Summary of MySQL database subquery syntax rules
This article brings you relevant knowledge about mysql, which mainly introduces the issues related to the syntax rules of database subquery. A subquery is a query nested in the query statement. This It's because when we extract data, there are many unknown data that have dependencies; let's take a look at them together, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended learning: mysql video tutorial
A subquery is a query nested inside the query statement. This is because we When extracting data, there are many unknown data that have dependencies. At this time, we need to first query the result set of a set of data, and then use this result set as the object of the next query. In the "Table Connection Chapter", we once talked about the low efficiency of subqueries. In fact, not all subqueries are inefficient. The "WHERE" subquery needs to be executed repeatedly when matching records. This is not true. It is recommended; but if you use the query result set as a table and make a connection with other tables, this is a subquery of the "FROM" clause. This subquery method is still recommended.
In detail, subqueries are divided into "single-row subquery", "multi-row subquery", "WHERE" subquery, "FROM" subquery and "SELECT" subquery; these are all in this chapter What we need to learn.
Introduction to subquery
A subquery is a query nested within a query statement
Ordinary query statements are divided into "SELECT" subquery and "FROM" Subquery, "WHERE" subquery; (It is strongly recommended to use "'FROM' subquery")
Examples of subqueries are as follows:
Query the information of employees whose base salary exceeds the company's average base salary. (We have used table joins to make this case before. Here we look at how to implement it through subqueries.)
SELECT
empno, ename, sal
FROM
t_emp
WHERE
sal >= (SELECT AVG(sal) FROM t_emp);
-- 正常情况下,将聚合函数作为 WHERE 子句的条件是不可以的,但是这里利用子查询与聚合函数先将平均底薪查询出来,这就变成具体的数据了
-- 这种情况下,作为 WHERE 子句的条件,就可以被使用了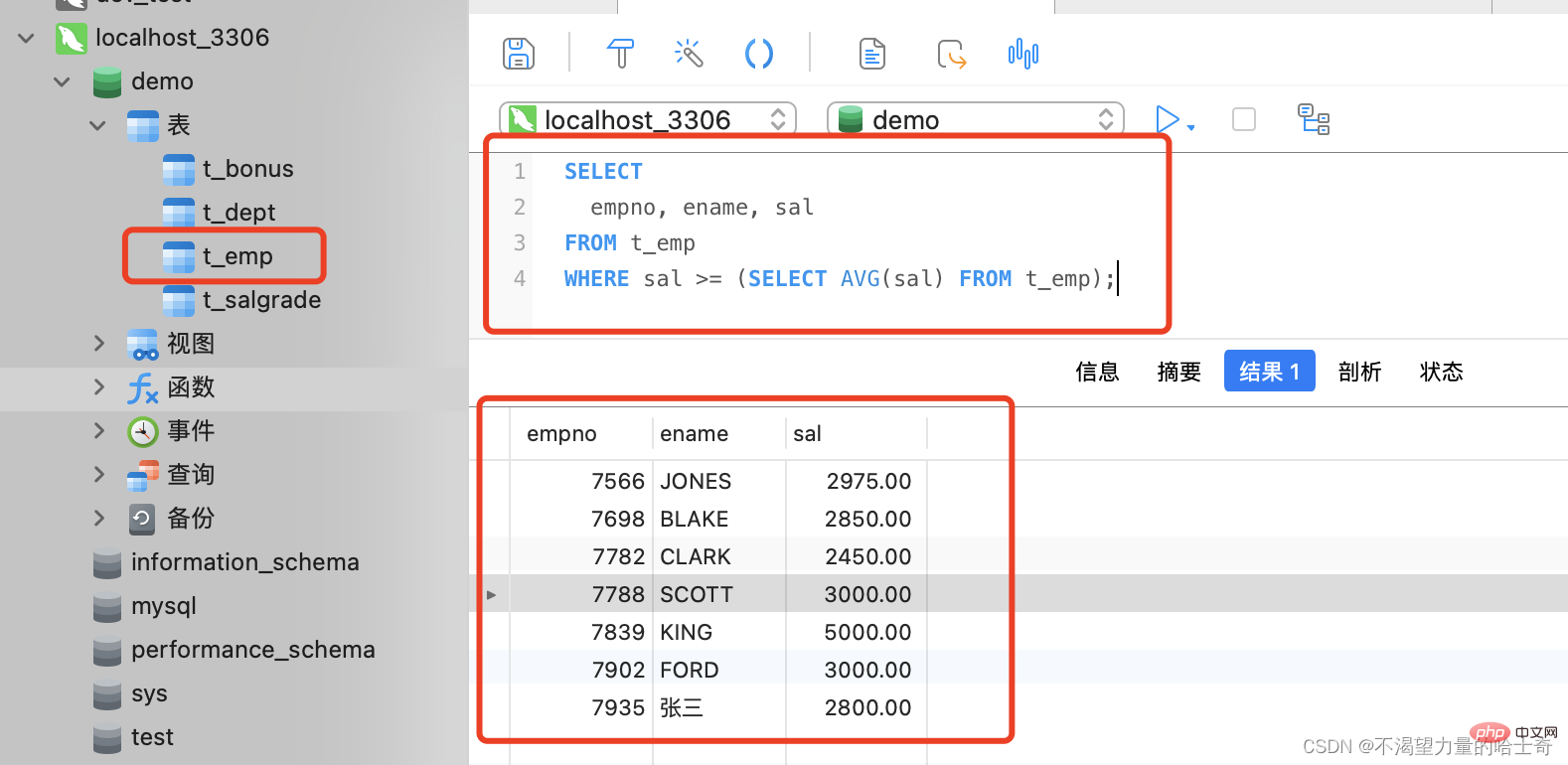
The above is the WHERE clause. Subquery, but the subquery of the WHERE clause is not recommended. Table joins should be used.
