Example analysis of the principle and use of ES6 Promise
1. Promise 之前
1.1 回调函数
回调函数:把函数A当作参数传递给另一个函数B调用,那么A就是回调函数。【推荐:JavaScript视频教程】
一些例子
具名回调
function 你有几只狗(fn){
fn('一只狗')
}function 数狗(数量){
console.log(数量)
}
你有几只狗(数狗) // 一只狗匿名回调
function 你有几只狗(fn){
fn('一只狗')
}
你有几只狗(function(数量){console.log(数量)
}) // 一只狗常见的例子
jQuery中使用回调函数,这里用的是匿名回调的方式
$("#btn").click(function(){
console.log('点到我了')
})1.2 回调地狱(回调缺点1)
回调地狱:指的是回调嵌套过多的情况,导致代码很难被看懂。
let info = []function 你有几只狗(fn){
fn('一只狗')
}function 你有几只猫(fn){
fn('一只猫')
}function 知道了(数量,callback){
info.push(数量)
console.log(info) if(callback){
callback()
}
}// 开始调用 如果比这再多几层,就不容易看懂了你有几只狗(function(狗数){
console.log(狗数)
知道了(狗数, function(){
你有几只猫(function(猫数){
console.log(猫数)
知道了(猫数)
})
})
})1.3 不使用Promise,如何解决
利用具名函数代替匿名函数
let info = []function 你有几只狗(fn){
fn('一只狗')
}function 你有几只猫(fn){
fn('一只猫')
}function 知道了(数量,callback){
info.push(数量)
console.log(info) if(callback){
callback()
}
}function 告诉你猫的个数(猫数){
console.log(猫数)
知道了(猫数)
}function 继续数(){
你有几只猫(告诉你猫的个数)
}function 告诉你狗的个数(狗数){
console.log(狗数)
知道了(狗数, 继续数)
}
你有几只狗(告诉你狗的个数) // 好像也没好到哪去。。。1.4 回调方式各不相同,需要单独记忆(回调缺点2)
readFile('C:\\1.txt',function (error, data) { // node.js 读取文件方法中的回调
if(error) {
console.log('成功')
console.log(data.toString())
} else {
console.log('读取文件失败')
}
})
$.ajax({ // jQuery中ajax方法中的回调
url:'/2.txt'
success: function(response) {
console.log('成功')
},
error: function(){
console.log('失败')
}
})2. Promise 的目的
Promise 是异步编程的一种解决方案,比传统的解决方案——回调函数和事件——更合理和更强大。它由社区最早提出和实现,ES6 将其写进了语言标准,统一了用法,原生提供了Promise对象。
3. Promise 的原理
3.1 实现原理
