How to use VueRouter4.x? Quick start guide
How to use VueRouter4.x? The following article will share with you a quick tutorial and introduce how to quickly get started with VueRouter4.x in 10 minutes. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

Vue Router is a routing plug-in developed by the Vue team that is deeply integrated with the core of Vue.js, making it very simple to build single-page programs with Vue; The latest version of Vue Router is 4.X, which is also the recommended version for Vue3. In this article, we will learn about Vue Router 4.X. (Learning video sharing: vue video tutorial)
URL.hash and History
There are two types of history## in Vue Router # (Record historical routing), respectively URL.hash and History provided in HTML5.
file://), or when the configuration server cannot handle arbitrary URLs, but hashing is very poor for SEO;
Installation and usage process
First we install Vue Router, the command is as follows:npm i vue-router
main.js Write the following code:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 1 引入 createRouter
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
// 2 定义路由映射表
const routes = [
/* more router */
]
// 3 创建路由实例,并传递对应配置
const router = createRouter({
// history 模式 这里使用createWebHistory
history: createWebHistory(),
// 传递路由映射表
routes
})
createApp(App).use(router).mount('#app')routes in the above code, you can define a router.js file and extract it, sample code As follows:
router.js
export default [ /* more router */ ]
main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 2 引入路由映射表
import routes from './router'
// 1 引入 createRouter
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
// 3 创建路由实例,并传递对应配置
const router = createRouter({
// history 模式 这里使用createWebHistory
history: createWebHistory(),
// 传递路由映射表
routes
})
createApp(App).use(router).mount('#app') and use it in main.js**( This method is more commonly used).
router-link
##
is a custom component provided by Vue, used to create links. The native is not used in Vue, because will be reset after changing the URL. Loading the page but will not; for details about which properties the component supports, please refer to the documentation. router-view
##
<template>
<router-link to="/hello"
><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="./assets/logo.png" class="lazy" alt="Vue logo"
/></router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
</template>Then our router.js code is as follows:
import RootComponent from './components/root.vue'
export default [
{
path: '/',
// 引入组件
component: RootComponent
},
{
path: '/hello',
// 路由懒加载引入组件
component: () => import('./components/HelloWorld.vue')
}
]For other configuration items, you can refer to the documentation.
The code running results are as follows:
Routing lazy loading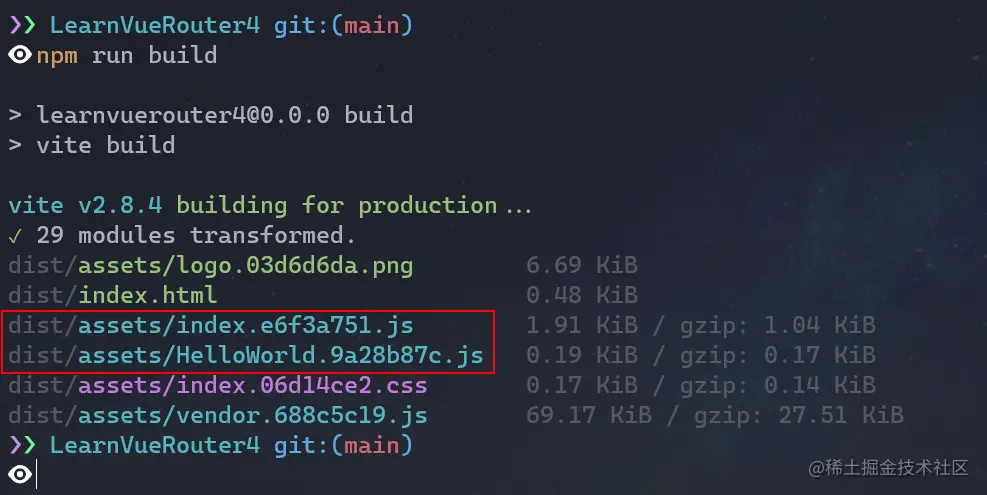
When our application becomes more and more When the JavaScript code is large, the packaged JavaScript code will also be particularly large. At this time, we need to split the entire application into different blocks, and Vue Router supports this function. We only need toreplace the static import with dynamic import. , such as the above code:
component: () => import('./components/HelloWorld.vue')
Then the packaging (webpack, Vite) tool will package these dynamically imported components separately, as shown in the following figure:
Dynamic routing
VueRouter allows us to dynamically set routing matching rules. For example, we now have a User component, and the content of the component will Different content is displayed according to different IDs. The setting method only needs to be set in the form of
:parameter name. For example: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>{
path: &#39;/user/:id&#39;,
component: () => import(&#39;@/components/User&#39;)
}</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div> Jump in the template as follows:
<router-link to="/user/10010"></router-link>
Or use the
pushmethod provided by
useRouter For example: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>import { useRouter } from &#39;vue-router&#39;
const {push} = useRouter()
push({
path: &#39;/user&#39;,
params: { id: 10010 }
})
// 或者
let id = 10010
push(&#39;/user/&#39; + id)</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div> You can obtain the routing address through the useRoute hook. The usage is consistent with
. Match all routes
VueRouter’s dynamic routing allows us to match routes that are not matched. The sample code is as follows: {
path: '/:pathMatch(.*)',
component: () => import('./components/Page404.vue'),
},Copy after loginThe current route If the match is unsuccessful, this route will be matched.
