
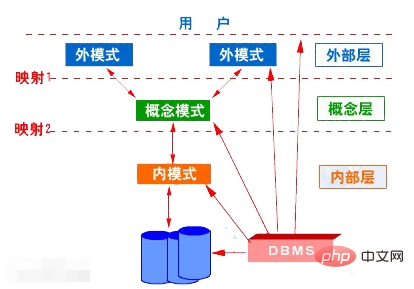
Among the three modes of database structure, "mode" or "logical mode" is the core of the database structure; logical mode is the description of the logical structure and characteristics of all data in the database, and is the common data of all users. Views and schemas are actually logical views of database data, and a database has only one schema.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 10 system, DELL G3 computer.
The mode is the core of the database structure
Schema
Schema, also called logical schema, is a description of the logical structure and characteristics of all data in the database, and is a common data view for all users. It is the middle layer of the database system schema structure. It does not involve the physical storage details of data, and has nothing to do with specific applications, application development tools and high-level programming languages used.
The schema is actually a logical view of database data. A database has only one schema. The database schema is based on a certain data model, comprehensively considers the needs of all users, and organically combines these needs into a logical whole. When defining a schema, it is not only necessary to define the logical structure of the data, such as which data items the data record consists of, the names, types, value ranges of the data items, etc.; it is also necessary to define the connection between the data, and define the security and integrity of the data. sexual requirements.
The database management system provides schema data definition language (schema DDL) to strictly define the schema.
The other two modes of database structure:
External schema (external schema)
External schema is also called subschema or user schema. It is a description of the logical structure and characteristics of local data that database users (including application programmers and end users) can see and use. It is the data view of database users. It is a logical representation of data related to an application.
Foreign schemas are usually a subset of schemas. A database can have multiple foreign schemas. Since it is the data view of each user, if different users have differences in application requirements, ways of viewing data, and requirements for data confidentiality, their external schema descriptions will be different. Even for the same data in the schema, the structure, type, length, confidentiality level, etc. of the external schema can be different. On the other hand, the same foreign mode can also be used by multiple application systems of a certain user, but an application can only use one foreign mode.
External mode is a powerful measure to ensure database security. Each user can only see and access the data in the corresponding foreign schema, and the rest of the data in the database is invisible.
Internal schema:
The internal schema is also called the storage schema. A database has only one internal schema. It is a description of how data is physically stored and stored, and how data is organized within the database. For example, should records be stored in a heap or in ascending (descending) order of a certain attribute value(s), or in clusters based on attribute values? In what way should the index be organized, whether it is a B-tree index or a hash index? ; Whether the data is compressed and stored, whether it is encrypted; what are the regulations for the storage record structure of the data, such as fixed-length structure or variable-length structure, a record cannot be stored across physical pages; etc.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of Among the three modes of database structure, what is the core of database structure?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!