
What can Vue computed properties do? What scenarios can it be applied to? The following article will take you to understand the Vue computed properties and compare them with methods and watches. I hope it will be helpful to you!

The calculated properties in Vue are the calculations of all properties, and these calculations are all in the filter value, and different values and operations are calculated through the continuous changes of the data. Different methods. In Vue, common scenarios where computed properties are used are:
Expressions in templates
properties Expressions that can be performed in v-bind. (Learning video sharing: vue video tutorial)
Expressions that can be carried out in the command
The above three The main advantage is simplicity. If it is just a small operation, such as some simple numerical values , character splicing, and ternary expressions, then it is quite convenient to use. Of course, the above methods also have their own disadvantages. Once the logic to be processed is complex, the amount of code becomes much larger and difficult to maintain. For example, if statements are used to control the process. Then you may think of using filter at this time. Let’s take a look at a simple example.
<div id="app">
<button @click="count++">{{count + '分'}}</button>
<div>
<input v-model="message" />
</div>
<p>{{ message.split(' ').reverse().join(' ') }}</p>
</div>let app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data () {
return {
count: 0,
message: ''
}
}
})The effect is as follows:
From the above example we can see:
We use string concatenation in the template, {{count 'fen'}}
specifies a binding through v-bind click event, it only does one thing, which is count , every time button is clicked, the count value increases by 1 , note that methods
input is not used here to make data bidirectional through v-model Binding, message is bound, and the message string is reversed in the p tag.
When calculating and converting message in the p tag, do you feel that the semantics are not very strong, so what method is better? Woolen cloth? This requires us to use the filter mentioned earlier.
We can use filter to modify the previous example. In fact, using filter in Vue has its own advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages: filter Give us some disadvantages for calculating and filtering some template expressions and v-bind attribute expressions. They will return the current calculated value, and you can pass parameters and share this in multiple places. Filtering method
Disadvantages: If we want to calculate the places where multiple data are combined with different changes, then filter will be more difficult to filter. , essentially filter is a one-to-one behavior. To filter a single data, parameters can be passed. The same method, but different parameters.
Put the above Example, modified with filter, it looks like the following:
<div id="app">
<button @click="count++">{{count + '分'}}</button>
<div>
<input v-model="message" />
</div>
<p>{{ message | reverseString }}</p>
</div>
let app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data () {
return {
count: 0,
message: ''
}
},
filters: {
reverseString (value) {
if (!value) return ''
value = value.split('').reverse().join('')
return value
}
}
})In this example, we use filter to implement it. Obviously the code The amount is a little more, but the overall semantics becomes quite obvious. When people look at this, they have to perform some filtering calculations. When they see reverseString, they know that it is string reversal.
I have said so much before, in fact, we are all here to pave the way for computed application scenarios. The question comes again, what can computed do? What scenarios can it be applied to?
computed in Vue actually avoids all the disadvantages of template syntax and filter. Its advantage lies in calculating all dependent data and then returning A value, remember can rely on all the data in the method. As long as one data changes, it will be recalculated to update the view change . Isn’t it interesting? I’m eager to know how it plays.
Let’s talk about usage scenarios. First, I will demonstrate a simple and practical application scenario to you, and then I will make a more interesting application scenario later.
