 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Detailed introduction to JavaScript binary trees and various traversal algorithms
Detailed introduction to JavaScript binary trees and various traversal algorithms
Detailed introduction to JavaScript binary trees and various traversal algorithms
This article brings you relevant knowledge about javascript. It mainly introduces the details of JavaScript binary trees and various traversal algorithms. The article provides a detailed introduction around the topic, which has certain reference value. Friends who need it can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

[Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end】
What is a binary tree
A binary tree is a tree in which each node can only have at most two child nodes, as shown in the following figure:
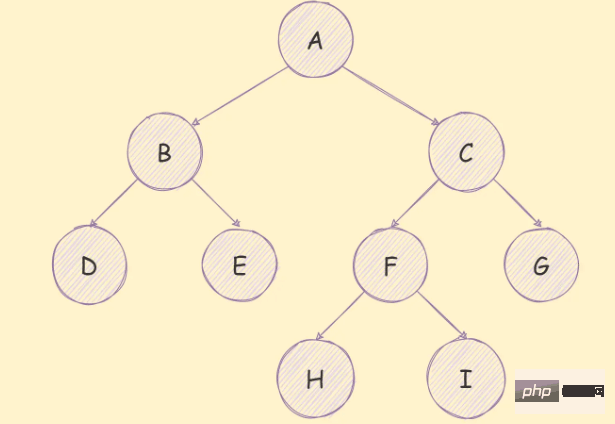
A binary tree has The following characteristics:
- There are only
2^(i-1)nodes at theilayer; - If the depth of this binary tree is
k, then the binary tree has at most2^k-1nodes; - In a non-empty binary tree, if Use
n0to represent the number of leaf nodes, andn2to be the number of non-leaf nodes with degree 2, then the two satisfy the relationshipn0 = n2 1.
Full Binary Tree
If in a binary tree, Except for the leaf nodes, each degree of the remaining nodes is 2, then the binary tree is a full binary tree,
As shown in the figure below:
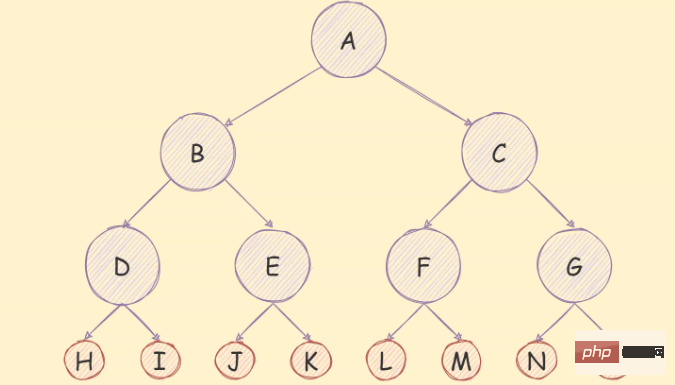
## In addition to satisfying the characteristics of ordinary binary trees, a full binary tree also has the following features: Characteristics:
- The
- n
th level of a full binary tree has2^(n-1)nodes;A full binary tree with a depth of - k
must have2^k-1nodes, and the number of leaf nodes is2^(k-1);The depth of a full binary tree with - n
nodes islog_2^(n 1).
If a binary tree is a full binary tree after removing the last layer, and the last node is distributed from left to right, then this A binary tree is a complete binary tree,
As shown in the figure below:
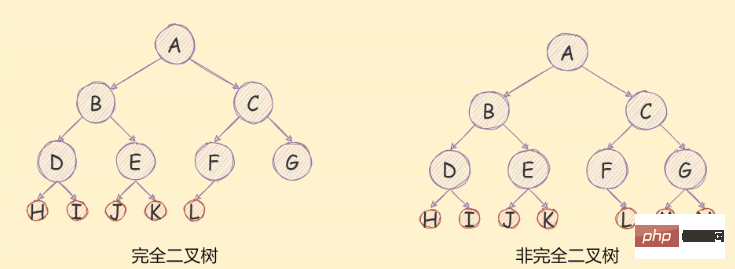
array storage, and the other is to use linked list storage.
