
This article brings you relevant knowledge about javascript, mainly introducing the JavaScript tree structure depth-first algorithm. The tree structure can be said to be one of the most common data structures in the front-end, for example Let’s take a look at DOM tree, cascade selection, and tree components. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

[Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end]
In real life, I believe everyone is familiar with trees, whether they are willows, poplars or peach trees. It can be said that trees can be seen everywhere in our lives; in the computer world, trees are a kind of layering The abstract model of the structure ,
is shown in the figure below:
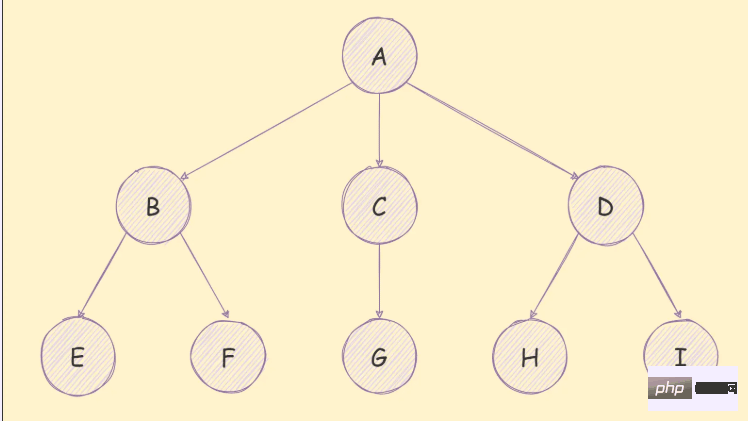
There are many applications of tree structure, For example, the organizational structure of a company can be represented by a tree, as shown below:
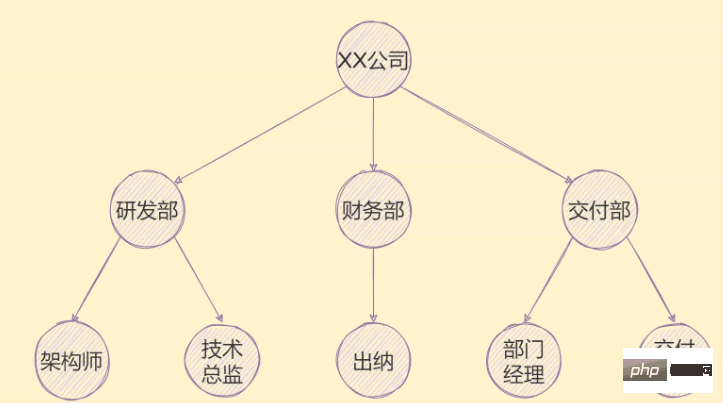
In addition to the organizational structure, tree structures such as genealogy, provinces and cities can also be used To represent.
There are many terms for trees, as shown below:
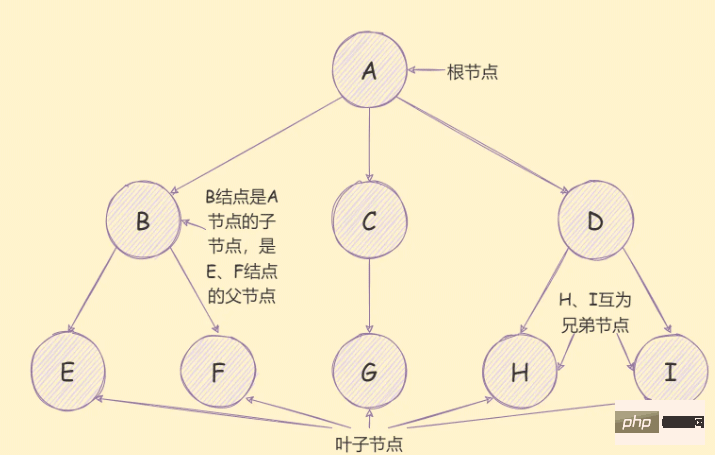
n=0, it is called an empty tree; A D H; The tree structure can be said to be one of the most common data structures in the front-end, such as DOM tree, cascading selection, tree component, etc.;
JavaScript does not provide a tree data structure, but we can simulate a tree through objects and arrays,
For example, the following code:
const tree = {
value: 'A',
children: [
{
value: 'B',
children: [
{ value: 'E', children: null },
{ value: 'F', children: null },
],
},
{
value: 'C',
children: [{ value: 'G', children: null }],
},
{
value: 'D',
children: [
