JavaScript dictionaries and collections (summary sharing)
This article brings you relevant knowledge about javascript, mainly introducing the detailed explanation of JavaScript dictionaries and collections. A collection is composed of a group of unordered and non-repeating elements. We can think of a set as a special kind of array. Its special feature is that it is unordered and non-repeating, which means that we cannot access it through subscripts, and there will be no duplicate elements in the set.

[Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end]
Dictionary
What is a dictionary
When it comes to dictionaries, the first thing that comes to mind is the Xinhua Dictionary. In fact, it is similar to the dictionary in programming. Both There is a characteristic that corresponds to one-to-one (yi yi dui ying), or maps .
Dictionaries are usually stored in **[key, value]** pairs. Because they are stored in the form of key-value pairs, it is more convenient to obtain value# through key
##For example, storing user information:
{
'username': '一碗周',
'age': 18
}Dictionary in JavaScript
In JavaScript, objects seem to have dictionaries All the features, butMap is added in ES6 to represent a dictionary. The map here is not translated into a map, but a mapping.
The sample code is as follows:
// 创建一个字典
const map = new Map()
// 往字典中存储信息
map.set('username', '一碗周')
map.set('age', 18)
console.log(map) // Map(2) { 'username' => '一碗周', 'age' => 18 }Valid brackets. The main idea of the question is to determine whether the brackets in the given string match. If they match, true will be returned, otherwise false will be returned. .
The problem-solving idea is as follows:
- Determine whether the length of the string is an even number. If it is not an even number, it will directly return
- false
, because of the parentheses They all appear in pairs;Create a new stack; Traverse the string, and when traversing each item, if it is a left bracket, push it onto the stack; if it is a right bracket, and Compare the top of the stack. If there is a match, pop the stack. If not, return - false
.
Our original solution:
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isValid = function(s) {
if (s.length % 2 !== 0) return false
const stack = []
for(let i = 0; i<s.length; i++) {
const c = s[i] // 记录当前项
if (c === '(' || c === '[' || c==='{') {
stack.push(c)
} else {
const t = stack[stack.length - 1] // 获取栈顶元素
if (
(t === '(' && c === ')') ||
(t === '[' && c === ']') ||
(t === '{' && c === '}')
) {
stack.pop()
} else {
return false
}
}
}
// 如果为0表示全部匹配,有剩余则表示不匹配
return stack.length === 0
};implementation code is as follows:
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isValid = function(s) {
// 1. 判断字符串的长度是否为偶数,不为偶数直接返回false,因为括号都是成对出现的;
if (s.length % 2 !== 0) return false
const stack = []
const map = new Map() // 将所有括号的对应关系存储在字典中
map.set('(', ')')
map.set('[', ']')
map.set('{', '}')
for(let i = 0; i<s.length; i++) {
const c = s[i] // 记录当前项
// 判断是否存在 key 也就是左括号,如果存储,将左括号存储在栈中
if (map.has(c)) {
stack.push(c)
} else {
const t = stack[stack.length - 1] // 获取栈顶元素
if (map.get(t) === c) { // 获取最后一个左括号,判断是否与右括号匹配
stack.pop() // 出栈
} else {
return false
}
}
}
// 如果为0表示全部匹配,有剩余则表示不匹配
return stack.length === 0
};if statement.
Set
What is a set
A set is a set ofunordered and non-repeating composed of elements. We can think of a set as a special array. Its special feature is that it is unordered and non-repeating, which means that we cannot access it through subscripts, and there will be no duplication in the set. Element;
Set in JS
provides the data structure of collection in JavaScript, that is,Set, in MDN The description is as follows:
Operations in the collectionSet
An object is a collection of values, and you can iterate over its elements in the order of insertion. The elements in the Set will onlyappear once, that is, the elements in the Set are unique.
There are mainly the following scene operations in the collection:
- Add elements to the collection;Delete an element in the set; Judge whether the element is in the set;Clear the set;Find intersection, union, and difference set;
Set object provides us with the corresponding method, The sample code is as follows:
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4, 5] // 利用set实现去重 const set = new Set(arr) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] // 往集合中添加元素 set.add(3) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] 添加失败,集合中不允许出现重复元素 set.add(6) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] // 判断元素是否在集合中 set.has(2) // true set.has(7) // false // 删除集合中的元素 set.delete(1) // [2, 3, 4, 5, 6] // 清空集合 set.clear()
- Union: For the given two sets, return a new set containing all elements in both sets
- Intersection:For the given two sets, return a new set containing the common elements in the two sets
- Difference set: For the given two sets, return a new set containing all elements that exist A new set of elements that are in the first set and do not exist in the second set
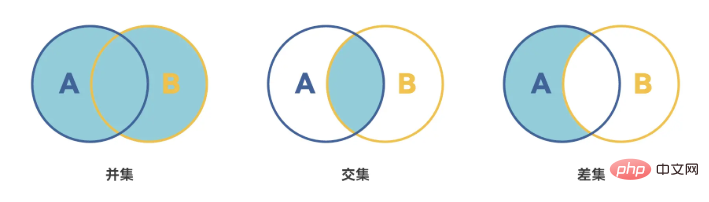
The encapsulated code is as follows:
// 求两个集合的并集
export function union(setA, setB) {
let _union = new Set(setA)
for (let elem of setB) {
_union.add(elem) // 因为集合中不存在重复元素
}
return _union
}
// 求两个集合的交集
export function intersection(setA, setB) {
let _intersection = new Set()
for (let elem of setB) {
if (setA.has(elem)) {
_intersection.add(elem)
}
}
return _intersection
}
// 求两个集合的差集
export function difference(setA, setB) {
let _difference = new Set(setA)
for (let elem of setB) {
_difference.delete(elem)
}
return _difference
}javascript video tutorial, web front-end】
The above is the detailed content of JavaScript dictionaries and collections (summary sharing). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service




