A detailed review of arrow functions in ES6
This article brings you relevant knowledge about javascript, which mainly introduces issues related to arrow functions in es6. ES6 allows the use of => to define functions. The arrow function is equivalent to an anonymous function and simplifies the function definition. Let’s take a look at it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

[Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end]
1. Introduction to arrow functions
1.1 What is an arrow function
ES6 allows the use of => to define functions. Arrow functions are equivalent to anonymous functions and simplify function definition.
1.2 Basic syntax
// 箭头函数let fn = (name) => {
// 函数体
return `Hello ${name} !`;};// 等同于let fn = function (name) {
// 函数体
return `Hello ${name} !`;};Arrow functions are much simpler in syntax than ordinary functions. Arrow functions use arrows => to define functions, omitting the keyword function.
The parameters of the function are placed in the parentheses before =>, and the function body is in the curly braces after =>
1.3 Parameters of the arrow function
If the arrow function has no parameters, write empty brackets
//没有参数,写空括号
let fn = () => {
console.log('hello');
};If the arrow function has one parameter, you can also omit the brackets surrounding the parameter
//只有一个参数,可以省去参数括号
let fn = name => {
console.log(`hello ${name}!`)
};If the arrow function The function has multiple parameters. Separate the parameters with commas (,) and wrap them in parentheses.
let fn = (val1, val2, val3, val4) => {
return [val1, val2, val3, val4];
}1.4 The function body of the arrow function
If the function body of the arrow function has only one execution code, simply return a variable or return a For simple js expressions, you can omit the function body curly braces { }
//返回某个简单变量vallet f = val => val;// 等同于let f = function (val) { return val };//返回一个简单的js表达式num1+num2let sum = (num1, num2) => num1 + num2;// 等同于let sum = function(num1, num2) {
return num1 + num2;};If the function body of the arrow function has only one line of code, what is returned is not a variable and a simple js expression, but an object.
//错误写法—花括号会被解释为函数体
let getItem = id => {
id: id,
name: 'gaby'
};//正确写法
let getItem = id => ({
id: id,
name: 'gaby'
});If the function body of the arrow function has only one statement and does not require a return value (most commonly used for callback functions), add the void keyword
let fn = () => void doesNotReturn();
The arrow function is used for callback functions, which is common and concise
//栗子1//普通函数
[1, 2, 3].map(function (x) {
return x + x;
});//ES6箭头函数[1, 2, 3].map(x => x + x);//栗子2//普通函数
var result = [2, 4, 5, 1, 6].sort(function (a, b) {
return a - b;
});//ES6箭头函数
var result = [2, 4, 5, 1, 6].sort((a, b) => a - b);2. The this pointing rule of the arrow function
2.1 The arrow function does not have a prototype prototype, so the arrow function does not have this pointing
let fn = () => {
console.log('Hello World !')
