Python crawler crawls web page data and parses the data
This article brings you relevant knowledge about Python. It mainly introduces how python crawlers crawl web page data and parse the data to help you better use crawlers to analyze web pages. Let’s do it together. Take a look, hope it helps everyone.

[Related recommendations: Python3 video tutorial ]
1. Basic concepts of web crawlers
Web crawlers (also known as web spiders and robots) simulate a client sending network requests and receiving request responses. It is a program that automatically captures Internet information according to certain rules.
As long as the browser can do anything, in principle, the crawler can do it.
2. Functions of web crawlers
Web crawlers can replace many things manually, such as search engines, You can also crawl pictures on websites. For example, some friends crawl all the pictures on certain websites and browse them together. At the same time, web crawlers can also be used in the field of financial investment. For example, they can automatically crawl some financial information and Conduct investment analysis, etc.
Sometimes, we may have several favorite news websites, and it is troublesome to open these news websites separately every time to browse. At this time, you can use a web crawler to crawl the news information from these multiple news websites and read them together.
Sometimes, when we browse information on the web, we will find a lot of advertisements. At this time, you can also use a crawler to crawl the information on the corresponding web page, so that these advertisements can be automatically filtered out to facilitate the reading and use of the information.
Sometimes, we need to conduct marketing, so how to find target customers and their contact information is a key issue. We can manually search on the Internet, but this will be very inefficient. At this time, we can use crawlers to set corresponding rules and automatically collect target users' contact information and other data from the Internet for our marketing use.
Sometimes, we want to analyze the user information of a certain website, such as analyzing the user activity, number of comments, popular articles and other information of the website. If we are not the website administrator, manual statistics will be a very difficult task. Huge project. At this time, crawlers can be used to easily collect these data for further analysis. All crawling operations are performed automatically. We only need to write the corresponding crawler and design the corresponding rules.