WHERE subquery
When writing SQL statements, WHERE subquery is most in line with our thinking logic
Although this kind of subquery is the simplest , the easiest to understand, but it is a very inefficient subquery
Let's take the query just demonstrated to query the information of employees whose base salary exceeds the company's average base salary. When the "WHERE" clause compares each employee record with the "SELECT" subquery, the subquery needs to be re-executed. If the employee table has 10,000 records, then the subquery needs to be executed 10,000 times. Repeated execution so many times is extremely inefficient.

In the query statement, the subquery that is queried repeatedly is called a "correlated subquery". The "WHERE" subquery here belongs to the "correlated subquery". It should Avoid using this kind of subquery.
FROM subquery
In the query statement, the "FROM" subquery will only be executed once, which is the opposite of the "WHERE" subquery, so the query efficiency Very high.
Similarly take the query of employee information whose base salary exceeds the company's average base salary as an example to see how the "FROM" subquery is implemented.
SELECT
e.empno, e.ename, e.sal, t.avg
FROM t_emp e
JOIN (SELECT deptno, AVG(sal) AS avg FROM t_emp GROUP BY deptno) t
ON e.deptno = t.deptno
AND e.sal >= t.avg;
-- 首先,按照每一个部门编号去分组,然后统计部门标号与该部门对应的平均月薪。将这个结果集作为一张临时的表与员工的表做连接。
-- 连接的条件为 "员工表" 的 "部门编号" = "结果集" 的 "部门编号",并且员工的月薪大于部门的平均月薪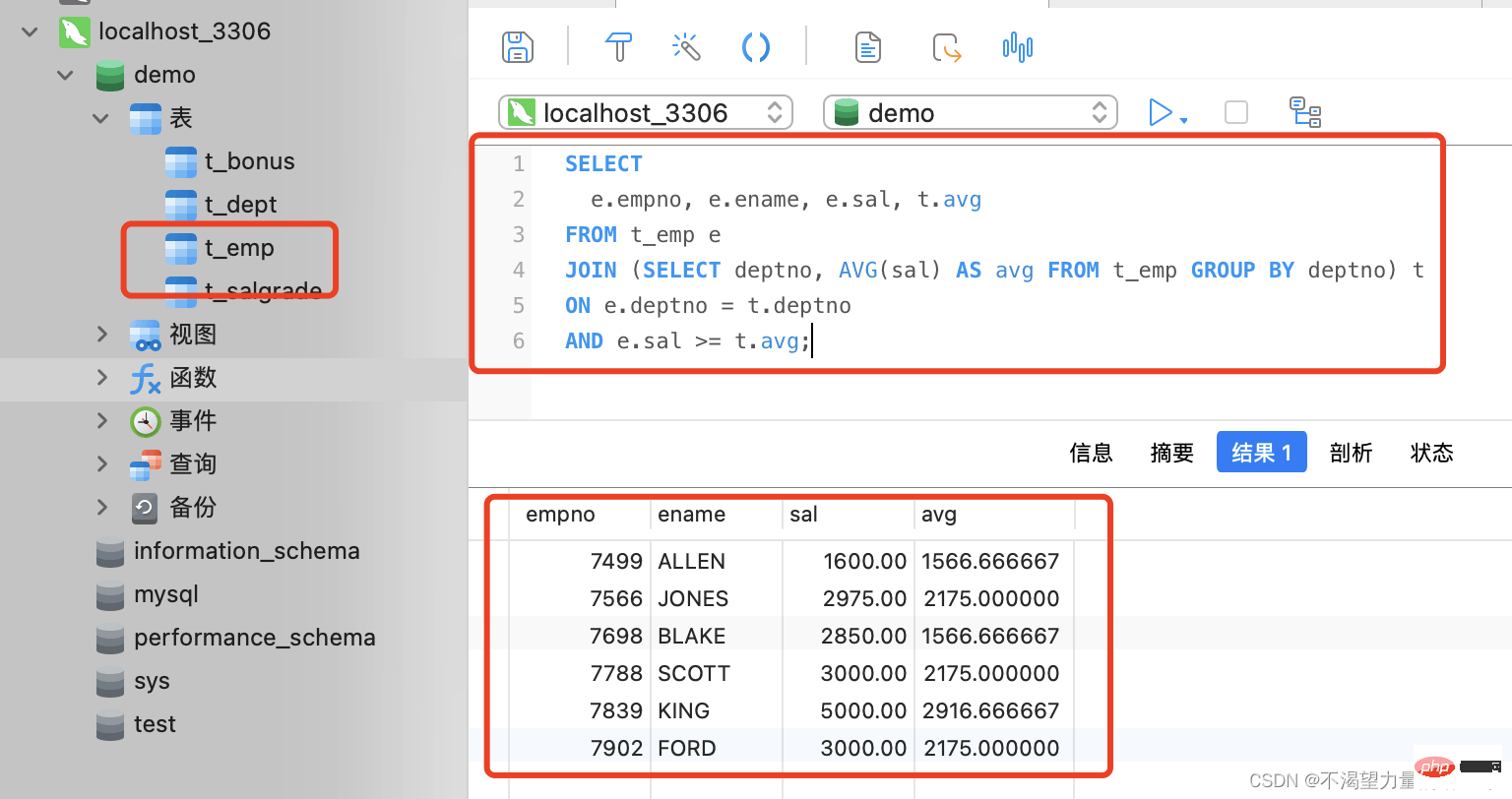
So this question can be easily implemented using the "FROM" subquery, and it is not necessary to use the "WHERE" subquery. Because the "FROM" subquery is not a correlated subquery, this subquery type should be limited when solving some problems.
SELECT subquery
To be honest, I have never seen this kind of subquery in all the projects I have experienced so far.