Array storageUse arrays to store binary trees. If you encounter a complete binary tree, the storage order is from top to bottom, from left to right, as shown in the following figure:
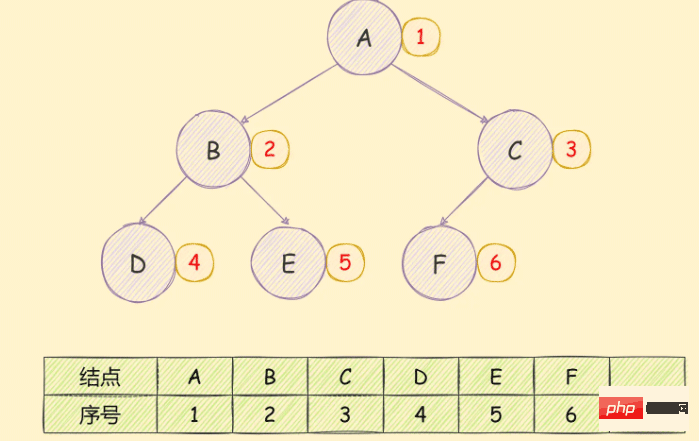
If it is a non-complete binary tree, as shown below:
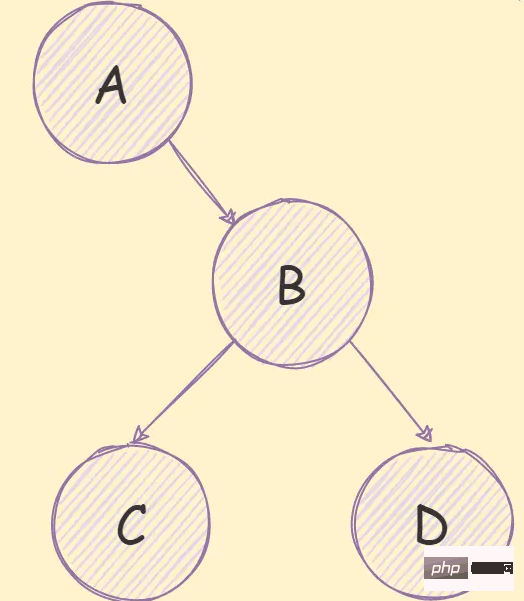
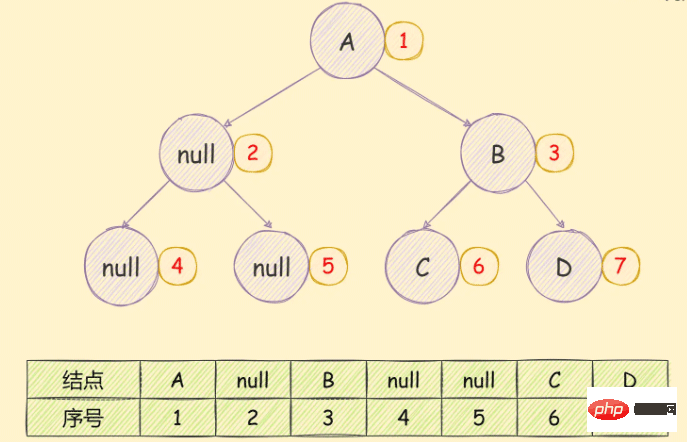 You can clearly see the waste of storage space.
You can clearly see the waste of storage space.
