Can es be deployed with docker?
es can be deployed using docker; deploying es clusters can be done directly using "docker-compose". "docker-compose" is a docker tool used to define and run complex applications, an application using docker containers , usually composed of multiple containers, using "docker-compose" eliminates the need to use shell scripts to start containers.

The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, docker version 19.03, Dell G3 computer.
Can es be deployed with docker?
Deployment of es cluster can be done directly using docker-compose
Docker Compose is a Docker tool used to define and run complex applications. An application using Docker containers usually consists of multiple containers. Using Docker Compose no longer requires shell scripts to start containers.
Compose manages multiple Docker containers through a configuration file. In the configuration file, all containers are defined through services, and then the docker-compose script is used to start, stop and restart the application, and the services in the application. As well as all containers that rely on services, it is very suitable for scenarios where multiple containers are combined for development.
Expand knowledge
Introduction to ES cluster
Why a cluster is needed
Single-machine elasticsearch When doing data storage, you will inevitably face two problems: massive data storage problem and single point of failure problem.
Massive data storage problem: Logically split the index library into N shards and store them on multiple nodes
Single point failure problem: Split the shard data in different locations Node backup (replica)
ES cluster related concepts
Cluster (cluster): a group of nodes with a common cluster name.
Node: An Elasticearch instance in the cluster
Shard: The index can be split into different parts Storage is called sharding. In a cluster environment, different shards of an index can be split into different nodes
Solve the problem: the amount of data is too large and the single-point storage capacity is limited.
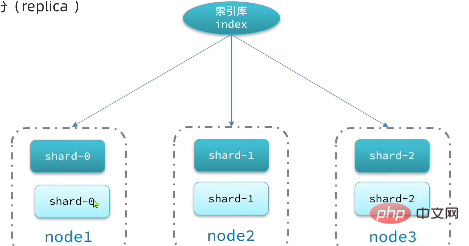
Here, we divide the data into 3 shards: shard0, shard1, shard2
Primary shard: Definition relative to replica shards.
Replica shard (Replica shard) Each primary shard can have one or more replicas, and the data is the same as the primary shard.
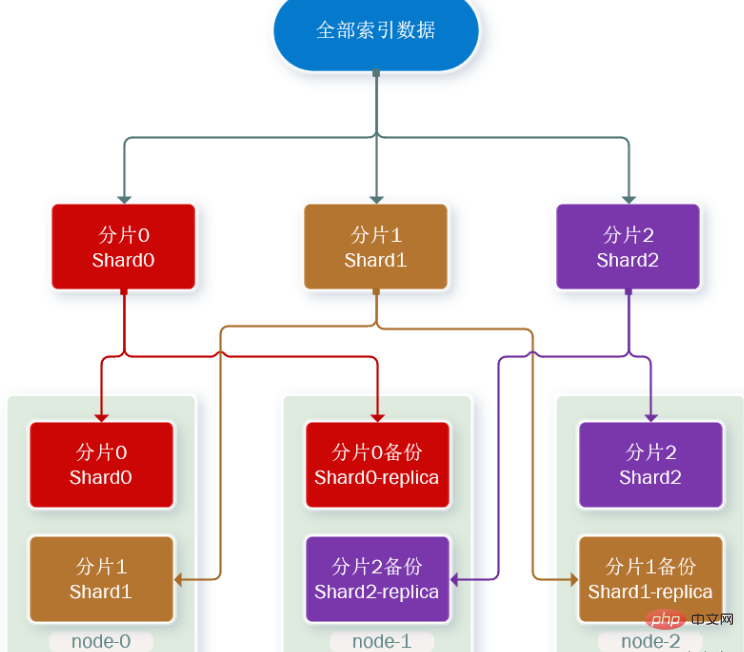
Data backup can ensure high availability, but one copy of each shard will double the number of nodes required, and the cost is too high!
In order to find a balance between high availability and cost, we can do this:
First shard the data and store it in different nodes
Then back up each shard and put it on the other node to complete mutual backup
This can greatly reduce the number of service nodes required, as shown in the figure, we use 3 shards, one copy of each shard is backed up as an example:
Build an ES cluster
Deploying an es cluster can be done directly using docker-compose, but your Linux virtual machine is required to have at least 4G of memory space
First write a docker-compose file with the following content:
version: '2.2'
services:
es01:
image: elasticsearch:7.12.1
container_name: es01
environment:
- node.name=es01
- cluster.name=es-docker-cluster
- discovery.seed_hosts=es02,es03
- cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02,es03
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
volumes:
- data01:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data
ports:
- 9200:9200
networks:
- elastic
es02:
image: elasticsearch:7.12.1
container_name: es02
environment:
- node.name=es02
- cluster.name=es-docker-cluster
- discovery.seed_hosts=es01,es03
- cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02,es03
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
volumes:
- data02:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data
ports:
- 9201:9200
networks:
- elastic
es03:
image: elasticsearch:7.12.1
container_name: es03
environment:
- node.name=es03
- cluster.name=es-docker-cluster
- discovery.seed_hosts=es01,es02
- cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02,es03
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
volumes:
- data03:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data
networks:
- elastic
ports:
- 9202:9200
volumes:
data01:
driver: local
data02:
driver: local
data03:
driver: local
networks:
elastic:
driver: bridgeFile content introduction:
version: complse version
es01: node
image: mirror
container_name: container name
environment: environment variable
node.name: node name
cluster.name: cluster name, es automatically creates a cluster
discovery.seed_hosts: the other two Address, you can use the container name to interconnect
cluster.initial_master_nodes: initialized master node, can participate in the election
"ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m": minimum and maximum JVM memory
volumes: Data volume address
ports: Port mapping
Recommended learning: "docker video tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of Can es be deployed with docker?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Steps to create a Docker image: Write a Dockerfile that contains the build instructions. Build the image in the terminal, using the docker build command. Tag the image and assign names and tags using the docker tag command.
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Troubleshooting steps for failed Docker image build: Check Dockerfile syntax and dependency version. Check if the build context contains the required source code and dependencies. View the build log for error details. Use the --target option to build a hierarchical phase to identify failure points. Make sure to use the latest version of Docker engine. Build the image with --t [image-name]:debug mode to debug the problem. Check disk space and make sure it is sufficient. Disable SELinux to prevent interference with the build process. Ask community platforms for help, provide Dockerfiles and build log descriptions for more specific suggestions.
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to save docker image
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:54 AM
How to save docker image
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:54 AM
To save the image in Docker, you can use the docker commit command to create a new image, containing the current state of the specified container, syntax: docker commit [Options] Container ID Image name. To save the image to the repository, you can use the docker push command, syntax: docker push image name [: tag]. To import saved images, you can use the docker pull command, syntax: docker pull image name [: tag].