Routing nesting{
path: '/:pathMatch(.*)',
component: () => import('./components/Page404.vue'),
},Now we have a requirement, which is to store two components under the HelloWorld component and need to switch between the two components.
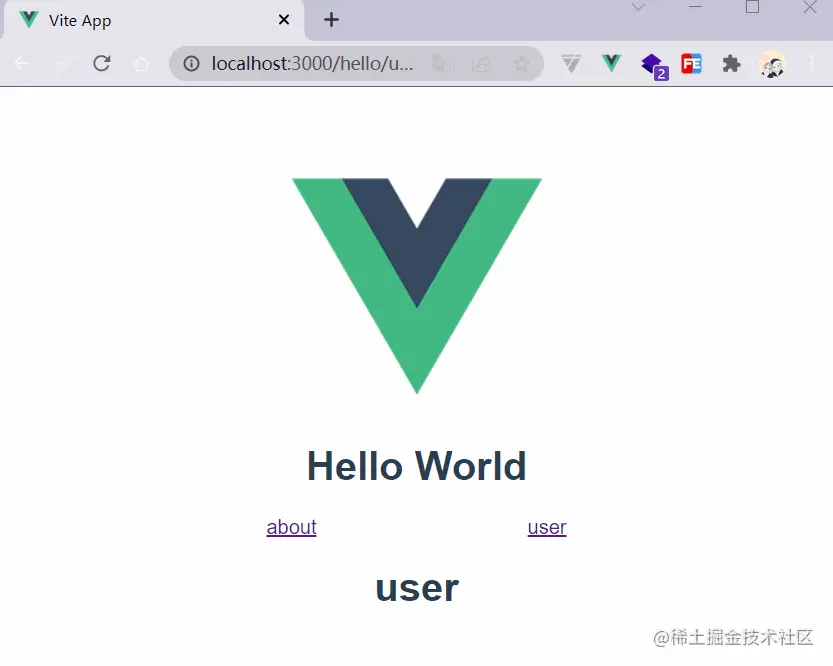
这个时候路由嵌套的就发挥作用了,其实路由嵌套比较简单,就是通过路由配置中的一个children属性来实现,示例代码如下:
HelloWorld.vue
<template>
<h1 id="Hello-nbsp-World">Hello World</h1>
<div
style="
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
width: 240px;
margin: 0 auto;
"
>
<router-link to="about">about</router-link>
<router-link to="user">user</router-link>
</div>
<router-view></router-view>
</template>router.js
{
path: '/hello',
// 路由懒加载引入组件
component: () => import('./components/HelloWorld.vue'),
children: [
{
path: 'about',
component: () => import('./components/about.vue'),
},
{
path: 'user',
component: () => import('./components/user.vue'),
},
],
},子组件比较简单,只有一个<h1></h1>标签,最终效果如下:
写在最后
这篇文章到这就结束了,总的来说比较简单没有什么太深入的东西,比较适合入门。
The above is the detailed content of How to use VueRouter4.x? Quick start guide. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js is suitable for small and medium-sized projects and fast iterations, while React is suitable for large and complex applications. 1) Vue.js is easy to use and is suitable for situations where the team is insufficient or the project scale is small. 2) React has a richer ecosystem and is suitable for projects with high performance and complex functional needs.
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.




