 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 CSS Tutorial
CSS Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of relative positioning of CSS positioning properties relative properties
Detailed explanation of relative positioning of CSS positioning properties relative properties
Detailed explanation of relative positioning of CSS positioning properties relative properties
This article brings you relevant knowledge about css, which mainly introduces issues related to relative positioning in CSS positioning attributes. Relative positioning is when the element moves. Relative to its original position, the element frame set to relative positioning will be offset by a certain distance. Let's take a look at it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

(Learning video sharing: css video tutorial, html video tutorial)
CSS positioning attribute Detailed explanation of relative positioning relative attribute
position:relative Detailed explanation of relative positioning
Relative positioning means that when an element moves, it is relative to its original position.
Characteristics of relative positioning:
-
It moves relative to its original position (when moving the position, the reference point is its original position)
The original position in the standard stream continues to be occupied, and the subsequent boxes still treat it as a standard stream (without going off the standard, continuing to retain the original position). Therefore, relative positioning is not out of standard. Its most typical application is for absolute positioning.
The element box set to relative positioning will be offset by a certain distance. The element retains its unpositioned shape and the space it originally occupied.
CSS Relative Positioning
Relative positioning is a very easy concept to master. If an element is positioned relatively, it will appear where it is. You can then move the element "relative to" its origin by setting a vertical or horizontal position.
If top is set to 20px, the box will be 20 pixels below the top of its original position. If left is set to 30 pixels, then 30 pixels of space will be created to the left of the element, which will move the element to the right.
#box_relative { position: relative; left: 30px; top: 20px; }As shown below:
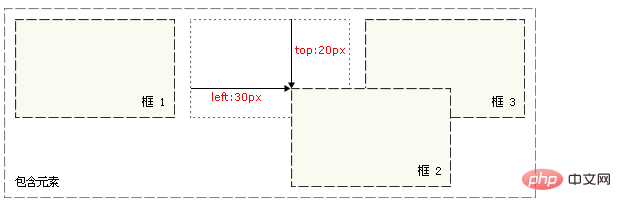
Note that when using relative positioning, the element still occupies the original space regardless of whether it is moved or not. Therefore, moving an element causes it to cover other boxes.
The example is as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<style type="text/css">
body{
margin:10px;
font-size:12px;
font-family:Arial;
}
.outside{
width:1000px;
height:600px;
background-color:#a9d6ff;
border:1px dashed black;
}
.inside{
padding:10px;
background-color:#fffcd3;
border:1px dashed black;
margin: 10px;
}
.inside1{
margin:10px;
padding: 10px;
background-color:#fffcd3;
border:1px dashed black;
/* 设置相对定位 ,相对点是当前div的原始位置的左上角*/
position: relative;
/* 距离div的原始位置的左边框 */
left:20px;
/* 距离div的原始位置的上边框 */
top:30px;
/*
right距离div的原始位置的右边框
bottom距离div的原始位置的下边框
*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outside">
<div class="inside">div1</div>
<div class="inside1">div2</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output result:

The impact of relative positioning on document flow
Code example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<style type="text/css">
body{
margin:10px;
font-size:12px;
font-family:Arial;
}
.outside{
width:1000px;
height:600px;
background-color:#a9d6ff;
border:1px dashed black;
}
.inside{
padding:10px;
background-color:#fffcd3;
border:1px dashed black;
margin: 10px;
position:relative;
left:30px;
top:30px;
/* div1相对定位脱离了文档流,
但是后续的div还会认为div1是在没有相对定位之前的状态
所有后续的div不会填补div1的空缺位置,而是继续按照文档流来排序
*/
}
.inside1{
margin:10px;
padding: 10px;
background-color:#fffcd3;
border:1px dashed black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outside">
<div class="inside">div1</div>
<div class="inside1">div2</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output result:

(Learning video sharing: css video tutorial, html Video tutorial)
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of relative positioning of CSS positioning properties relative properties. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
There are two ways to create a Bootstrap split line: using the tag, which creates a horizontal split line. Use the CSS border property to create custom style split lines.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
To adjust the size of elements in Bootstrap, you can use the dimension class, which includes: adjusting width: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust height: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-
 How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use the Bootstrap button? Introduce Bootstrap CSS to create button elements and add Bootstrap button class to add button text
 How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
To set up the Bootstrap framework, you need to follow these steps: 1. Reference the Bootstrap file via CDN; 2. Download and host the file on your own server; 3. Include the Bootstrap file in HTML; 4. Compile Sass/Less as needed; 5. Import a custom file (optional). Once setup is complete, you can use Bootstrap's grid systems, components, and styles to create responsive websites and applications.
 How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
There are several ways to insert images in Bootstrap: insert images directly, using the HTML img tag. With the Bootstrap image component, you can provide responsive images and more styles. Set the image size, use the img-fluid class to make the image adaptable. Set the border, using the img-bordered class. Set the rounded corners and use the img-rounded class. Set the shadow, use the shadow class. Resize and position the image, using CSS style. Using the background image, use the background-image CSS property.