};
console.log(fn.prototype); // undefined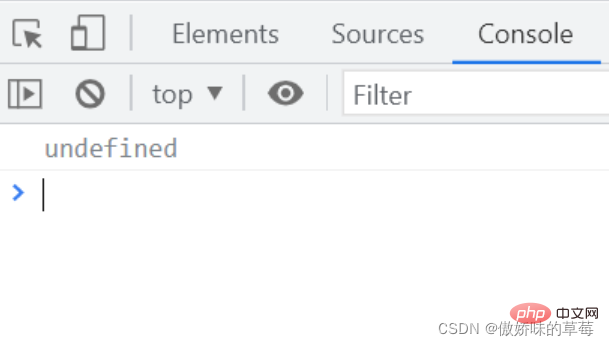
2.2 The arrow function will not create its own this. If there is the first ordinary function in the outer layer, its this will be inherited when it is defined
The arrow function does not have its own this pointer. It will capture the outer execution environment in which its definition is located, and inherit this this value. The this point of an arrow function is determined when it is defined and will never change later. (! Forever)
(1) Chestnut 1
var id = 'Global';
//普通函数
function fn1() {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(this.id)
}, 1000);
}
//箭头函数
function fn2() {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(this.id)
}, 1000);
}
fn1.call({
id: 'obj'
});//Global
fn2.call({
id: 'obj'
});//obj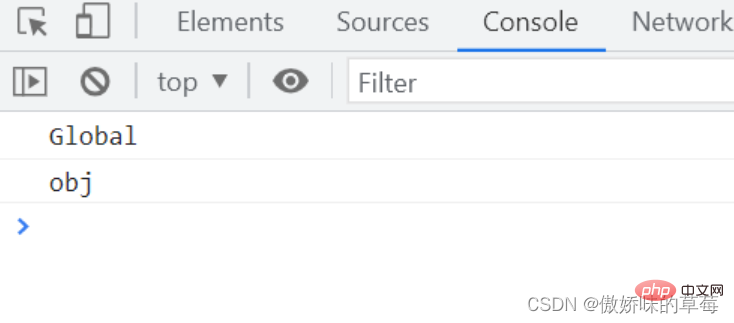
Analysis: The setTimeout of an ordinary function is executed globally after one second Scope, all this points to the window object, this.id points to the global variable id, and Golbal is output. The this of the arrow function is determined when it is defined. It inherits the this in the execution environment of fn2. The this of fn2 points to the object obj that is changed by the call method.
(2) Chestnut 2
var id = 'Global';
var obj = {
id: 'OBJ',
a: function () {
console.log(this.id)
},//方法a普通函数定义
b: () => {
console.log(this.id)
}//方法b用箭头函数定义
};
obj.a();//OBJ
obj.b();//Global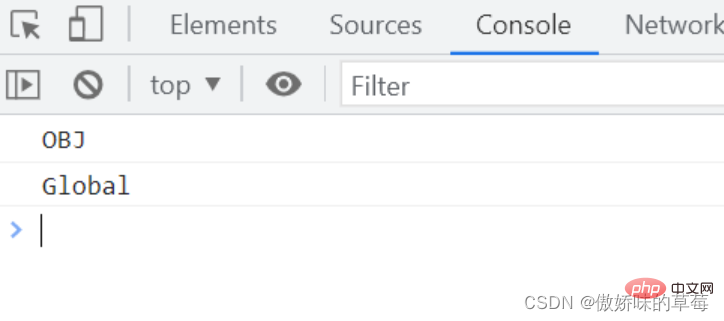
Analysis: Ordinary functions are called as methods of objects, this points to the object it belongs to (whoever calls it points to), this.id is obj.id; The arrow function inherits this that defines its execution environment, points to the window object, points to the global variable, and outputs Global. Curly braces {} cannot form a separate execution environment, so it is still in the global context.
2.3 The this of the arrow function is inherited and will never change, nor can call/apply/bind change
.call( )/.apply()/.bind() method can be used to dynamically modify the point of this when the function is executed, but because the this of the arrow function is already determined when it is defined and will never change
var name = 'gaby'
var person = {
name: 'gabrielle',
say: function () {
console.log('say hello', this.name)
}, //普通函数
say2: () => {
console.log('say2 hello', this.name)
} //箭头函数
}
person.say.call({
name: 'Mike'
})
person.say2.call({
name: 'Amy'
})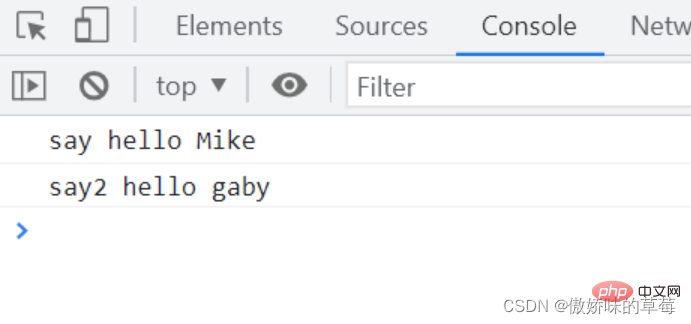
Analysis: say's ordinary function has changed this pointer through call. The say2 arrow function calls the call binding to try to change the this pointer, but it still prints out the this pointer of the outer ordinary function and the global variable name of the window object.
