SpringCloud Tencent complete solution one
What is Spring Cloud Tencent?
Spring Cloud Tencent is Tencent’s open source one-stop microservice solution. Spring Cloud Tencent implements the Spring Cloud standard microservice SPI. Developers can quickly develop Spring Cloud microservice architecture applications based on Spring Cloud Tencent. The core of Spring Cloud Tencent relies on Tencent's open source one-stop service discovery and governance platform Polarismesh to implement various distributed microservice scenarios.
The capabilities provided by Spring Cloud Tencent include but are not limited to:

Project address:https://github. com/Tencent/spring-cloud-tencent
Project source code address
https://github.com/lltx/spring-cloud-tencent-demo
1. Install Polaris
Polaris is Tencent’s open source service discovery and governance center dedicated to solving service visibility, fault tolerance, flow control and security issues in distributed or microservice architectures. Although "there are already some components in the industry that can solve some of these problems", there is a lack of a standard, multi-language, framework-independent implementation.
Tencent has a large number of distributed services, coupled with the diversity of business lines and technology stacks, it has accumulated dozens of related components, large and small. Starting in 2019, we have abstracted and integrated these components through Polaris to create a unified service discovery and governance solution for the company to help the business improve R&D efficiency and operational quality.
Polaris installation is very simple. Download the zip of the response platform and run it directly,Download address:https://github.com/polarismesh/polaris/releases/tag/v1 .9.0
2. Service registration and discovery
Service adds polaris-discovery dependency
<dependency> <groupId>com.tencent.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-tencent-polaris-discovery</artifactId> </dependency>
application.yaml Connect to polaris server
spring: cloud: polaris: address: grpc://127.0.0.1:8091
Start service observation polaris console

Service call example
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/consumer")
public String consumer() {
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://lengleng-tencent-discovery-provider/provider/lengleng", String.class);
}3. Configuration management
During the Bootstrap phase of application startup, Spring Cloud will call PolarisConfigFileLocator to obtain the configuration file from the Polaris server and load it into the Spring context. Configuration content can be obtained through Spring Boot's standard @Value,@ConfigurationProperties annotation. Dynamic configuration refresh capability is implemented through Spring Cloud's standard @RefreshScope mechanism.
Service adds polaris-config dependency
<dependency> <groupId>com.tencent.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-tencent-polaris-config</artifactId> </dependency>
bootstrap.yaml access polaris-config
spring:
cloud:
polaris:
address: grpc://127.0.0.1:8081
config:
groups:
- name: ${spring.application.name}
files: "application"Special note: This needs to be configured in bootstrap, spring-cloud-tencent is not adapted to the latest file loading mechanism of spring boot
Polaris console added configuration

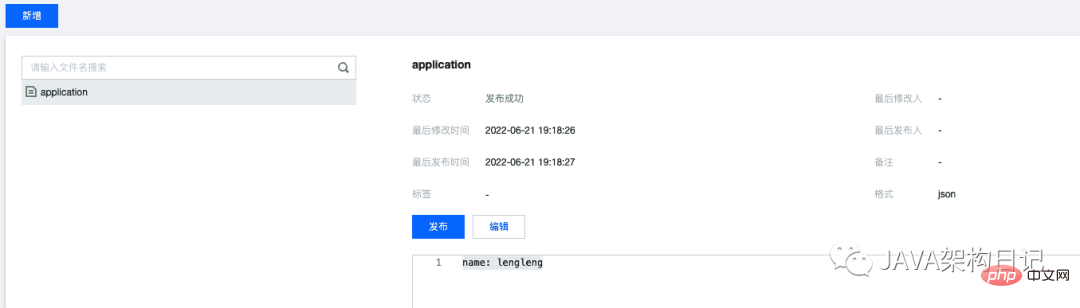
- ##Code usage configuration
@Value("${name:}")
private String name;Service current limiting is one of the most common service self-protection measures to prevent traffic peaks from overwhelming the service . The Spring Cloud Tencent Rate Limit module has built-in current limiting Filter for Spring Web and Spring WebFlux scenarios, combined with the current limiting function of Polaris to help businesses quickly access the current limiting capability.
