
This article brings you relevant knowledge about javascript, which mainly introduces issues related to HTML DOM navigation. Let’s take a look at it together. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

[Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end】
With the HTML DOM, you can use node relationships to navigate the node tree.
According to the W3C HTML DOM standard, Everything in an HTML document is a node:
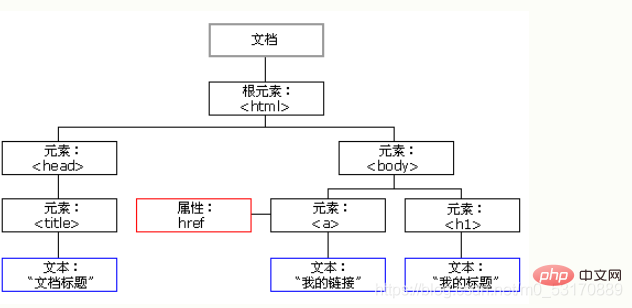
Be able to create new nodes, and also modify and delete all nodes.
The nodes in the node tree have a certain hierarchical relationship with each other.
eg:
<title>DOM 教程</title> <h1>DOM 第一课</h1> <p>Hello world!</p>
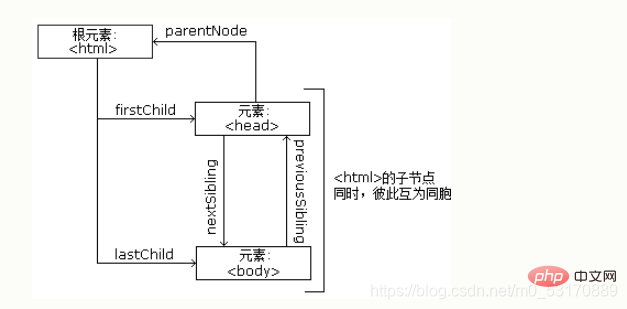
从以上的 HTML 中您能读到以下信息: - 是根节点 - 没有父 - 是 和 的父 - 是 的第一个子 - 是 的最后一个子 **同时:** - 有一个子:<title> - <title> 有一个子(文本节点):"DOM 教程" - </title> </title> 有两个子:<h1> 和 </h1><p> - </p><h1> 有一个子:"DOM 第一课" - </h1><p> 有一个子:"Hello world!" - </p><h1> 和 </h1><p> 是同胞</p>
Through JavaScript, you can navigate between nodes using the following node properties :
Example:
<title>DOM 教程</title>
var myTitle = document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML;var myTitle = document.getElementById("demo").firstChild.nodeValue;var myTitle = document.getElementById("demo").childNodes[0].nodeValue;
<h1>我的第一张页面</h1>
<p>Hello!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("id02").innerHTML = document.getElementById("id01").innerHTML;
</script>
<h1>我的第一张页面</h1>
<p>Hello!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("id02").innerHTML = document.getElementById("id01").firstChild.nodeValue;
</script>
<h1>我的第一张页面</h1>
<p>Hello!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("id02").innerHTML = document.getElementById("id01").childNodes[0].nodeValue;
</script>
The DOM root node
document.body - the body of the document
document.documentElement - the complete document
Instance
<p>Hello World!</p>
<div>
<p>DOM 很有用!</p>
<p>本例演示 <b>document.body</b> 属性。</p>
</div>
<script>
alert(document.body.innerHTML);
</script>
 Instance
Instance
<p>Hello World!</p>
<div>
<p>DOM 很有用!</p>
<p>本例演示 <b>document.documentElement</b> 属性。</p>
</div>
<script>
alert(document.documentElement.innerHTML);
</script>

 nodeName Attribute
nodeName Attribute
Attribute specifies the name of the node.
<h1>我的第一张网页</h1>
<p>Hello!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("id02").innerHTML = document.getElementById("id01").nodeName;
</script>Notes
: nodeName always contains the uppercase
tag name of the HTML element. nodeValue attribute
<h1>我的第一张网页</h1>
<p>Hello!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("id02").innerHTML = document.getElementById("id01").nodeType;
</script>
The most important nodeType attribute is: 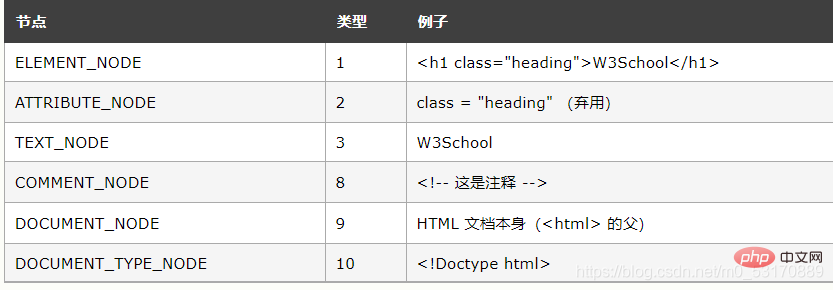
【Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end】
The above is the detailed content of JavaScript HTML DOM navigation (summary sharing). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!