2.4 The this point of the arrow function can only be modified indirectly
Indirect modification: modify the this point of the inherited ordinary function, the this point of the arrow function The direction will also change accordingly.
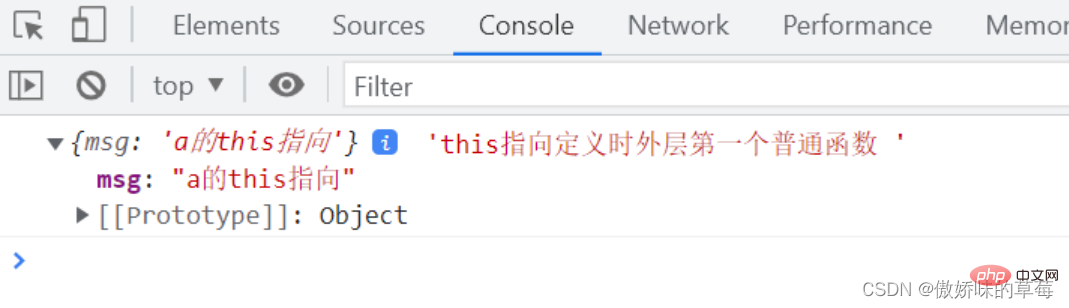
箭头函数的this指向定义时所在的外层第一个普通函数,跟使用的位置没有关系。
let al let aObj = {
msg: 'a的this指向'
};
bObj = {
msg: 'b的this指向'
};
a.call(aObj); //将a的this指向aObj
b.call(bObj); //将b普通函数的this指向bObj 箭头函数内部的this指向也会指向bObj
function b() {
al();
}
function a() {
al = () => {
console.log(this, 'this指向定义时外层第一个普通函数 ')
};
}
2.5 箭头函数外层没有函数,严格模式和非严格模式下它的this都会指向window全局对象
箭头函数的this指向继承自外层第一个普通函数的this,那么如果没有外层函数,它的this指向哪里?
this的绑定规则:非严格模式下,默认绑定的this指向全局对象,严格模式下this指向undefined。
如果箭头函数外层没有普通函数继承,箭头函数在全局作用域下,严格模式和非严格模式下它的this都会指向window(全局对象)
2.6 多层嵌套函数this指向
箭头函数中的this引用的是最近作用域中的this,是向外层作用域中,一层层查找this,直到有this的定义。
2.7 箭头函数不能作为构造函数使用new
构造函数做了什么?