The reason is that the "SELECT" subquery is also a correlated subquery. It will be executed repeatedly in the SQL statement, and the query efficiency is very low.
Here we will give an example: For example, if we want to query the department information of each employee,
SELECT
e.empno,
e.ename,
(SELECT dname FROM t_dept WHERE deptno = e.deptno) AS 部门名称
FROM t_emp e;
-- 先试用 "SELECT" 子查询查询出 "部门表" 中的部门名称,约束条件为 "部门表"中的 "部门编号" 与 "员工表"中的 "部门编号" 一致
-- 将 "SELECT" 子查询得到的 "部门名称" 作为SQL语句中的一个字段进行输出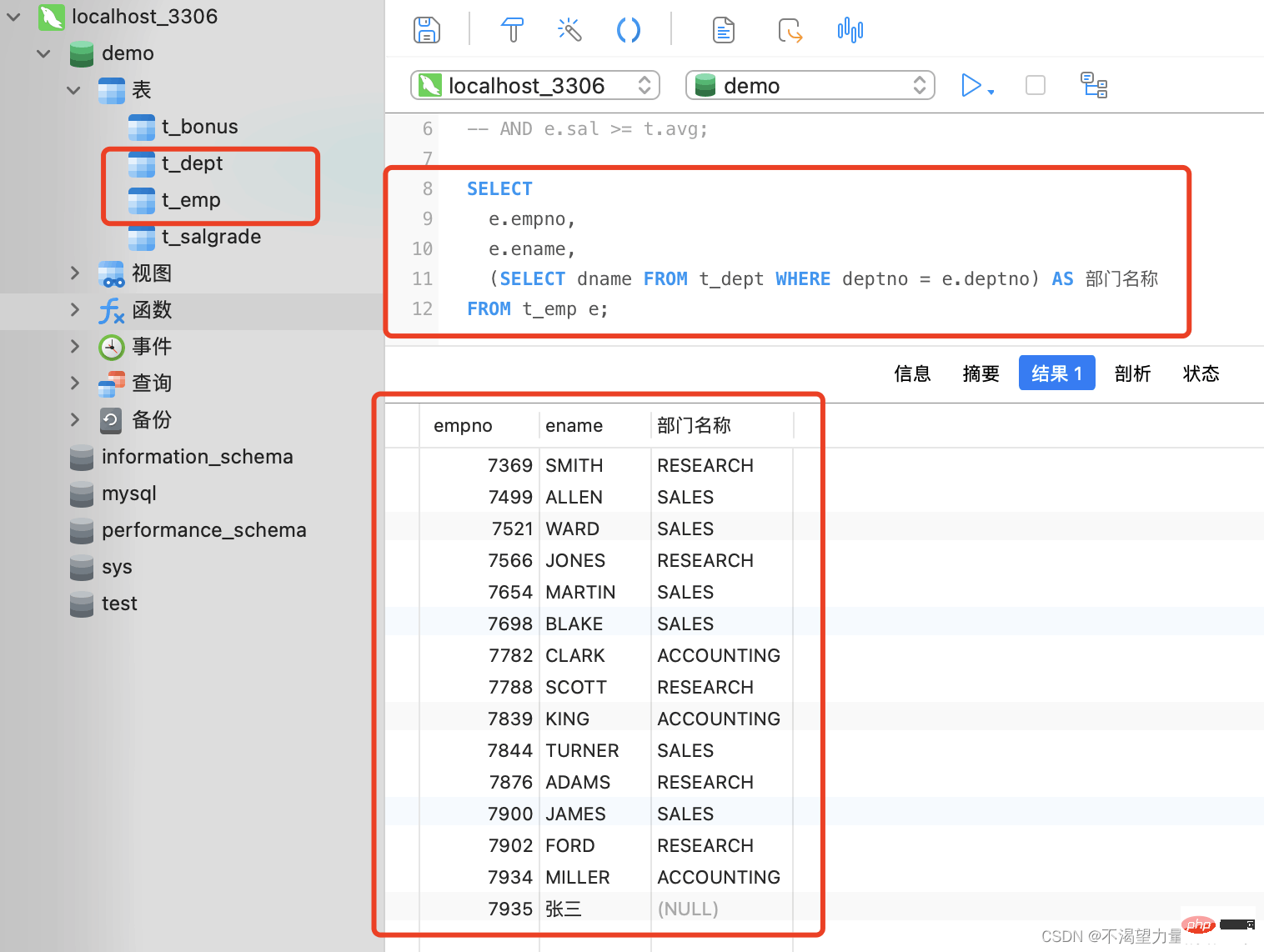
Although the execution result is correct, However, the execution efficiency is too low, so this "SELECT" subquery method is not recommended. Just understand it. When we see other people using the "SELECT" subquery, it is best to be kind. remind.
Recommended learning: mysql video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Summary of MySQL database subquery syntax rules. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system. 1) Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2) Basic operations: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and SELECT. 3) Advanced operations: JOIN, subquery and transaction processing. 4) Debugging skills: Check syntax, data type and permissions. 5) Optimization suggestions: Use indexes, avoid SELECT* and use transactions.
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Create a database using Navicat Premium: Connect to the database server and enter the connection parameters. Right-click on the server and select Create Database. Enter the name of the new database and the specified character set and collation. Connect to the new database and create the table in the Object Browser. Right-click on the table and select Insert Data to insert the data.
 How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