Linked list storage
Using linked list storage, the binary tree is usually divided into 3 parts, as shown below:

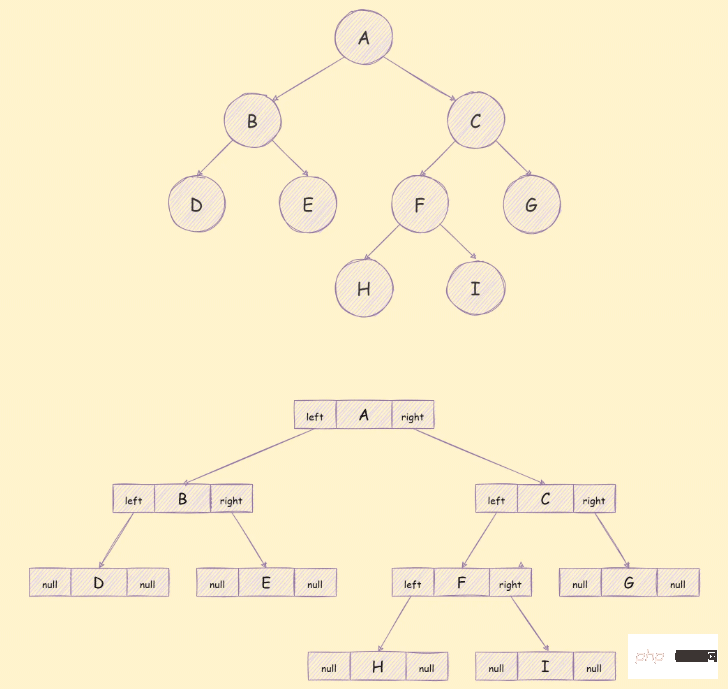 Algorithms related to binary trees
Algorithms related to binary trees
:// tree.js
const bt = {
val: 'A',
left: {
val: 'B',
left: { val: 'D', left: null, right: null },
right: { val: 'E', left: null, right: null },
},
right: {
val: 'C',
left: {
val: 'F',
left: { val: 'H', left: null, right: null },
right: { val: 'I', left: null, right: null },
},
right: { val: 'G', left: null, right: null },
},
}
module.exports = bt
visits the root node;
- visits the left
- of the root node.
To access the root noderight repeat the second and third steps
const bt = {
val: 'A',
left: {
val: 'B',
left: { val: 'D', left: null, right: null },
right: { val: 'E', left: null, right: null },
},
right: {
val: 'C',
left: {
val: 'F',
left: { val: 'H', left: null, right: null },
right: { val: 'I', left: null, right: null },
},
right: { val: 'G', left: null, right: null },
},
}
function dfs(root) {
if (!root) return
console.log(root.val)
root.left && dfs(root.left)
root.right && dfs(root.right)
}
dfs(bt)
/** 结果
A B D E C F H I G
*/
Create a queue and add the root node to the queue
- Exit the opponent Queue and access
- Add the left
- and
rightat the head of the queue to the queue in sequenceRepeat steps 2 and 3 until the queue is empty
function bfs(root) {
if (!root) return
const queue = [root]
while (queue.length) {
const node = queue.shift()
console.log(node.val)
node.left && queue.push(node.left)
node.right && queue.push(node.right)
}
}
bfs(bt)
/** 结果
A B C D E F G H I
*/
如下图所示: 递归方式实现如下: 迭代方式实现如下: 二叉树的中序遍历实现思想如下: 如下图所示: 递归方式实现如下: 迭代方式实现如下: 二叉树的后序遍历实现思想如下: 如下图所示: 递归方式实现如下: 迭代方式实现如下: 【相关推荐:javascript视频教程、web前端】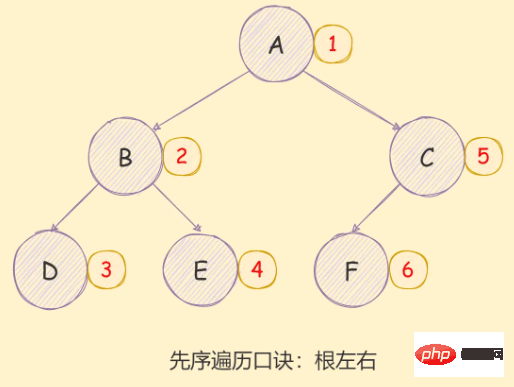
const bt = require('./tree')
function preorder(root) {
if (!root) return
console.log(root.val)
preorder(root.left)
preorder(root.right)
}
preorder(bt)
/** 结果
A B D E C F H I G
*/// 非递归版
function preorder(root) {
if (!root) return
// 定义一个栈,用于存储数据
const stack = [root]
while (stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop()