JS内部首先会先生成一个对象
再把函数中的this指向该对象
然后执行构造函数中的语句
最终返回该对象实例
箭头函数没有自己的this,this继承外层执行环境中的this,且this永远不会改变。new会报错
let fn = (name, age) => {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
};
let person = new fn('gaby', 20)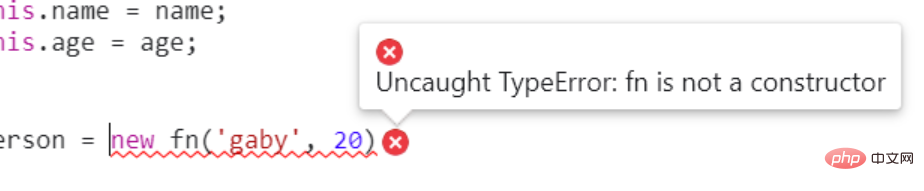
2.8 箭头函数不支持new.target
ES6新引入的属性,普通函数可以通过new调用,new.target返回该函数的引用。用于确定构造函数是否为new调用。箭头函数并不能作为构造函数使用new,自然也不支持new.targer。
(1)箭头函数的this指向全局对象,在箭头函数中使用箭头函数会报错
let fn = () => {
console.log(new.target)
};
fn()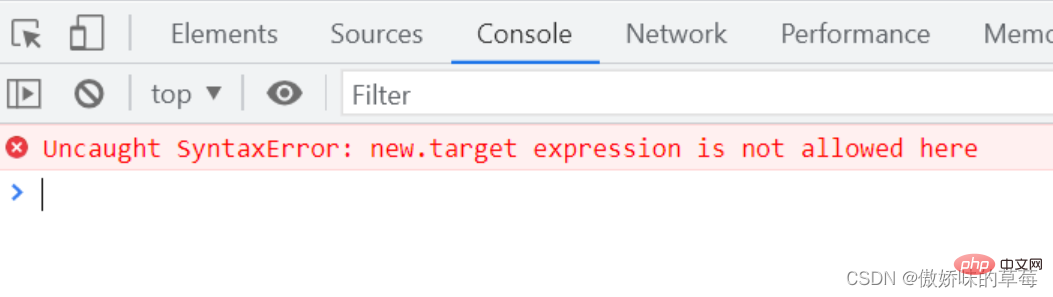
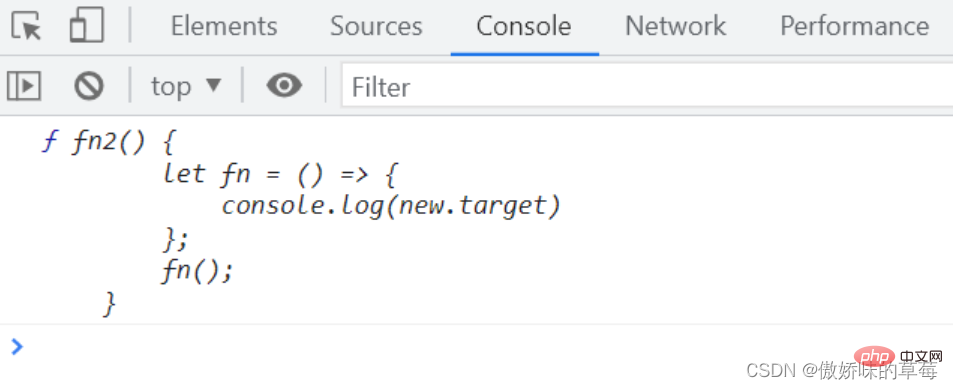
(2)箭头函数的this指向普通函数,它的new.target就是指向该普通函数的引用
new fn2();
function fn2() {
let fn = () => {
console.log(new.target)
};
fn();
}
三、箭头函数的arguments规则
3.1 箭头函数没有自己的arguments
(1)箭头函数处于全局作用域中
箭头函数的this指向全局对象,会报arguments未声明的错。
let fn = name => {
console.log(arguments)
}
let fn2 = function (name) {
console.log(arguments)
}
//fn()
fn2()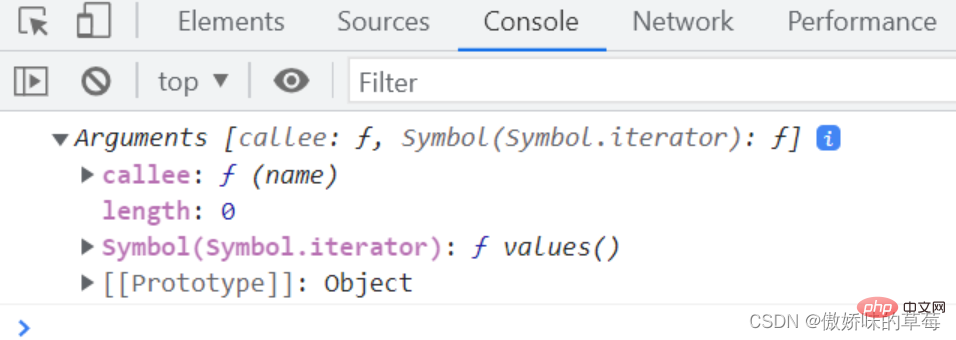
let fn = name => {
console.log(arguments)
}
let fn2 = function (name) {
console.log(arguments)
