
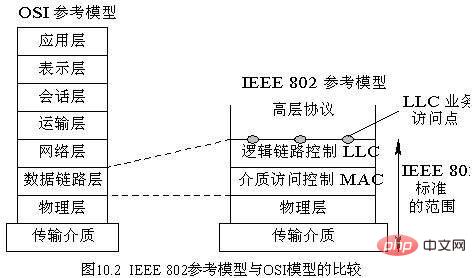
The ieee802 standard divides the LAN hierarchical model into three layers: 1. Physical layer (PHY), which mainly processes the bit stream transmitted on the physical link, realizes the transmission and reception of the bit stream, and the generation and synchronization preamble. Delete; 2. Media Access Control (MAC), responsible for the implementation of the media access control mechanism, that is, to deal with the contention problem of each station in the LAN for the shared communication medium; 3. Logical Link Control (LLC), responsible for shielding the MAC sublayer Different implementations are turned into a unified LLC interface to provide consistent services to the network layer.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
According to the IEEE802 standard, the LAN architecture is divided into three layers, namely the physical layer (PHY, Physical), the media link control layer (MAC, MediaAccessControl), and the logical link control layer (LLC, LogicalLinkControl). Actually two layers, the standard splits the data link layer into the more specific media link control layer and logical link control layer.
1. Physical layer (PHY)
The physical layer in the LAN has the same function as the physical layer in the computer network OSI reference model. It mainly handles transmission on the physical link. The bit stream implements the transmission and reception of bit streams, the generation and deletion of synchronization preambles; establishes, maintains, and cancels physical connections, and handles mechanical, electrical, and process characteristics.
2. Media Access Control (MAC)
Sublayer The MAC sublayer is responsible for the implementation of the media access control mechanism, that is, it handles the control of shared communication media by each site in the LAN. Contention issues, different types of LANs usually use different media access control protocols, and the MAC sublayer also involves physical addressing in the LAN.
3. Logical Link Control (LLC)
The LLC sublayer is responsible for shielding different implementations of the MAC sublayer and turning them into a unified LLC interface, thereby providing The network layer provides consistent services.
LLC provides data link layer services defined in the OSI/RM model, which enables upper-layer protocols to run on top of LAN standards. MAC solves the problem of how to allocate the right to use the channel when there is competition for the use of the sensitive word channel in the local area network.
Explanation:
The LLC sublayer and MAC sublayer in the LAN architecture jointly complete functions similar to the data link layer in the OSI reference model, forming data into Frames are transmitted, and sequence control, error control and flow control of data frames are performed to turn unreliable links into reliable links.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What does the ieee802 standard divide the local area network hierarchical model into. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What is LAN
What is LAN
 What is LAN
What is LAN
 What are the characteristics of LAN
What are the characteristics of LAN
 How to connect to LAN
How to connect to LAN
 How to establish a local area network in xp
How to establish a local area network in xp
 Why is there no sound in Tencent meetings?
Why is there no sound in Tencent meetings?
 How to write mysql check constraints
How to write mysql check constraints
 How to make charts and data analysis charts in PPT
How to make charts and data analysis charts in PPT
 The most prominent features of computer networks
The most prominent features of computer networks