 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Summary of 7 commonly used iterative processing methods for arrays in JavaScript
Summary of 7 commonly used iterative processing methods for arrays in JavaScript
Summary of 7 commonly used iterative processing methods for arrays in JavaScript
This article brings you relevant knowledge about javascript, which mainly introduces the related issues about the 7 commonly used iterative processing methods of arrays in JavaScript. Let’s take a look at it together. I hope it will help Everyone is helpful.

[Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end】
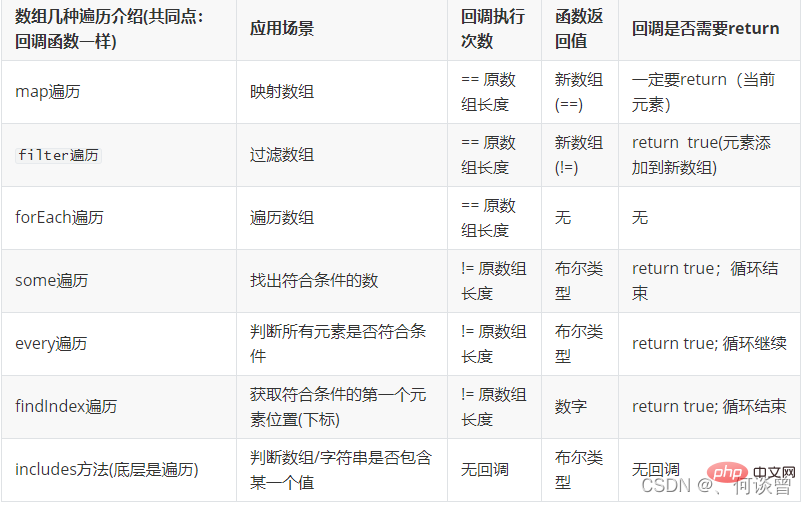
1.map() method
1.1 Application scenario: Use a certain rule to map a new array (traverse each element in the array, perform corresponding processing on each element, and return a new array)
For example :Change each element in the array to 1
let arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
//item数组每一项的值,index数组的下标
let newArr = arr.map((item, index) => {
return item + 1
})
console.log(newArr)//[11, 21, 31, 41, 51]1.2 Notes:
(1). The number of executions of the callback function is equal to the length of the array
(2).map function The length of the new array returned is equal to the length of the original array
(3). You must return in the callback function. What is returned is the value of the currently traversed element. If you do not return, each element of the new array will be undefined
2.forEach() method
2.1 Application scenario: used to traverse an array, equivalent to another way of writing a for loop
let arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
arr.forEach((item, index) => {
console.log(`下标为${index}的元素是${item}`)
})
//控制台打印结果
//下标为0的元素是10
//下标为1的元素是20
//下标为2的元素是30
//下标为3的元素是40
//下标为4的元素是502.2 Notes:
(1). The number of executions of the callback function is equal to the length of the array
(2). The forEach function has no return value
(3). The callback function does not need to return, even if it is returned manually, it will not Will end the loop
3.filter() method
3.1 Application scenario: Used to filter the elements in the array that meet the conditions and return the filtered new array
For example: find Get the even numbers in the array
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
let newArr = arr.filter((item, index) => {
//return一个布尔值
return item % 2 == 0
})
console.log(newArr)//[2,4,6,8]3.2 Notes:
(1). The number of executions of the callback function is equal to the length of the array
(2).The new array returned by the filter function The length is not equal to the length of the original array
(3). The callback function must return a Boolean value. If the return value is true, the currently traversed element will be added to the new array. If the return value is false, , it will not be added to the new array
4.some() method
4.1 Application scenario: used to determine whether there are elements that meet the conditions in the array
For example: Determine whether there is a number greater than 100 in the array (if it exists, the return value is true, if it does not exist, the return value is false)
let arr = [10, 50, 150, 200, 60, 30]
let bol = arr.some((item, index) => {
return item > 100
})
console.log(bol)//true4.2 Notes:
(1). Execution of the callback function The number of times is not equal to the array length