In addition, crawlers can also achieve many powerful functions. In short, the emergence of crawlers can replace manual access to web pages to a certain extent. Therefore, operations that previously required manual access to Internet information can now be automated using crawlers, so that effective information in the Internet can be used more efficiently. .
3. Install third-party libraries
Before crawling data and parsing data, you need to download and install the third-party library requests in the Python running environment.
In Windows system, open the cmd (command prompt) interface, enter pip install requests in the interface, and press Enter to install. (Pay attention to the network connection) As shown below
The installation is completed, as shown in the picture
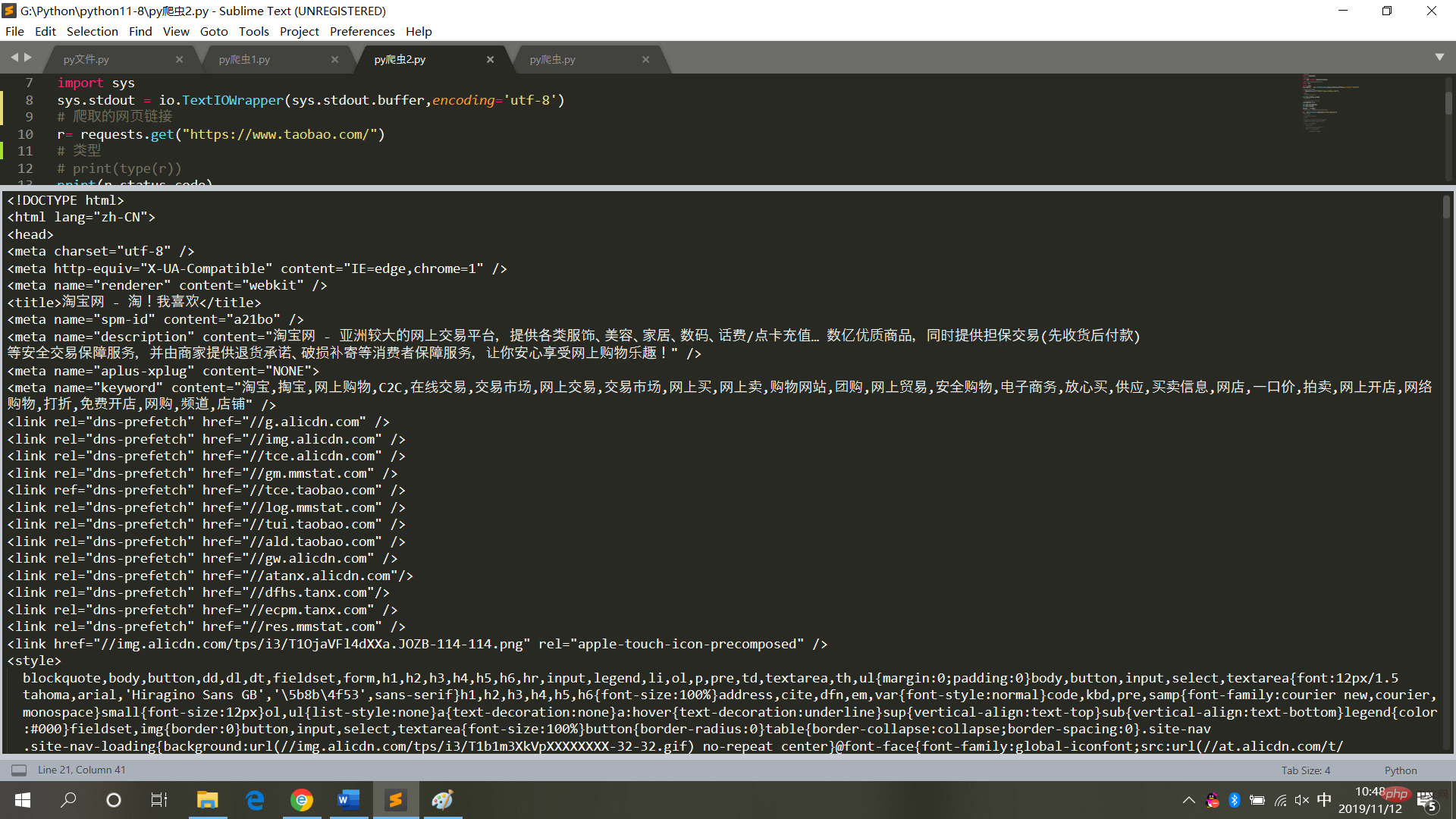
4. Crawl Taobao Home page
# 请求库
import requests
# 用于解决爬取的数据格式化
import io
import sys
sys.stdout = io.TextIOWrapper(sys.stdout.buffer,encoding='utf-8')
# 爬取的网页链接
r= requests.get("https://www.taobao.com/")
# 类型
# print(type(r))
print(r.status_code)
# 中文显示
# r.encoding='utf-8'
r.encoding=None
print(r.encoding)
print(r.text)
result = r.textThe running result is as shown in the figure
5. Crawl and parse Taobao home page
# 请求库
import requests
# 解析库
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 用于解决爬取的数据格式化
import io
import sys
sys.stdout = io.TextIOWrapper(sys.stdout.buffer,encoding='utf-8')
# 爬取的网页链接
r= requests.get("https://www.taobao.com/")
# 类型
# print(type(r))
print(r.status_code)
# 中文显示
# r.encoding='utf-8'
r.encoding=None
print(r.encoding)
print(r.text)
result = r.text
# 再次封装,获取具体标签内的内容
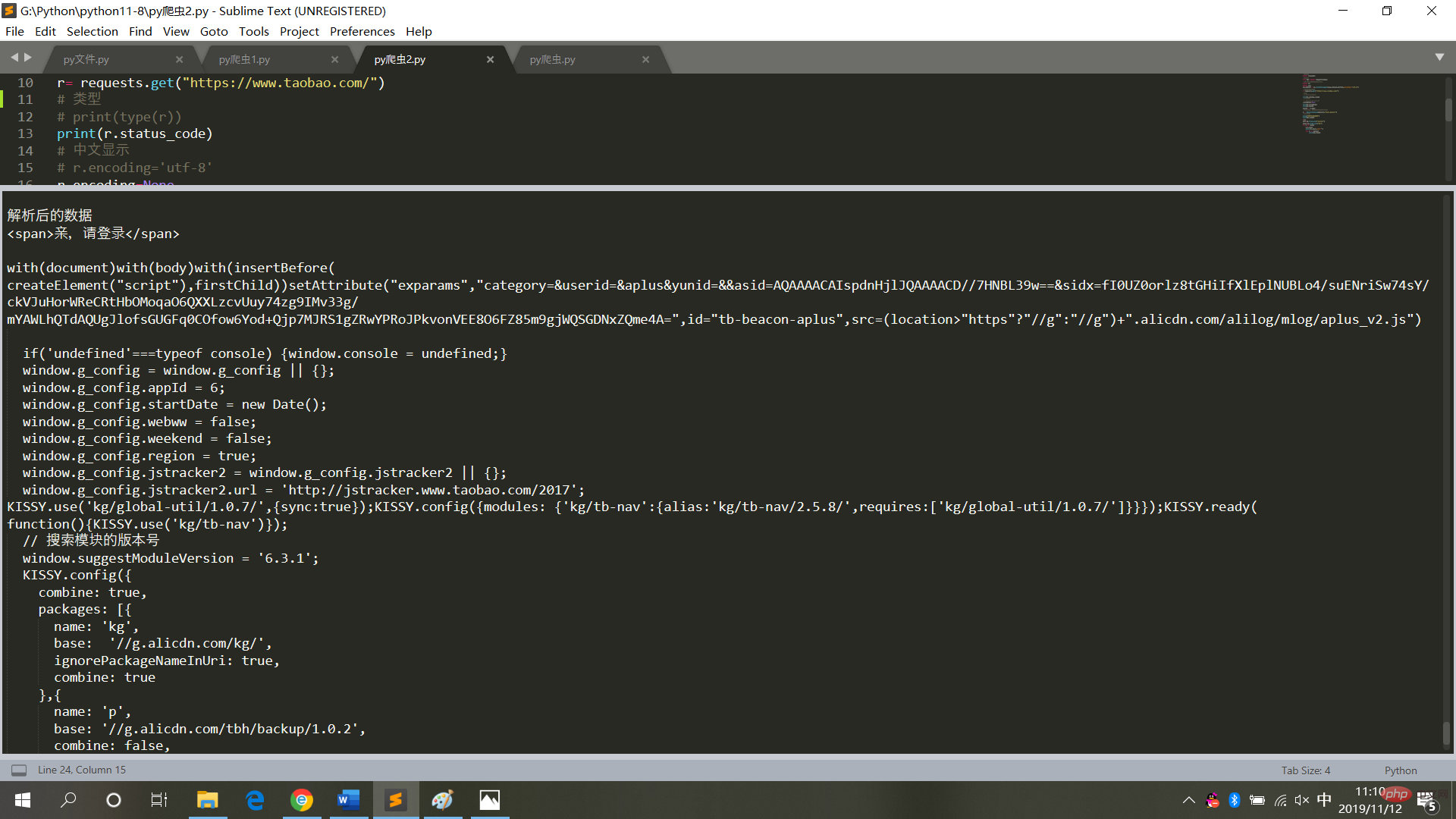
bs = BeautifulSoup(result,'html.parser')
# 具体标签
print("解析后的数据")
print(bs.span)
a={}
# 获取已爬取内容中的script标签内容
data=bs.find_all('script')
# 获取已爬取内容中的td标签内容
data1=bs.find_all('td')
# 循环打印输出
for i in data:
a=i.text
print(i.text,end='')
for j in data1:
print(j.text)Running results, as shown in the figure
6. Summary
When crawling web page code, do not do it frequently operation, and do not set it into an infinite loop mode (each crawl is an access to a web page, frequent operations will cause the system to crash, and legal liability will be pursued).
So after obtaining the web page data, save it in local text mode and then parse it (no need to access the web page anymore).