ES6 规定,Promise对象是一个构造函数,用来生成Promise实例。通过在函数内部return 一个 Promise对象的实例,这样就可以使用Promise的属性和方法进行下一步操作了。
function 函数名(){ return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// ... some code if (/* 异步操作成功 */){
resolve(value); // 异步操作成功时调用,把结果作为参数传递出去
} else {
reject(error); // 异步失败时调用,把错误作为参数传递出去
}
})
}3.2 调用逻辑

S1和E1两个都没有报错,执行S2(resolve执行,系统认为搞定了,没报错)
S1和E1任何一个有报错,执行E2(reject执行,系统认为没搞定,报错了)
4. Promise 的使用
4.1 Promise 的属性与方法
属性
Promise.prototype 表示 Promise 构造器的原型
方法
Promise.prototype.then()
返回一个 Promise 。它最多需要有两个参数:Promise 的成功和失败情况的回调函数。
Promise.prototype.catch()
返回一个Promise,并且处理拒绝的情况。等价于Promise.prototype.then(undefined, onRejected)
Promise.prototype.finally()
finally() 方法返回一个Promise,在执行then()和catch()后,都会执行finally指定的回调函数。避免同样的语句需要在then()和catch()中各写一次的情况。
Promise.all(iterable)
返回一个 Promise 实例,iterable参数内所有的 promise 都resolved后,才回调完成resolve。
Promise.race(iterable)
返回一个 promise ,并伴随着 promise对象解决的返回值或拒绝的错误原因, 只要 iterable 中有一个 promise 对象”解决(resolve)”或”拒绝(reject)”。
Promise.resolve()
返回一个以给定值解析后的Promise对象。但如果这个值是个thenable(即带有then方法),返回的promise会“跟随”这个thenable的对象,采用它的最终状态(指resolved/rejected/pending/settled);如果传入的value本身就是promise对象,则该对象作为Promise.resolve方法的返回值返回;否则以该值为成功状态返回promise对象。
Promise.reject()
返回一个带有拒绝原因reason参数的Promise对象。
4.2 将回调地狱中的例子,改写为Promise的形式
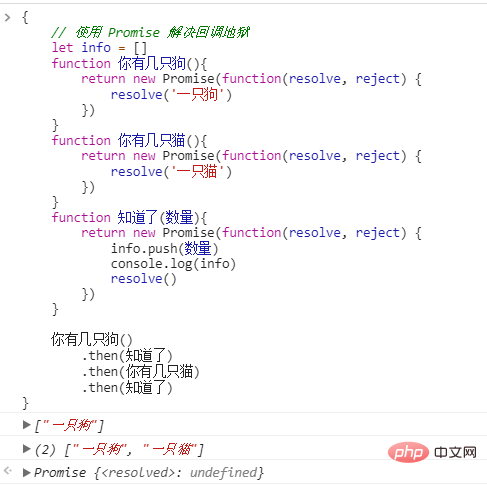
可以看到使用 Promise后,逻辑变得非常直观
写得更完整一些 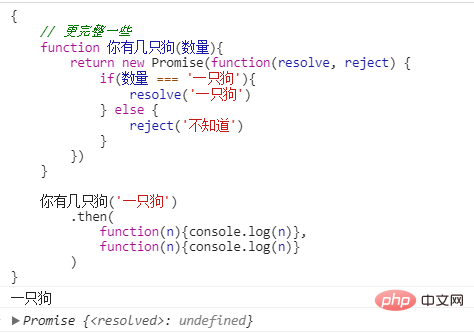
Promise套Promise时,也就是Promise链的时候——注意信息的传递
一个失败的例子,当我们使用Promise链的时候,如果每一步都需要上一步的数据时,就需要传参,成功通过resolve传参,失败通过reject传参,如果忘记传参,就得不到想要的结果。
resolve把成功的数据返回给下一个回调