}
fn()
fn2()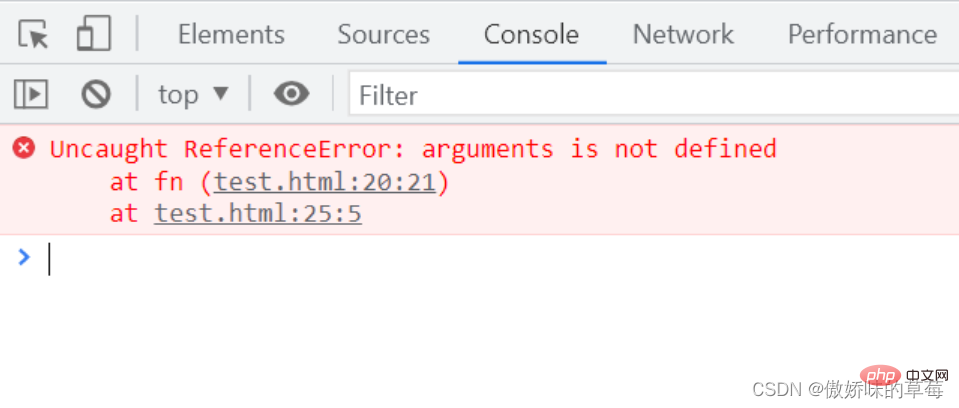
解析:普通函数可以打印arguments,箭头函数报错。因为箭头函数处于全局作用域中,在全局作用域没有arguments的定义,箭头函数本身没有arguments,所以报错。
(2)箭头函数的this如果指向普通函数,它的argumens继承于该普通函数
let fn2 = function (name) {
console.log('fn2:', arguments)
let fn = name => {
console.log('fn:', arguments)
}
fn()
}
fn2('gaby')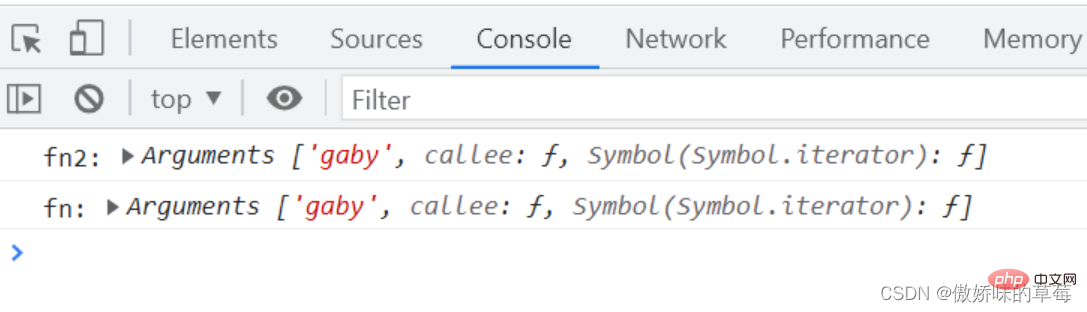
解析:两个函数打印的argument相同,都是fn2函数的arguments。
总结
箭头函数没有自己的arguments对象。在箭头函数中访问arguments实际上获得的是外层局部(函数)执行环境中的值。
3.2 可以用rest替代,rest参数获取函数的多余参数
rest是ES6的API,用于获取函数不定数量的参数数组。这个API可以用来替代arguments。
(1)基本用法
//形式是...变量名
let fn = (first, ...arr) => {
console.log(first, arr);
}
fn(1, 2, 3, 4);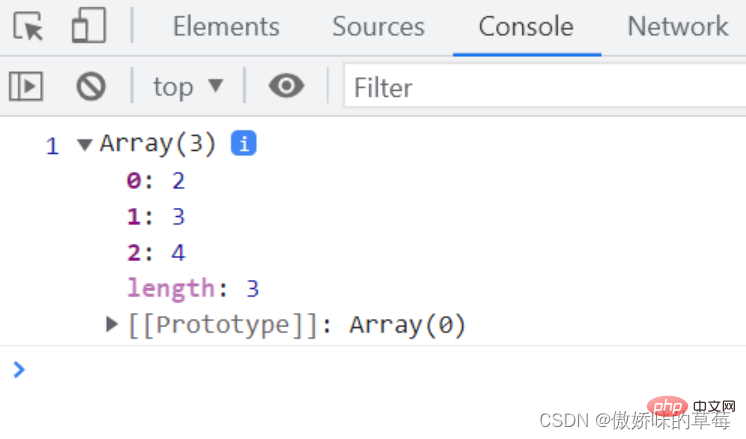
解析:rest 参数搭配的变量是一个数组,该变量将多余的参数放入数组中。获取函数的第一个确定的参数,以及用一个变量接收其他剩余函数的实例。
(2)使用注意事项
rest必须是函数的最后一位参数
let a = (first, ...rest, three) => {
console.log(first, rest, three);
};
a(1, 2, 3, 4);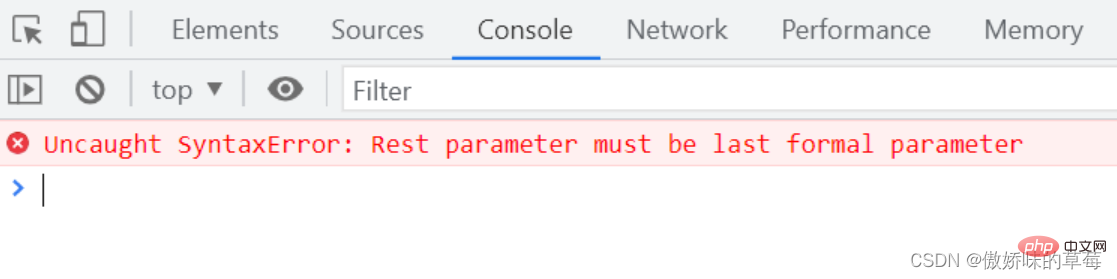
函数的length属性不包括rest
(3)rest和arguments函数比较
箭头函数和普通函数都可以使用rest参数,而arguments只能普通函数用。
接收参数rest比arguments更加灵活,完全可以自定义。