(2). The return value of some function is a Boolean value
(3). The callback function returns a Boolean type value to end the traversal, if the return value is true, the traversal ends, and the return value of some function is false. If the return value is false, the traversal continues, and the return value of some function is false
5.every() method
5.1 Application scenario: Used to determine whether all elements in the array meet the conditions (switch idea). It has similar functions to the some() method and can be compared and understood
For example: determine whether all elements in the array are greater than 100 (Both are greater than 100, the return value is true, as long as one element is less than 100, the return value is false)
let arr = [10, 50, 150, 200, 60, 30]
let bol = arr.every((item, index) => {
return item > 100
})
console.log(bol)//false5.2 Note:
(1). The number of executions of the callback function is not Equal to the length of the array
(2). The return value of every function is a Boolean value
(3). The callback function returns a Boolean type value to end the traversal. If the return value is true, Then the traversal continues, and the return value of every function is true. If the return value is false, it continues to end, and the return value of every function is false
6.findIndex() method
6.1 Application scenario: Suitable for elements in the array being of object type, more efficient than the traditional for loop
6.2 Function: Get the position (subscript) of the first element that meets the conditions
let arr = [
{ name: '张三', age: 20 },
{ name: '李四', age: 30 },
{ name: '王五', age: 25 },
{ name: '赵六', age: 33 },
{ name: '小七', age: 10 },
];
let i=arr.findIndex((item,index)=>{
return item.age>30
})
//打印的i为符合条件的第一个元素下标
console.log(i)//36.2 Note:
(1). If the value of return is true, the traversal ends, and the return value of the findIndex method is the current index value; if the value of return is false, the traversal continues. If the entire array is traversed, If it still does not return true, the return value of the findIndex method is -1
7.reduce() method
7.1 Application scenario: array sum/average/maximum/minimum value
7.2 Function: Traverse the array elements and execute a callback function for each element
//数组求和
let arr = [10, 20, 30, 40]
//sum:初始值,默认为数组的第一个元素
//item:数组的每一个元素,默认为数组的第二个元素
let getSum = arr.reduce((sum, item) => {
//这里必须要return,相当于把本次计算得结果赋值给下一次得sum : sum = sum + item;
return sum + item
})
console.log(getSum)//1007.2 Notes:
(1). It is best to give an initial value to avoid empty array errors.
//数组求和
let arr = [10, 20, 30, 40]
//加了初始值0之后,此时sum开始默认为0,item则默认为数组的第一个元素
let getSum = arr.reduce((sum, item) => {
//这里必须要return,相当于把本次计算得结果赋值给下一次得sum : sum = sum + item;
return sum + item
},0)
console.log(getSum)//100
//数组求最大值
let max = arr.reduce((sum, item) => {
return Math.max(sum, item)
}, 0)
console.log(max)//40Special attention here is that the sum value of each round is the return value of the previous round
8. Summary
Extended example:
arr.reduce(function(sum,value,index,arr){}) method
reduce() method receives a function as an accumulator, Each value in the array starts decreasing (from left to right) and eventually counts to one value.
reduce() can be used as a higher-order function for compose of functions.
Note: reduce() will not execute the callback function for an empty array.
