Can docker install cuda?
cuda can be installed in docker; upload the downloaded software package to the specified directory and execute "sudo sh cuda_downloaded version_linux.run" to install it. cuda is the operation exited by the graphics card manufacturer NVIDIA Platform, after the installation is complete, you can use "nvidia-smi" to view the installed cuda version.

The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, docker version 19.03, Dell G3 computer.
docker can install cuda
CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a computing platform launched by graphics card manufacturer NVIDIA. CUDA is a general-purpose parallel computing architecture introduced by NVIDIA that enables GPUs to solve complex computing problems. It includes the CUDA instruction set architecture (ISA) and the parallel computing engine inside the GPU. Developers can use C language to write programs for the CUDA™ architecture, and the written programs can run at ultra-high performance on CUDA™-enabled processors. CUDA3.0 has begun to support C and FORTRAN.
The example is as follows:
Installing cuda under docker_Ubuntu16.04
(1) Download the installation file. First go to NVIDIA official website to download the cuda installation package: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit-archive
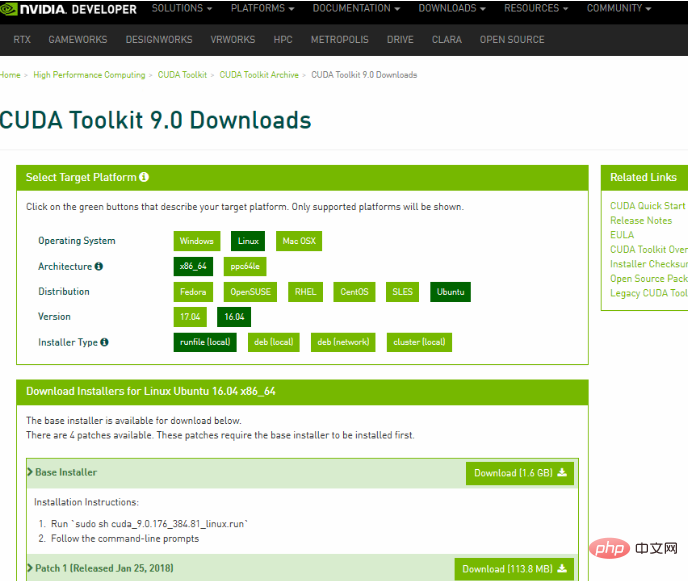
(2) Update the system driver
System Settings - Software and Updates - Additional Drivers - Update nvidia and intel
If there is a problem of looping into the system when updating the driver, please uninstall the driver first, and then use the installation method with the driver to solve the problem (panacea ).
How to uninstall the driver at this time: Since the graphical user interface (GUI) cannot be entered after logging in, we can enter the text user interface (TUI). In the login interface state, press Ctrl Alt f1 to enter the TUI Execute
sudo /usr/bin/nvidia-uninstall
and then restart
sudo reboot
(3) cuda installation
After uploading the downloaded software package to the directory you defined, execute the following command
sudo sh cuda_9.0.176_384.81_linux.run
Then Use the corner of a book to hold down the Enter key until the Terms of Service display reaches 100%. Then follow the steps below to select
Accept
n (Do not install the driver)
y
y
- failed--compilation aborted at ./cuda-installer.pl line 5
sudo apt install freeglut3-dev build-essential libx11-dev libxmu-dev libxi-dev libgl1-mesa-glx libglu1-mesa libglu1-mesa-dev libglfw3-dev libgles2-mesa-dev
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/cuda-9.0/lib64 export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/cuda-9.0/bin export CUDA_HOME=$CUDA_HOME:/usr/local/cuda-9.0
然后在终端运行: cat /usr/local/cuda/version.txt
docker Video Tutorial
»The above is the detailed content of Can docker install cuda?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Docker process viewing method: 1. Docker CLI command: docker ps; 2. Systemd CLI command: systemctl status docker; 3. Docker Compose CLI command: docker-compose ps; 4. Process Explorer (Windows); 5. /proc directory (Linux).
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Steps to create a Docker image: Write a Dockerfile that contains the build instructions. Build the image in the terminal, using the docker build command. Tag the image and assign names and tags using the docker tag command.
 What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Troubleshooting steps for failed Docker image build: Check Dockerfile syntax and dependency version. Check if the build context contains the required source code and dependencies. View the build log for error details. Use the --target option to build a hierarchical phase to identify failure points. Make sure to use the latest version of Docker engine. Build the image with --t [image-name]:debug mode to debug the problem. Check disk space and make sure it is sufficient. Disable SELinux to prevent interference with the build process. Ask community platforms for help, provide Dockerfiles and build log descriptions for more specific suggestions.