【Related recommendations: Python3 video tutorial】
The above is the detailed content of Python crawler crawls web page data and parses the data. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
To generate images through XML, you need to use graph libraries (such as Pillow and JFreeChart) as bridges to generate images based on metadata (size, color) in XML. The key to controlling the size of the image is to adjust the values of the <width> and <height> tags in XML. However, in practical applications, the complexity of XML structure, the fineness of graph drawing, the speed of image generation and memory consumption, and the selection of image formats all have an impact on the generated image size. Therefore, it is necessary to have a deep understanding of XML structure, proficient in the graphics library, and consider factors such as optimization algorithms and image format selection.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 Is there a mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:45 PM
Is there a mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:45 PM
There is no APP that can convert all XML files into PDFs because the XML structure is flexible and diverse. The core of XML to PDF is to convert the data structure into a page layout, which requires parsing XML and generating PDF. Common methods include parsing XML using Python libraries such as ElementTree and generating PDFs using ReportLab library. For complex XML, it may be necessary to use XSLT transformation structures. When optimizing performance, consider using multithreaded or multiprocesses and select the appropriate library.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 How to evaluate the quality of XML conversion to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to evaluate the quality of XML conversion to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
The quality evaluation of XML to pictures involves many indicators: Visual fidelity: The picture accurately reflects XML data, manual or algorithm evaluation; Data integrity: The picture contains all necessary information, automated test verification; File size: The picture is reasonable, affecting loading speed and details; Rendering speed: The image is generated quickly, depending on the algorithm and hardware; Error handling: The program elegantly handles XML format errors and data missing.
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.