rest是一个真正的数组可以使用数组API,arguments只是一个类数组。
3.3 箭头函数不支持重复函数参数的名称
function fn(name, name) {
console.log('fn2:', name)
}
let fn2 = (name, name) => {
console.log('fn:', name)
}
fn('wang', 'gaby')
fn2('wang', 'gaby')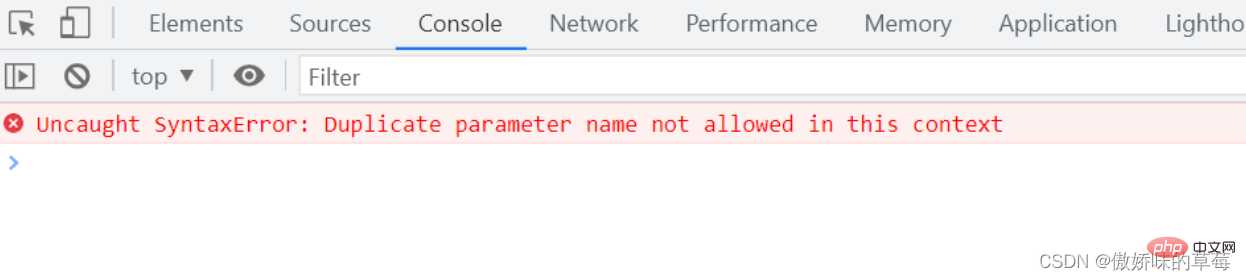
3.4 箭头函数不能用作Generator,不能使用yeild关键字
四、箭头函数的注意事项
函数箭头一条语句返回对象字面量,需要加括号。
箭头函数在参数和箭头之间不能换行
箭头函数的解析顺序相对||靠前
五、箭头函数不适用场景
(1)对象方法,且方法使用了this
对象无法构造单独的作用域
var name = 'gaby'
var person = {
name: 'gabrielle',
say: function () {
console.log('say hello', this.name)
}, //普通函数
say2: () => {
console.log('say2 hello', this.name)
} //箭头函数
}
person.say()
person.say2()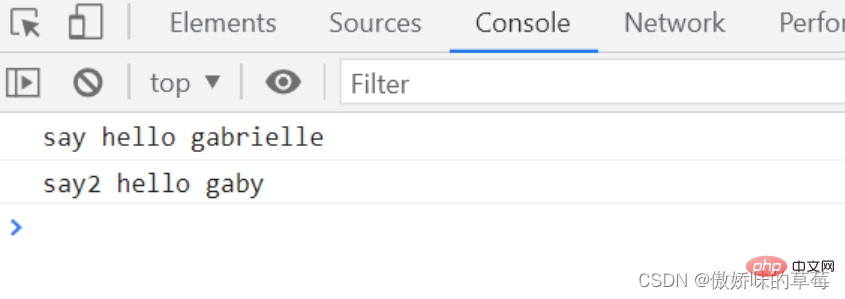
解析:person.say2()方法是一个箭头函数,调用person.say2()的时候this指向全局对象,达不到预期。对象无法构成单独的作用域,定义say2()箭头函数的时候作用域在全局作用域。
(2)回调函数的动态this
var button = document.querySelector('.btn');
button.addEventListener('click', () => {
this.classList.toggle('on');
});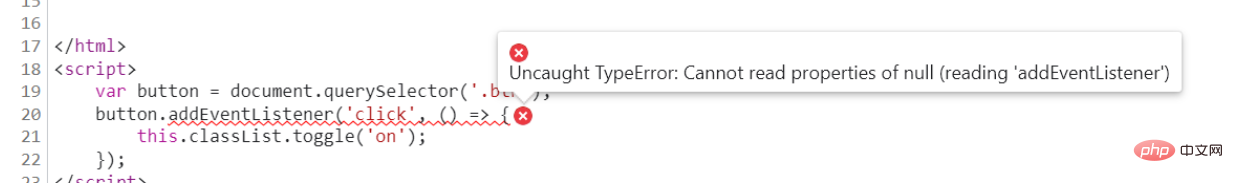
解析:报错。按钮点击是一个回调函数,而箭头函数内部的this指向外一层普通函数的this,在这里就是window,所以报错。改成普通函数就不会报错
六、箭头函数与普通函数简单区别总结
(1)箭头函数语法更简洁清晰,快捷。
(2)箭头函数没有原型prototype,并不会自己创建this,并且this不能被修改,call等都不能修改到。只能间接修改被继承的this
(3)箭头函数的this在定义时就定了,继承外一层的普通函数
(4)如果箭头函数外一层再外一层都不能找到普通函数,在严格和非严格情况下都会指向window对象
(5)箭头函数的this指向全局,使用arguments会报未声明的错误
(6)箭头函数的this指向外一层的普通函数,使用argument继承该普通函数
(7)箭头函数不能构造函数,不能new.target,不能new,没有constructor
(8)箭头函数不支持重复命名参数,普通函数可以重复命名参数
【相关推荐:javascript视频教程、web前端】
The above is the detailed content of A detailed review of arrow functions in ES6. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
async is es7. async and await are new additions to ES7 and are solutions for asynchronous operations; async/await can be said to be syntactic sugar for co modules and generator functions, solving js asynchronous code with clearer semantics. As the name suggests, async means "asynchronous". Async is used to declare that a function is asynchronous; there is a strict rule between async and await. Both cannot be separated from each other, and await can only be written in async functions.