- Service adds polaris-ratelimit dependency,Add discovery when using the current limiting component to facilitate editing of the service list
<dependency> <groupId>com.tencent.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-tencent-polaris-discovery</artifactId> </dependency>com.tencent.cloud spring-cloud-starter-tencent-polaris-ratelimit
- Service access polaris-ratelimit
spring: cloud: polaris: address: grpc://127.0.0.1:8091 namespace: default ratelimit: reject-http-code: 403 reject-request-tips: "lengleng test rate limit"
- Polaris console adds current limiting rules
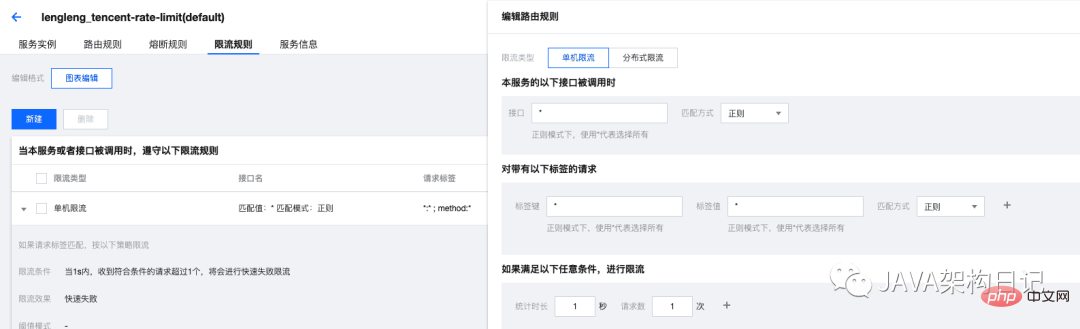
polaris can implement more routing forms than metadata routing, nearest routing, rule routing, custom routing, etc.,This article Demonstration of metadata routing,As shown below, only services with the same metadata information will be routed

- service adds polaris-router Dependencies
<dependency> <groupId>com.tencent.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-tencent-polaris-router</artifactId> </dependency>
- Service mark metadata
spring: cloud: polaris: address: grpc://127.0.0.1:8091 tencent: metadata: content: version: local
六、限流熔断
故障实例熔断是常见的一种容错保护机制。故障实例熔断能实现主调方迅速自动屏蔽错误率高或故障的服务实例,并启动定时任务对熔断实例进行探活。在达到恢复条件后对其进行半开恢复。在半开恢复后,释放少量请求去进行真实业务探测。并根据真实业务探测结果去判断是否完全恢复正常。
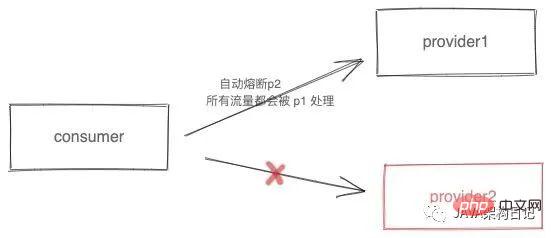
添加限流熔断相关的依赖 polaris-circuitbreaker
com.tencent.cloud spring-cloud-starter-tencent-polaris-circuitbreaker <dependency> <groupId>com.tencent.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-tencent-polaris-discovery</artifactId> </dependency> org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-circuitbreaker-spring-retry org.springframework.cloud spring-cloud-starter-openfeign
提供 Feign 服务调用实现
spring-cloud-tencent 当前版本仅支持 feign 熔断
@FeignClient(contextId = "demoFeign", value = "lengleng-circuitbreaker-tencent-circuitbreaker-provider",
fallback = DemoFeignFallback.class)
public interface DemoFeign {
@GetMapping("/provider")
String get(@RequestParam String name);
}服务接入 polaris-circuitbreaker
spring: cloud: polaris: address: grpc://127.0.0.1:8091 #开启断路器 feign: circuitbreaker: enabled: true
编写熔断规则 polaris.yml
consumer: circuitBreaker: checkPeriod: 100ms chain: - errorCount - errorRate plugin: errorCount: continuousErrorThreshold: 1 metricNumBuckets: 1 errorRate: errorRateThreshold: 100 metricStatTimeWindow: 1s requestVolumeThreshold: 1
The above is the detailed content of SpringCloud Tencent complete solution one. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 PHP Frameworks and Microservices: Cloud Native Deployment and Containerization
Jun 04, 2024 pm 12:48 PM
PHP Frameworks and Microservices: Cloud Native Deployment and Containerization
Jun 04, 2024 pm 12:48 PM
Benefits of combining PHP framework with microservices: Scalability: Easily extend the application, add new features or handle more load. Flexibility: Microservices are deployed and maintained independently, making it easier to make changes and updates. High availability: The failure of one microservice does not affect other parts, ensuring higher availability. Practical case: Deploying microservices using Laravel and Kubernetes Steps: Create a Laravel project. Define microservice controllers. Create Dockerfile. Create a Kubernetes manifest. Deploy microservices. Test microservices.
