Which one has higher priority, v-if or v-for in vue?
In vue2, v-for has a higher priority than v-if; in vue3, v-if has a higher priority than v-for. In Vue, never use v-if and v-for on the same element at the same time, which will cause a waste of performance (each rendering will loop first and then perform conditional judgment); if you want to avoid this situation, Templates can be nested in the outer layer (page rendering does not generate DOM nodes), v-if judgment is performed at this layer, and then v-for loop is performed internally.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, vue3 version, DELL G3 computer. The
v-if directive is used to conditionally render a piece of content. Directives are used to conditionally render a block of content. This content will only be rendered if the directive's expression returns true. The v-for directive renders a list based on an array. The v-for directive requires special syntax in the form of item in items, where items is the source data array or object, and item is Is an alias for the array element being iterated.
When v-for, it is recommended to set the key value and ensure that each key value is unique, this is diffAlgorithm optimization.
<modal></modal>
Priority
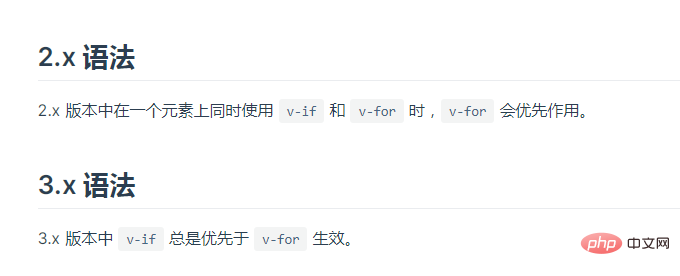
In fact, the answers in vue2 and vue3 are completely opposite.
In vue2, v-for has a higher priority than v-if
In vue3, v-if has a higher priority In v-for
## v-for and v-if
in vue2 v-if and v-for are both directives in the vue template system.
vue template is compiled, the command system will be converted into an executable render function.
p tag and use v-if and v-for
<div>
<p>
{{ item.title }}
</p>
</div>vue Example, store isShow and items data.
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
items: [
{ title: "foo" },
{ title: "baz" }]
}
},
computed: {
isShow() {
return this.items && this.items.length > 0
}
}
})ƒ anonymous() {
with (this) { return
_c('div', { attrs: { "id": "app" } },
_l((items), function (item)
{ return (isShow) ? _c('p', [_v("\n" + _s(item.title) + "\n")]) : _e() }), 0) }
}_l is the list rendering function of vue, and a if judgment will be made inside the function. Preliminary conclusion:
v-for has a higher priority than v-if. Then put
v-for and v-if in different labels
<div>
<template>
<p>{{item.title}}</p>
</template>
</div>render function
ƒ anonymous() {
with(this){return
_c('div',{attrs:{"id":"app"}},
[(isShow)?[_v("\n"),
_l((items),function(item){return _c('p',[_v(_s(item.title))])})]:_e()],2)}
}v-for and v-if act on different tags, they are judged first and then the list is rendered.
export function genElement (el: ASTElement, state: CodegenState): string {
if (el.parent) {
el.pre = el.pre || el.parent.pre
}
if (el.staticRoot && !el.staticProcessed) {
return genStatic(el, state)
} else if (el.once && !el.onceProcessed) {
return genOnce(el, state)
} else if (el.for && !el.forProcessed) {
return genFor(el, state)
} else if (el.if && !el.ifProcessed) {
return genIf(el, state)
} else if (el.tag === 'template' && !el.slotTarget && !state.pre) {
return genChildren(el, state) || 'void 0'
} else if (el.tag === 'slot') {
return genSlot(el, state)
} else {
// component or element
...
}if judgment, v-for is judged before v-if.
v-for has a higher priority than v-if.
v-for and v-if in vue3
In vue3, v-if has a higher priority than v-fo, so when v-if is executed , the variable it calls does not exist yet, it will cause an exceptionExplanation: There are usually two situations that cause us to do this:
1. In order to filter the list Projects, such as:v-for="user in users" v-if="user.isActive"
- In vue2, put them together. It can be seen from the output rendering function that the loop will be executed first and then the conditions will be judged, even if we only render a small part of the list elements, you have to traverse the entire list every time you re-render, which will be wasteful
- In vue3, v-if has a higher priority than v-fo, so when v-if is executed, it calls The variable does not exist yet, it will cause an exception
activeUsers) and let it return the filtered list (such as users.filter(u=>u.isActive)).
v-for="user in users" v-if="shouldShowUsers"
- Similarly, in vue2, put them together, and it can be seen from the output rendering function that it will be executed first Loop and then judge the conditions. Even if we only render a small part of the elements in the list, we have to traverse the entire list every time we re-render, which will be wasteful.
- In vue3, writing this way will not report an error. , but the official still does not recommend doing this outside
v-if to the container element (such as ul, ol) or wrap a layer of template on the outside.
Note
Never use v-if and v-for on the same element at the same time, which will cause a waste of performance (Each rendering will loop first and then perform conditional judgment)- If you want to avoid this situation, nest the template in the outer layer (page rendering does not generate dom nodes), in this layer Make v-if judgment, and then perform v-for loop internally
<template v-if="isShow">
<p v-for="item in items">
</template>- If the condition appears inside the loop, you can filter out those that are not in advance through the calculated attribute Items to be displayed
computed: {
items: function() {
return this.list.filter(function (item) {
return item.isShow
})
}
}The above is the detailed content of Which one has higher priority, v-if or v-for in vue?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js is suitable for small and medium-sized projects and fast iterations, while React is suitable for large and complex applications. 1) Vue.js is easy to use and is suitable for situations where the team is insufficient or the project scale is small. 2) React has a richer ecosystem and is suitable for projects with high performance and complex functional needs.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 Vue realizes marquee/text scrolling effect
Apr 07, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
Vue realizes marquee/text scrolling effect
Apr 07, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
Implement marquee/text scrolling effects in Vue, using CSS animations or third-party libraries. This article introduces how to use CSS animation: create scroll text and wrap text with <div>. Define CSS animations and set overflow: hidden, width, and animation. Define keyframes, set transform: translateX() at the beginning and end of the animation. Adjust animation properties such as duration, scroll speed, and direction.
 How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
You can query the Vue version by using Vue Devtools to view the Vue tab in the browser's console. Use npm to run the "npm list -g vue" command. Find the Vue item in the "dependencies" object of the package.json file. For Vue CLI projects, run the "vue --version" command. Check the version information in the <script> tag in the HTML file that refers to the Vue file.