reject把失败的数据返回给下一个回调。 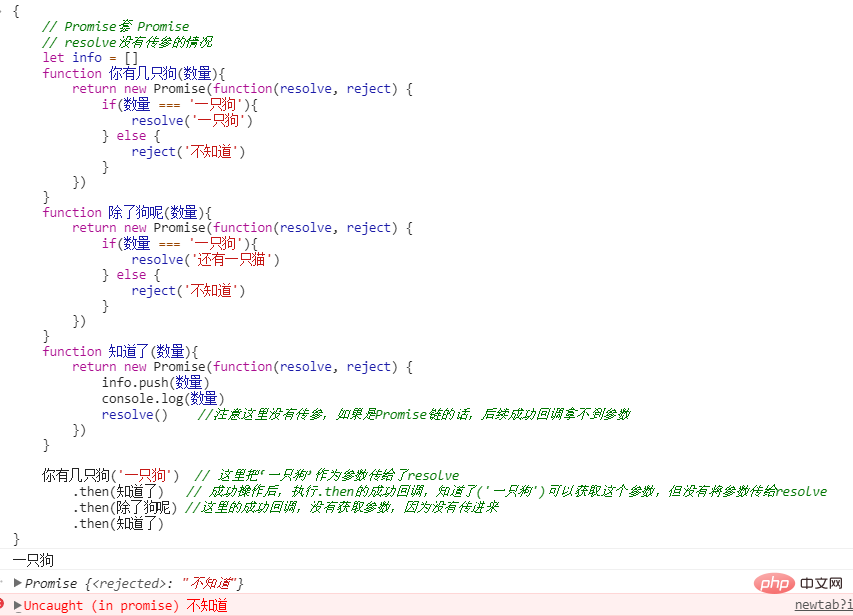
给这里的resolve传一个参 
改成失败的例子
先不给reject传参,如果失败的话,下一个回调拿不到数据 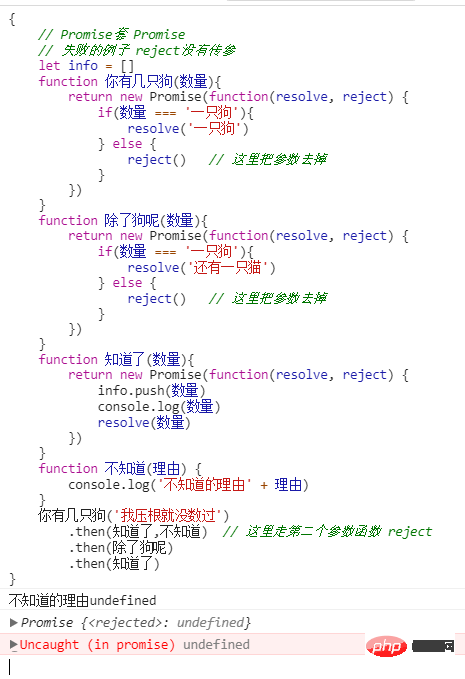
给 reject传参 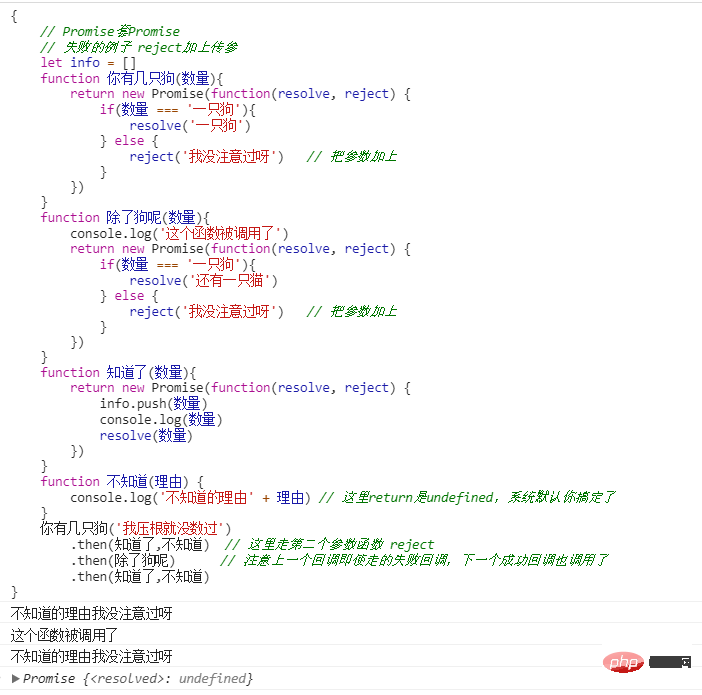
我们可以看到,即使是走的失败回调,下一个成功回调还是执行了,由于 不知道() 默认返回undefined, 相当于失败已经处理了,在成功和失败都被处理的情况下,下一个回调会执行的。
改成符合预期的,即失败不调用。 
失败不调用的简写形式 
上述情况执行后 .then(除了狗呢)里面的成功回调没有执行,我们增加一个失败回调看看 
同样也可以返回 resolve,让后面成功回调可以执行 
4.3 应用
加载图片
将图片的加载写成一个Promise,一旦加载完成,Promise的状态就发生变化。
const preloadImage = function (path) {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
const image = new Image();
image.onload = resolve;
image.onerror = reject;
image.src = path;
});
};Generator 函数与 Promise 的结合(详情见参考链接,阮一峰的教程)
5. 干掉Promise中的回调
5.1 await
成功的情况 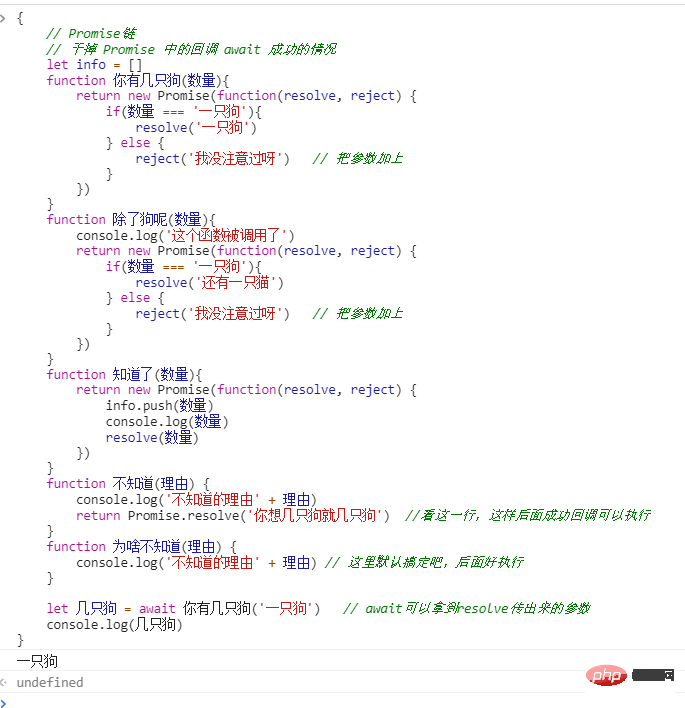
失败的情况
利用 try catch 
await 配合 try catch使用,比较完整
6. 总结
能利用Promise对象,把普通函数改成返回Promise的形式,解决回调地狱的问题。
明白Promise的成功失败调用逻辑,可以灵活的进行调整。
理解核心知识,先用起来,慢慢整合吸收知识。
The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of the principle and use of ES6 Promise. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
async is es7. async and await are new additions to ES7 and are solutions for asynchronous operations; async/await can be said to be syntactic sugar for co modules and generator functions, solving js asynchronous code with clearer semantics. As the name suggests, async means "asynchronous". Async is used to declare that a function is asynchronous; there is a strict rule between async and await. Both cannot be separated from each other, and await can only be written in async functions.