 How to reverse an array in ES6
Oct 26, 2022 pm 06:19 PM
How to reverse an array in ES6
Oct 26, 2022 pm 06:19 PM
In ES6, you can use the reverse() method of the array object to achieve array reversal. This method is used to reverse the order of the elements in the array, putting the last element first and the first element last. The syntax "array.reverse()". The reverse() method will modify the original array. If you do not want to modify it, you need to use it with the expansion operator "...", and the syntax is "[...array].reverse()".
 Why does the mini program need to convert es6 to es5?
Nov 21, 2022 pm 06:15 PM
Why does the mini program need to convert es6 to es5?
Nov 21, 2022 pm 06:15 PM
For browser compatibility. As a new specification for JS, ES6 adds a lot of new syntax and API. However, modern browsers do not have high support for the new features of ES6, so ES6 code needs to be converted to ES5 code. In the WeChat web developer tools, babel is used by default to convert the developer's ES6 syntax code into ES5 code that is well supported by all three terminals, helping developers solve development problems caused by different environments; only in the project Just configure and check the "ES6 to ES5" option.
 How to find different items in two arrays in es6
Nov 01, 2022 pm 06:07 PM
How to find different items in two arrays in es6
Nov 01, 2022 pm 06:07 PM
Steps: 1. Convert the two arrays to set types respectively, with the syntax "newA=new Set(a);newB=new Set(b);"; 2. Use has() and filter() to find the difference set, with the syntax " new Set([...newA].filter(x =>!newB.has(x)))", the difference set elements will be included in a set collection and returned; 3. Use Array.from to convert the set into an array Type, syntax "Array.from(collection)".
 How to implement array deduplication in es5 and es6
Jan 16, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
How to implement array deduplication in es5 and es6
Jan 16, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
In es5, you can use the for statement and indexOf() function to achieve array deduplication. The syntax "for(i=0;i<array length;i++){a=newArr.indexOf(arr[i]);if(a== -1){...}}". In es6, you can use the spread operator, Array.from() and Set to remove duplication; you need to first convert the array into a Set object to remove duplication, and then use the spread operator or the Array.from() function to convert the Set object back to an array. Just group.
 What does es6 temporary Zenless Zone Zero mean?
Jan 03, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
What does es6 temporary Zenless Zone Zero mean?
Jan 03, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
In es6, the temporary dead zone is a syntax error, which refers to the let and const commands that make the block form a closed scope. Within a code block, before a variable is declared using the let/const command, the variable is unavailable and belongs to the variable's "dead zone" before the variable is declared; this is syntactically called a "temporary dead zone". ES6 stipulates that variable promotion does not occur in temporary dead zones and let and const statements, mainly to reduce runtime errors and prevent the variable from being used before it is declared, resulting in unexpected behavior.
 Is require an es6 syntax?
Oct 21, 2022 pm 04:09 PM
Is require an es6 syntax?
Oct 21, 2022 pm 04:09 PM
No, require is the modular syntax of the CommonJS specification; and the modular syntax of the es6 specification is import. require is loaded at runtime, and import is loaded at compile time; require can be written anywhere in the code, import can only be written at the top of the file and cannot be used in conditional statements or function scopes; module attributes are introduced only when require is run. Therefore, the performance is relatively low. The properties of the module introduced during import compilation have slightly higher performance.
 Is es6 map ordered?
Nov 03, 2022 pm 07:05 PM
Is es6 map ordered?
Nov 03, 2022 pm 07:05 PM
The map is ordered. The map type in ES6 is an ordered list that stores many key-value pairs. The key names and corresponding values support all data types; the equivalence of key names is determined by calling the "Objext.is()" method. Implemented, so the number 5 and the string "5" will be judged as two types, and can appear in the program as two independent keys.




