
}
}Post list data returned from resolver. Now, you need a route to configure resolver, get the data from the route, and then display the data in the component. In order to perform routing jumps, we need to create a component.
$ ng g c components/post-list --skipTests=true
To make the route visible, add router-outlet in app.component.ts.
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
Now, you can configure the app-routing.module.ts file. The following code snippet will help you understand routing configuration resolver.
app-routing-module.ts
import { NgModule } from "@angular/core";
import { Routes, RouterModule } from "@angular/router";
import { PostListComponent } from "./components/post-list/post-list.component";
import { DemoResolverService } from "./resolvers/demo-resolver.service";
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: "posts",
component: PostListComponent,
resolve: {
posts: DemoResolverService
}
},
{
path: "",
redirectTo: "posts",
pathMatch: "full"
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule {}A resolve has been added to the routing configuration, which will initiate a HTTP request, then allow the component to initialize when the HTTP request returns successfully. The route will assemble the data returned by the HTTP request.
How to apply a preloaded navigation
To show the user that a request is in progress, we write a common and simple ## in AppComponent #loader. You can customize it as needed.
app.component.html
<router-outlet></router-outlet>Loading...
app.component.ts
import { Component } from "@angular/core";
import {
Router,
RouterEvent,
NavigationStart,
NavigationEnd
} from "@angular/router";
@Component({
selector: "app-root",
templateUrl: "./app.component.html",
styleUrls: ["./app.component.scss"]
})
export class AppComponent {
isLoader: boolean;
constructor(private _router: Router) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.routerEvents();
}
routerEvents() {
this._router.events.subscribe((event: RouterEvent) => {
switch (true) {
case event instanceof NavigationStart: {
this.isLoader = true;
break;
}
case event instanceof NavigationEnd: {
this.isLoader = false;
break;
}
}
});
}
}当导航开始,isLoader 值被赋予 true,页面中,你将看到下面的效果。
当 resolver 处理完之后,它将会被隐藏。
现在,是时候从路由中获取值并将其展示出来。
port-list.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from "@angular/core";
import { Router, ActivatedRoute } from "@angular/router";
import { Post } from "src/app/models/post";
@Component({
selector: "app-post-list",
templateUrl: "./post-list.component.html",
styleUrls: ["./post-list.component.scss"]
})
export class PostListComponent implements OnInit {
posts: Post[];
constructor(private _route: ActivatedRoute) {
this.posts = [];
}
ngOnInit() {
this.posts = this._route.snapshot.data["posts"];
}
}如上所示,post 的值来自 ActivatedRoute 的快照信息 data。这值都可以获取,只要你在路由中配置了相同的信息。
我们在 HTML 进行如下渲染。
<div class="post-list grid-container">
<div class="card" *ngFor="let post of posts">
<div class="title"><b>{{post?.title}}</b></div>
<div class="body">{{post.body}}</div>
</div>
</div>CSS 片段样式让其看起来更美观。
port-list.component.css
.grid-container {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: calc(100% / 3) calc(100% / 3) calc(100% / 3);
}
.card {
margin: 10px;
box-shadow: black 0 0 2px 0px;
padding: 10px;
}推荐使用 scss 预处理器编写样式
从路由中获取数据之后,它会被展示在 HTML 中。效果如下快照。
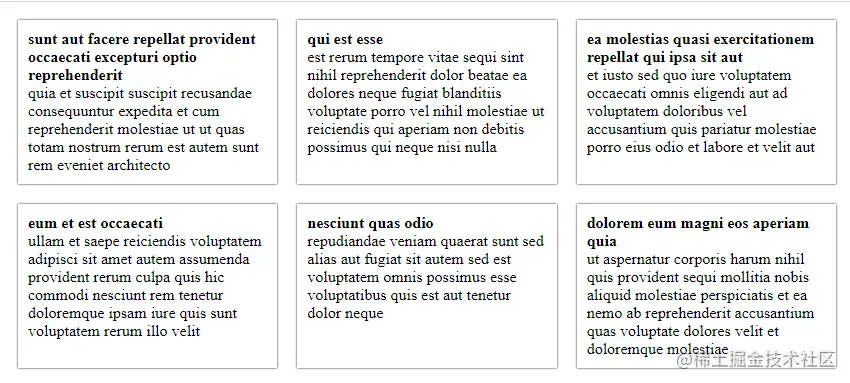
至此,你已经了解完怎么应用 resolver 在你的项目中了。
总结
结合用户体验设计,在 resolver 的加持下,你可以提升你应用的表现。了解更多,你可以戳官网。
本文是译文,采用的是意译的方式,其中加上个人的理解和注释,原文地址是:
https://www.pluralsight.com/guides/prefetching-data-for-an-angular-route
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about how to obtain data in advance in Angular Route. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Let's talk about metadata and decorators in Angular
Feb 28, 2022 am 11:10 AM
Let's talk about metadata and decorators in Angular
Feb 28, 2022 am 11:10 AM
This article continues the learning of Angular, takes you to understand the metadata and decorators in Angular, and briefly understands their usage. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 How to install Angular on Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
How to install Angular on Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:20 PM
Angular.js is a freely accessible JavaScript platform for creating dynamic applications. It allows you to express various aspects of your application quickly and clearly by extending the syntax of HTML as a template language. Angular.js provides a range of tools to help you write, update and test your code. Additionally, it provides many features such as routing and form management. This guide will discuss how to install Angular on Ubuntu24. First, you need to install Node.js. Node.js is a JavaScript running environment based on the ChromeV8 engine that allows you to run JavaScript code on the server side. To be in Ub
 Detailed explanation of angular learning state manager NgRx
May 25, 2022 am 11:01 AM
Detailed explanation of angular learning state manager NgRx
May 25, 2022 am 11:01 AM
This article will give you an in-depth understanding of Angular's state manager NgRx and introduce how to use NgRx. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 A brief analysis of how to use monaco-editor in angular
Oct 17, 2022 pm 08:04 PM
A brief analysis of how to use monaco-editor in angular
Oct 17, 2022 pm 08:04 PM
How to use monaco-editor in angular? The following article records the use of monaco-editor in angular that was used in a recent business. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 An article exploring server-side rendering (SSR) in Angular
Dec 27, 2022 pm 07:24 PM
An article exploring server-side rendering (SSR) in Angular
Dec 27, 2022 pm 07:24 PM
Do you know Angular Universal? It can help the website provide better SEO support!
 Angular + NG-ZORRO quickly develop a backend system
Apr 21, 2022 am 10:45 AM
Angular + NG-ZORRO quickly develop a backend system
Apr 21, 2022 am 10:45 AM
This article will share with you an Angular practical experience and learn how to quickly develop a backend system using angualr combined with ng-zorro. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 What should I do if the project is too big? How to split Angular projects reasonably?
Jul 26, 2022 pm 07:18 PM
What should I do if the project is too big? How to split Angular projects reasonably?
Jul 26, 2022 pm 07:18 PM
The Angular project is too large, how to split it reasonably? The following article will introduce to you how to reasonably split Angular projects. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Let's talk about how to customize the angular-datetime-picker format
Sep 08, 2022 pm 08:29 PM
Let's talk about how to customize the angular-datetime-picker format
Sep 08, 2022 pm 08:29 PM
How to customize the angular-datetime-picker format? The following article talks about how to customize the format. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!