You can create a new MySQL connection in Navicat by following the steps: Open the application and select New Connection (Ctrl N). Select "MySQL" as the connection type. Enter the hostname/IP address, port, username, and password. (Optional) Configure advanced options. Save the connection and enter the connection name.
 MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL are essential skills for developers. 1.MySQL is an open source relational database management system, and SQL is the standard language used to manage and operate databases. 2.MySQL supports multiple storage engines through efficient data storage and retrieval functions, and SQL completes complex data operations through simple statements. 3. Examples of usage include basic queries and advanced queries, such as filtering and sorting by condition. 4. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues, which can be optimized by checking SQL statements and using EXPLAIN commands. 5. Performance optimization techniques include using indexes, avoiding full table scanning, optimizing JOIN operations and improving code readability.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Recovering deleted rows directly from the database is usually impossible unless there is a backup or transaction rollback mechanism. Key point: Transaction rollback: Execute ROLLBACK before the transaction is committed to recover data. Backup: Regular backup of the database can be used to quickly restore data. Database snapshot: You can create a read-only copy of the database and restore the data after the data is deleted accidentally. Use DELETE statement with caution: Check the conditions carefully to avoid accidentally deleting data. Use the WHERE clause: explicitly specify the data to be deleted. Use the test environment: Test before performing a DELETE operation.
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.