Do you still remember that when we were playing Weibo, there was a character limit when posting on Weibo, for example, only 140 characters could be entered. In order to make the user experience better, when entering content in the text field, there is also a prompt message telling the user how many characters you can enter. Then it will be much easier to use Vue to do such things. For example, the following example:
<div id="app">
<div class="twitter">
<img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="imgUrl" class="lazy" : / alt="What can the Vue computed property do? Brief analysis of application scenarios" >
<div class="content">
<textarea v-model="content" :maxlength="totalcount">有什么新鲜事情?</textarea>
<p>您还可以输入{{ reduceCount }}字</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
let app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data () {
return {
imgUrl: '//pbs.twimg.com/profile_images/468783022687256577/eKHcWEIk_normal.jpeg',
totalcount: 140, // 总共只给输入140字
content: ''
}
},
computed: {
reduceCount () {
return this.totalcount - this.content.length
}
}
})The effect is as follows:
你可以尝试在文本域中输入内容,你将体验的效果类似下图一样:
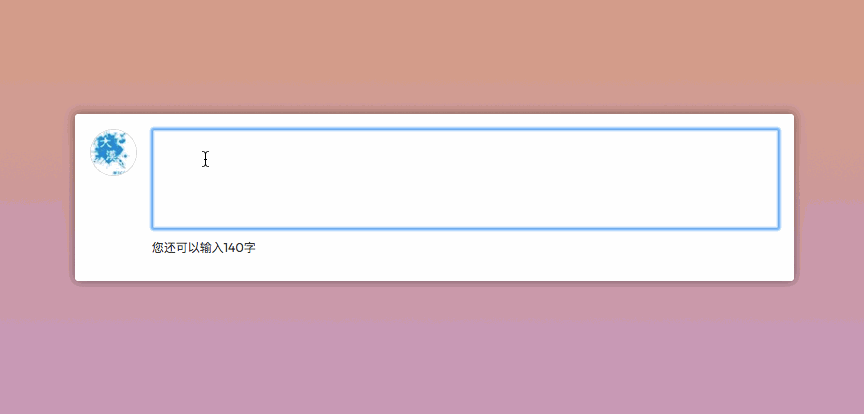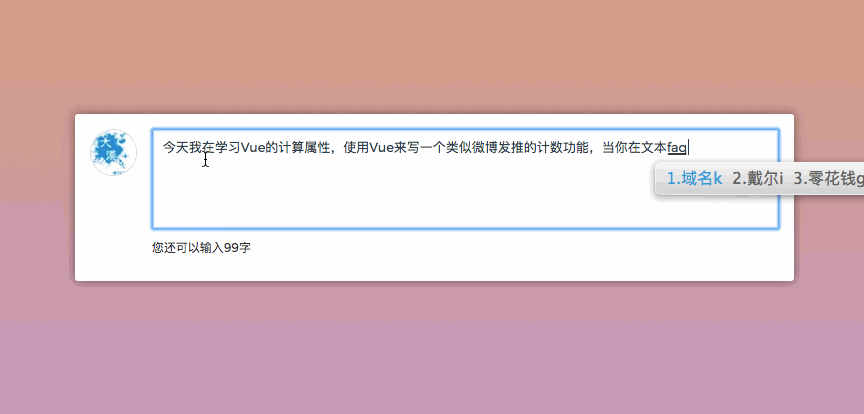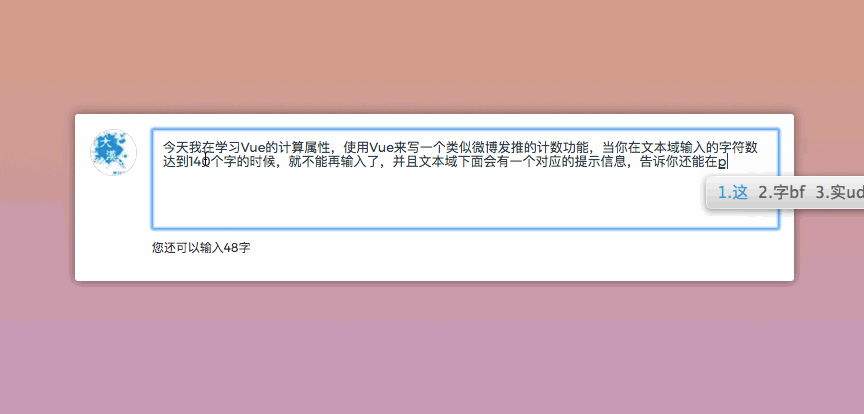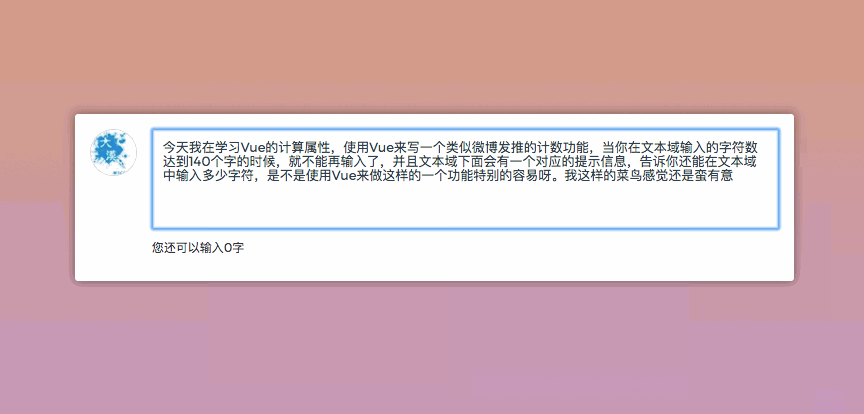
在computed创建了一个reduceCount,一直在监听文字的字符长度,来再次进行计算,返回值给视图,让视图进行变化。这也是一个很简单的示例。前面也提到过,我们可以监听多个数据,只要一个数据变了,整个方法就会重新计算,然后反馈到视图,这个方法只是一个简单的应用。咱们再来看一个示例,这样会更好的帮助我们理解。
这个示例是一个足球比赛记分的示例。简单的对示例进行分析:
比赛时间,用time来维护
比赛双方的进球数,用对象team来维护
比赛的播报情况,在90分钟内,要显示中国领先或者韩国领先或者双方僵持,如果到了90分钟我们要显示中国队赢还是韩国队赢,还是平局
第三个数据相对而言比较复杂,也是比较关键的数据。那么我们用什么方式来维护,可以说比赛情况是多样化的,用一个数据去定死,这样不符合我们的场景。那么我们先列出将会改变的地方:
我们需要检测双方的进球数
通过时间来比对,确定比赛是否结果,然后显示对应的方案
这样我们就要不断的监听两个维护的数据,一是比赛时间,二是比赛两队进球数。
<div id="app">
<h1>比赛时间:{{ time }}s</h1>
<h2>直播播报:{{ result }}</h2>
<div class="team">
<div>
<span>中国队进球数:{{ team.china }}</span>
<button @click="team.china++">点击中国队进一球</button>
</div>
<div>
<span>韩国队进球数:{{ team.korea }}</span>
<button @click="team.korea++">点击韩国队进一球</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
let app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data () {
return {
time: 0,
team: {
china: 0,
korea: 0
}
}
},
created () {
let time = setInterval(() => {
this.time++
if (this.time == 90) {
clearInterval(time)