 Why does the mini program need to convert es6 to es5?
Nov 21, 2022 pm 06:15 PM
Why does the mini program need to convert es6 to es5?
Nov 21, 2022 pm 06:15 PM
For browser compatibility. As a new specification for JS, ES6 adds a lot of new syntax and API. However, modern browsers do not have high support for the new features of ES6, so ES6 code needs to be converted to ES5 code. In the WeChat web developer tools, babel is used by default to convert the developer's ES6 syntax code into ES5 code that is well supported by all three terminals, helping developers solve development problems caused by different environments; only in the project Just configure and check the "ES6 to ES5" option.
 Keeping your word: The pros and cons of delivering on your promises
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:06 PM
Keeping your word: The pros and cons of delivering on your promises
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:06 PM
In daily life, we often encounter problems between promises and fulfillment. Whether in a personal relationship or a business transaction, delivering on promises is key to building trust. However, the pros and cons of commitment are often controversial. This article will explore the pros and cons of commitments and give some advice on how to keep your word. The promised benefits are obvious. First, commitment builds trust. When a person keeps his word, he makes others believe that he is a trustworthy person. Trust is the bond established between people, which can make people more
 How to implement array deduplication in es5 and es6
Jan 16, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
How to implement array deduplication in es5 and es6
Jan 16, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
In es5, you can use the for statement and indexOf() function to achieve array deduplication. The syntax "for(i=0;i<array length;i++){a=newArr.indexOf(arr[i]);if(a== -1){...}}". In es6, you can use the spread operator, Array.from() and Set to remove duplication; you need to first convert the array into a Set object to remove duplication, and then use the spread operator or the Array.from() function to convert the Set object back to an array. Just group.
 What should I do if I encounter Uncaught (in promise) TypeError in a Vue application?
Jun 25, 2023 pm 06:39 PM
What should I do if I encounter Uncaught (in promise) TypeError in a Vue application?
Jun 25, 2023 pm 06:39 PM
Vue is a popular front-end framework, and you often encounter various errors and problems when developing applications. Among them, Uncaught(inpromise)TypeError is a common error type. In this article, we will discuss its causes and solutions. What is Uncaught(inpromise)TypeError? Uncaught(inpromise)TypeError error usually appears in
 What does es6 temporary Zenless Zone Zero mean?
Jan 03, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
What does es6 temporary Zenless Zone Zero mean?
Jan 03, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
In es6, the temporary dead zone is a syntax error, which refers to the let and const commands that make the block form a closed scope. Within a code block, before a variable is declared using the let/const command, the variable is unavailable and belongs to the variable's "dead zone" before the variable is declared; this is syntactically called a "temporary dead zone". ES6 stipulates that variable promotion does not occur in temporary dead zones and let and const statements, mainly to reduce runtime errors and prevent the variable from being used before it is declared, resulting in unexpected behavior.
 Learn more about Promise.resolve()
Feb 18, 2024 pm 07:13 PM
Learn more about Promise.resolve()
Feb 18, 2024 pm 07:13 PM
Detailed explanation of Promise.resolve() requires specific code examples. Promise is a mechanism in JavaScript for handling asynchronous operations. In actual development, it is often necessary to handle some asynchronous tasks that need to be executed in sequence, and the Promise.resolve() method is used to return a Promise object that has been fulfilled. Promise.resolve() is a static method of the Promise class, which accepts a
 Will es6 import promote variables?
Jan 18, 2023 pm 07:44 PM
Will es6 import promote variables?
Jan 18, 2023 pm 07:44 PM
ES6 import will cause variable promotion. Variable hoisting is the promotion of a variable declaration to the very beginning of its scope. js has to go through the compilation and execution phases. During the compilation phase, all variable declarations will be collected and variables declared in advance, and other statements will not change their order. Therefore, during the compilation phase, the first step is already is executed, and the second part is executed only when the statement is executed in the execution phase.