| 参数 | 详情 |
|---|---|
| sum第一个参数 | 第一次为数组的第一个数组元素的值(下标为0),依次往后是返回计算结果的值 |
| value 第二个参数 | 开始为数组元素第二个的值(下标为1),依次往后循环 |
| index第三个参数 | 依次为数组元素的下标 |
| arr第四个参数 | 为数组的整体 |
| initialValue | 为第一参数的默认值,设置的话,第一个参数的默认值为initialValue的值,则 第二个参数则将使用数组第一个元素(下标为0 ),没有设置的话,第一个参数将使用数组第一个元素,而 第二个参数 将使用数组第二个元素。 |
function sum(arr){
return arr.reduce(function(sum,value,index,arr){
console.log(sum);
console.log(value);
console.log(index);
console.log("~~")
console.log(arr)
return sum+y },initialValue)}console.log(sum([1,2,3,4,5]))arr.every(function(value,index,arr){})
every() 方法用于检测数组所有元素是否都符合指定条件(通过函数提供)。 every() 方法使用指定函数检测数组中的所有元素: 如果数组中检测到有一个元素不满足,则整个表达式返回 false ,且剩余的元素不会再进行检测。 如果所有元素都满足条件,则返回 true。 注意: every() 不会对空数组进行检测。 注意: every() 不会改变原始数组。
| 参数 | 详情 |
|---|---|
| value | 数组元素 |
| index | 数组下标 |
| arr | 当前数组的整体 |
function sum(arr){
return arr.every(function(value,index,arr){
console.log(value);
console.log(index);
console.log("~~")
return value>=1
})}console.log(sum([1,2,3,4,5]))arr.some(function(value,index,arr){})
some() 方法用于检测数组中的元素是否满足指定条件(函数提供)。 some() 方法会依次执行数组的每个元素: 如果有一个元素满足条件,则表达式返回true , 剩余的元素不会再执行检测。 如果没有满足条件的元素,则返回false。 注意: some() 不会对空数组进行检测。 注意: some() 不会改变原始数组。
| 参数 | 详情 |
|---|---|
| value | 数组元素 |
| index | 数组下标 |
| arr | 当前数组的整体 |
function sum(arr){
return arr.some(function(value,index,arr){
console.log(value);
console.log(index);
console.log("~~")
return value>=1
})}console.log(sum([1,2,3,4,5]))arr.filter(function(value,index,arr){})
filter()方法过滤查找全部,对数组元素进行判断,满足条件的会组成一个新的数组返回 注意:如果都不符合条件,会得到一个空数组 注意:如果所有元素都符合条件,会得到一个包含所有元素的新数组它与原数组进行===或==比较会得到false
| 参数 | 详情 |
|---|---|
| value | 数组元素 |
| index | 数组下标 |
| arr | 当前数组的整体 |
function sum(arr){
return arr.filter(function(value,index,arr){
console.log(value);
console.log(index);
console.log("~~")
return value>=5
})}console.log(sum([1,2,3,4,5]))arr.map(function(value,index,arr){})
map对数组元素进行循环,有返回值,返回值会组成一个新的数组 注意:map可以处理一对一的元素映射
| 参数 | 详情 |
|---|---|
| value | 数组元素 |
| index | 数组下标 |
| arr | 当前数组的整体 |
const source = [1,2,3,4]const target = source.map(n=>({id:n,label:`label${n}`}))console.log(target)function sum(arr){
return arr.map(function(value,index,arr){
console.log(value);
console.log(index);
console.log("~~")
return value>=1
})}console.log(sum([1,2,3,4,5]))arr.forEach(function(value,index,arr){})
forEach()方法对数组元素进行循环,没有返回值和for循环的功能一样,但是不能使用break和countinue 注意:map和forEach的区别:map有返回值,forEach没有返回值
| 参数 | 详情 |
|---|---|
| value | 数组元素 |
| index | 数组下标 |
| arr | 当前数组的整体 |
function sum(arr){
return arr.forEach(function(value,index,arr){
console.log(value);
console.log(index);
console.log("~~")
return value>=1
})}console.log(sum([1,2,3,4,5]))【相关推荐:javascript视频教程、web前端】
The above is the detailed content of Summary of 7 commonly used iterative processing methods for arrays in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript is a programming language widely used in web development, while WebSocket is a network protocol used for real-time communication. Combining the powerful functions of the two, we can create an efficient real-time image processing system. This article will introduce how to implement this system using JavaScript and WebSocket, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to clarify the requirements and goals of the real-time image processing system. Suppose we have a camera device that can collect real-time image data