}
}, 1000)
},
computed: {
result () {
if (this.time < 90) {
if (this.team.china > this.team.korea) {
return '中国队领先'
} else if (this.team.china < this.team.korea) {
return '韩国领先'
} else {
return '双方僵持'
}
} else {
if (this.team.china > this.team.korea) {
return '中国队赢'
} else if (this.team.china < this.team.korea) {
return '韩国队赢'
} else {
return '平局'
}
}
}
}
})看到的效果如下:
注:这里时间90分钟是一个写死的时间值。如果要让Demo更为完美,这个时间我们可以写一个90分钟的倒计时效果。如果你感兴趣的话,可以自己动手修改上面的Demo,然后在下面的评论中与我们一起分享。
这个示例中,用了点击事件来进行双方进球数,这个Demo帮助我们能能更充分的理解Vue中的computed的含义。说到底是观察一个或多个数据,每当其中一个数据改变的时候,这个函数就会重新计算,还有就是通过观察所有数据来维护一个状态,就是所谓的返回一个状态值。从上面这个Demo,我们就可以很容易的知道computed到底用在什么场景,如何去维护返回一个多状态的场景。
在Vue中,使用methods可以做computed同样的事情,不同的是,computed可以进行缓存。什么意思呢?就是在上个例子中我们对比赛时间和两个球队的进球数进行了检测数据。如果随着时间的改变,但是球数没动,对于computed来说只会重新计算这个球数,进入缓存,而不会再次计算,而重新计算的是这个时间,而且页面的DOM更新也会触发methods来重新计算属性。所以,如果不想让计算属性进入缓存,请使用methods,但我个人更推荐使用computed,语义化会更好一点。毕竟是什么选项里就应该做什么事,methods里面就是应该来管事件的。
computed和watch都可以做同一件事,就像跑步运动员都可以跑步,但是分100米和1000米,术业有专攻嘛,两个选项都是对数据进行时时监听,但是两个的适用场景就不一样了:
computed前面说了是适用于对多数据变动进行监听,然后来维护一个状态,就是返回一个状态
wacth是对一个数据监听,在数据变化时,会返回两个值,一个是value(当前值),二是oldvalue是变化前的值
我们可以通过这些变化也可以去维护一个状态,但是不符合场景。那么watch主要用于什么地方呢?其主要用于监听一个数据来进行复杂的逻辑操作。
<div id="app">
<h1>比赛时间:{{ time }}s</h1>
<h2>直播播报:{{ result }}</h2>
<div class="team">
<div>
<span>中国队进球数:{{ team.china }}</span>
<button @click="team.china++">点击中国队进一球</button>
</div>
<div>
<span>韩国队进球数:{{ team.korea }}</span>
<button @click="team.korea++">点击韩国队进一球</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
let app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data () {
return {
time: 0,
team: {
china: 0,
korea: 0
},
result: '双方僵持'
}
},
created () {
let time = setInterval(() => {
this.time++
if (this.time == 90) {
clearInterval(time)
}
}, 1000)
},
wacth: {
time (value, oldval) {
if (value < 90) {
if (this.team.china > this.team.korea) {
this.result = '中国队领先'
} else if (this.team.china < this.team.korea) {
this.result = '韩国队领先'
} else {
this.result = '双方僵持'
}
} else {
if (this.team.china > this.team.korea) {
this.result = '中国队赢'
} else if (this.team.chian < this.team.korea) {
this.result = '韩国队赢'
} else {
this.result = '平局'
}
}
},
team (value, oldval) {
if (this.time < 90) {
if (value.china > value.korea) {
this.result = '中国队领先'
} else if (value.china < value.korea) {