{ value: 'H', children: null },
{ value: 'I', children: null },
],
},
],
}The so-called depth-first traversal algorithm is to search the branches of the tree as deeply as possible. Its traversal sequence is as follows :
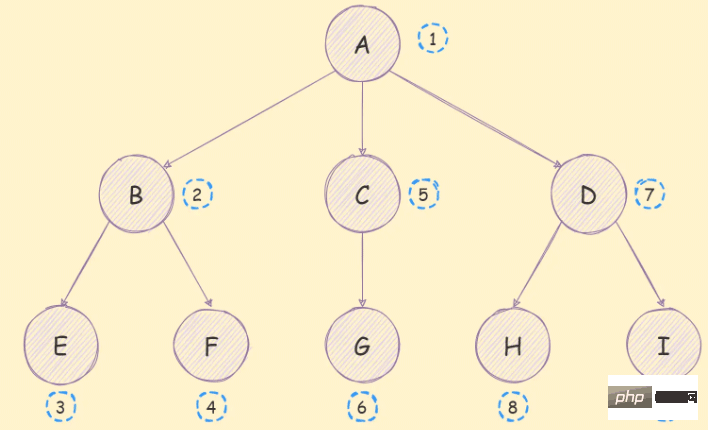
The implementation idea is as follows:
children of the node continues to perform depth-first traversal (recursive); The implementation code is as follows:
function dfs(root) {
console.log(root.value)
root.children && root.children.forEach(dfs) // 与下面一致
// if (root.children) {
// root.children.forEach(child => {
// dfs(child)
// })
// }
}
dfs(tree) // 这个tree就是前面定义的那个树
/* 结果
A
B
E
F
C
G
D
H
I
*/As you can see, and the figure The order in is consistent, which means there is no problem with our algorithm.
The so-called breadth priority is to visit the nodes closest to the root node in sequence. Its traversal sequence is as follows:
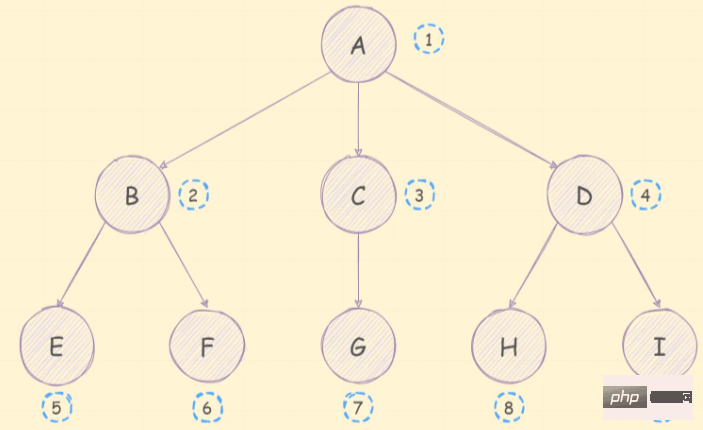
The implementation ideas are as follows:
children at the head of the queue into the queue in turn; The implementation code is as follows:
function bfs(root) {
// 1. 新建队列 跟节点入队
const q = [root]
// 4 重复执行
while (q.length > 0) {
const node = q.shift() // 2 队头出队
console.log(node.value)
// 3 队头 children 依次入队
node.children &&
node.children.forEach(child => {
q.push(child)
})
}
}
bfs(tree)
/* 结果
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
*/As you can see, it is consistent with the order in the picture, which means there is no problem with our algorithm.
【Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end】
The above is the detailed content of Master the JavaScript tree structure depth-first algorithm in one article. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!