console.log(node.val)
/* 由于栈存在先入后出的特性,所以需要先入右子树才能保证先出左子树 */
node.right && stack.push(node.right)
node.left && stack.push(node.left)
}
}
preorder(bt)
/** 结果
A B D E C F H I G
*/中序遍历
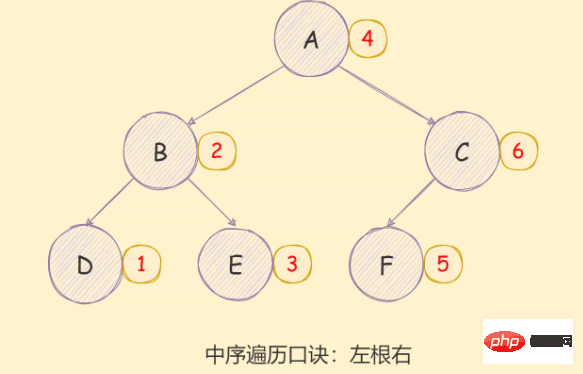
const bt = require('./tree')
// 递归版
function inorder(root) {
if (!root) return
inorder(root.left)
console.log(root.val)
inorder(root.right)
}
inorder(bt)
/** 结果
D B E A H F I C G
*/// 非递归版
function inorder(root) {
if (!root) return
const stack = []
// 定义一个指针
let p = root
// 如果栈中有数据或者p不是null,则继续遍历
while (stack.length || p) {
// 如果p存在则一致将p入栈并移动指针
while (p) {
// 将 p 入栈,并以移动指针
stack.push(p)
p = p.left
}
const node = stack.pop()
console.log(node.val)
p = node.right
}
}
inorder(bt)
/** 结果
D B E A H F I C G
*/后序遍历
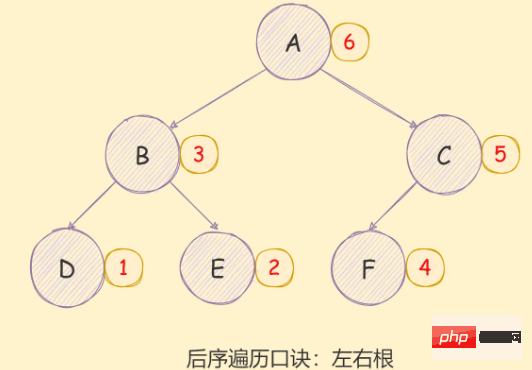
const bt = require('./tree')
// 递归版
function postorder(root) {
if (!root) return
postorder(root.left)
postorder(root.right)
console.log(root.val)
}
postorder(bt)
/** 结果
D E B H I F G C A
*/// 非递归版
function postorder(root) {
if (!root) return
const outputStack = []
const stack = [root]
while (stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop()
outputStack.push(node)
// 这里先入left需要保证left后出,在stack中后出,就是在outputStack栈中先出
node.left && stack.push(node.left)
node.right && stack.push(node.right)
}
while (outputStack.length) {
const node = outputStack.pop()
console.log(node.val)
}
}
postorder(bt)
/** 结果
D E B H I F G C A
*/
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to JavaScript binary trees and various traversal algorithms. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript is a programming language widely used in web development, while WebSocket is a network protocol used for real-time communication. Combining the powerful functions of the two, we can create an efficient real-time image processing system. This article will introduce how to implement this system using JavaScript and WebSocket, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to clarify the requirements and goals of the real-time image processing system. Suppose we have a camera device that can collect real-time image data