this.result = '韩国队领先'
} else {
this.result = '双方僵持'
}
} else {
if (value.china > value.korea) {
this.result = '中国队赢'
} else if(value.chian < value.korea) {
this.result = '韩国队赢'
} else {
this.result = '平局'
}
}
}
}
})以上代码和computed产生的效果是一模一样,但是很明显,就像我对computed和watch阐述过了应用场景,这个场景只是维护了一个比赛状态,而不牵扯到逻辑操作。虽然也能完成,但无论从代码量的比对还是可读性,还是可维护性的都不胜于computed。但说到底谁更强大呢?我还是老实说watch更强大,哪里有然他有场景的局限性,但是他可以做牵扯到计算属性的一切操作,缺点是watch只能一个一个监听。
我相信图片预加载大家肯定都有接触过,当图片量大的时候,为了保证页面图片都加载出来的时候,才渲染页面,再进行一些 Ajax请求,或者逻辑操作。那些时你用computed对这种监听一个数据然后进行一系列逻辑操作和Ajax请求,那watch再适合不过了,如果用computed的话,那是无法实现的。
<template>
<div v-show=show>
<img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.alicdn.com/simba/img/TB14sYVQXXXXXc1XXXXSutbFXXX.jpg" class="lazy" alt="">
<img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="//img.alicdn.com/tfs/TB1iZ6EQXXXXXcsXFXXXXXXXXXX-520-280.jpg_q90_.webp" class="lazy" alt="">
<img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.alicdn.com/simba/img/TB1C0dOPXXXXXarapXXSutbFXXX.jpg" class="lazy" alt="">
<img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="//img.alicdn.com/tfs/TB1iZ6EQXXXXXcsXFXXXXXXXXXX-520-280.jpg_q90_.webp" class="lazy" alt="">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
mounted () {
var _this = this
let imgs = document.querySelectorAll('img')
console.log(imgs)
Array.from(imgs).forEach((item)=>{
let img = new Image()
img.onload = ()=>{
this.count++
}
img.src=item.getAttribute('src')
})
},
data () {
return {
count : 0,
show : false
}
},
watch : {
count (val,oldval) {
if(val == 4){
this.show = true
alert("加载完毕")
//然后可以对后台发送一些ajax操作
}
}
}
}
</script>我们可以发现四张图片都加载完毕的时候,页面才渲染出来。
Vue官方有一句话说得很重要:
虽然计算属性在大多数情况下更合适,但有时也需要一个自定义的
watcher。这是为什么Vue提供一个更通用的方法,使用wacth来响应数据的变化。当你想要在数据变化响应时,执行异步操作或开销较大的操作,这是很有用的。
基于这个描述,我对computed和watch的总结:
computed:监听多个数据或者一个数据来维护返回一个状态值,只要其中一个或多个数据发生了变化,则会重新计算整个函数体,重新返回状态值
watch:只能一个一个监听数据,只要这个数据发生变化,就会返回两个参数,第一个是当前的值,第二个是变化前的值。每当变化的时候,则会触发函数体的逻辑行为,根据逻辑行为做后续的操作
其实,computed、watch这几个都不是有多难,如果从表层上来说都很易理解,但从深层面上看,很多时候还是会存在问题。比如说会滥用,混用。这篇文章通过一些示例来讲解Vue的计算属性,并且对其做了一定的分析。我想这些对学习Vue的初级人员或许会有一些帮助。
原文地址:https://www.w3cplus.com/vue/vue-computed.html
The above is the detailed content of What can the Vue computed property do? Brief analysis of application scenarios. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!