 How does the Java framework support horizontal scaling of microservices?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
How does the Java framework support horizontal scaling of microservices?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
The Java framework supports horizontal expansion of microservices. Specific methods include: Spring Cloud provides Ribbon and Feign for server-side and client-side load balancing. NetflixOSS provides Eureka and Zuul to implement service discovery, load balancing and failover. Kubernetes simplifies horizontal scaling with autoscaling, health checks, and automatic restarts.
 Create distributed systems using the Golang microservices framework
Jun 05, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Create distributed systems using the Golang microservices framework
Jun 05, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Create a distributed system using the Golang microservices framework: Install Golang, choose a microservices framework (such as Gin), create a Gin microservice, add endpoints to deploy the microservice, build and run the application, create an order and inventory microservice, use the endpoint to process orders and inventory Use messaging systems such as Kafka to connect microservices Use the sarama library to produce and consume order information
 What role does Spring Boot play in microservices architecture?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 02:34 PM
What role does Spring Boot play in microservices architecture?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 02:34 PM
SpringBoot plays a crucial role in simplifying development and deployment in microservice architecture: providing annotation-based automatic configuration and handling common configuration tasks, such as database connections. Support verification of API contracts through contract testing, reducing destructive changes between services. Has production-ready features such as metric collection, monitoring, and health checks to facilitate managing microservices in production environments.
 Java framework's microservice architecture data consistency guarantee
Jun 02, 2024 am 10:00 AM
Java framework's microservice architecture data consistency guarantee
Jun 02, 2024 am 10:00 AM
Data consistency guarantee in microservice architecture faces the challenges of distributed transactions, eventual consistency and lost updates. Strategies include: 1. Distributed transaction management, coordinating cross-service transactions; 2. Eventual consistency, allowing independent updates and synchronization through message queues; 3. Data version control, using optimistic locking to check for concurrent updates.
 What are the challenges in building a microservices architecture using Java frameworks?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 03:22 PM
What are the challenges in building a microservices architecture using Java frameworks?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 03:22 PM
Building a microservice architecture using a Java framework involves the following challenges: Inter-service communication: Choose an appropriate communication mechanism such as REST API, HTTP, gRPC or message queue. Distributed data management: Maintain data consistency and avoid distributed transactions. Service discovery and registration: Integrate mechanisms such as SpringCloudEureka or HashiCorpConsul. Configuration management: Use SpringCloudConfigServer or HashiCorpVault to centrally manage configurations. Monitoring and observability: Integrate Prometheus and Grafana for indicator monitoring, and use SpringBootActuator to provide operational indicators.
 Microservice architecture monitoring and alarming in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
Microservice architecture monitoring and alarming in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
Microservice architecture monitoring and alarming in the Java framework In the microservice architecture, monitoring and alarming are crucial to ensuring system health and reliable operation. This article will introduce how to use Java framework to implement monitoring and alarming of microservice architecture. Practical case: Use SpringBoot+Prometheus+Alertmanager1. Integrate Prometheus@ConfigurationpublicclassPrometheusConfig{@BeanpublicSpringBootMetricsCollectorspringBootMetric
 PHP framework and microservices: data consistency and transaction management
Jun 02, 2024 pm 04:59 PM
PHP framework and microservices: data consistency and transaction management
Jun 02, 2024 pm 04:59 PM
In PHP microservice architecture, data consistency and transaction management are crucial. The PHP framework provides mechanisms to implement these requirements: use transaction classes, such as DB::transaction in Laravel, to define transaction boundaries. Use an ORM framework, such as Doctrine, to provide atomic operations such as the lock() method to prevent concurrency errors. For distributed transactions, consider using a distributed transaction manager such as Saga or 2PC. For example, transactions are used in online store scenarios to ensure data consistency when adding to a shopping cart. Through these mechanisms, the PHP framework effectively manages transactions and data consistency, improving application robustness.




