8 Web APIs you may not know about but are very useful

In Web API, there are very useful objects, properties, and functions that can be used to perform small tasks such as accessing the DOM, to complex tasks such as processing audio and video. Common APIs include Canvas, Web Worker, History, Fetch, etc. Let’s take a look at some uncommon but useful Web APIs!
Full text overview:
Web Audio API
-
Fullscreen API
Web Speech API
Web Bluetooth API
Vibration API
-
Broadcast Channel API
Clipboard API
Web Share API
1. Web Audio API
Audio API allows us to operate audio streams on the Web. It can be used to add effects and filters to audio sources on the Web. The audio source can come from <audio></audio>, a video/audio source file, or an audio network stream. [Related recommendations: javascript learning tutorial]
Let’s look at an example:
<header>
<h2>Web APIs<h2>
</h2>
</h2></header>
<div>
<div>
<div>
Demo - Audio
</div>
<div>
<div></div>
<div>
<audio></audio>
</div>
<div>
<button>Init</button>
<button>Play</button>
<button>Pause</button>
<button>Stop</button>
</div>
<div>
<span>Vol: <input></span>
<span>Pan: <input></span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const l = console.log
let audioFromAudioFile = (function() {
var audioContext
var volNode
var pannerNode
var mediaSource
function init() {
l("Init")
try {
audioContext = new AudioContext()
mediaSource = audioContext.createMediaElementSource(audio)
volNode = audioContext.createGain()
volNode.gain.value = 1
pannerNode = new StereoPannerNode(audioContext, { pan:0 })
mediaSource.connect(volNode).connect(pannerNode).connect(audioContext.destination)
}
catch(e) {
error.innerHTML = "此设备不支持 Web Audio API"
error.classList.remove("close")
}
}
function play() {
audio.play()
}
function pause() {
audio.pause()
}
function stop() {
audio.stop()
}
function changeVolume() {
volNode.gain.value = this.value
l("Vol Range:",this.value)
}
function changePan() {
pannerNode.gain.value = this.value
l("Pan Range:",this.value)
}
return {
init,
play,
pause,
stop,
changePan,
changeVolume
}
})()
</script>In this example, the audio is removed from the <audio></audio> element Transferred to AudioContext, sound effects (such as panning) are added to the audio source before being output to the audio output (speaker).
Button Init calls the init function when clicked. This will create an AudioContext instance and set it to audioContext. Next, it creates a media source createMediaElementSource(audio), passing the audio element as the audio source. Volume node volNode is created by createGain and can be used to adjust the volume. Next use StereoPannerNode to set the panning effect, and finally connect the node to the media source.
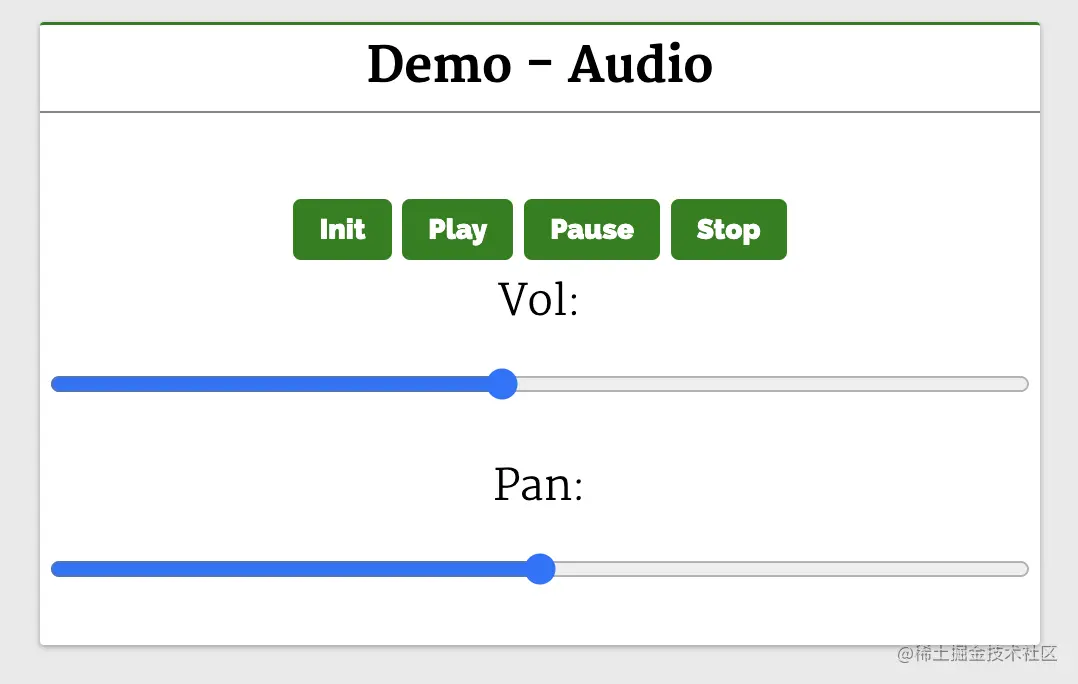
Click the buttons (Play, Pause, Stop) to play, pause and stop the audio. The page has a volume and pan range slider, and you can adjust the audio volume and pan effect by sliding the slider.
Related resources:
- Demo: web-api-examples.github.io/audio.html
- MDN Documentation: developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/…
2. Fullscreen API
Fullscreen API is used to enable full screen mode in web applications. Use it to view pages/elements in full screen mode. On Android phones, it overflows the browser window and the status bar at the top of Android (where network status, battery status, etc. are displayed).
Fullscreen API methods:
-
requestFullscreen: Displays the selected element in full screen mode on the system, closing other applications as well as browser and system UI elements. -
exitFullscreen: Exit full screen mode and switch to normal mode.
Let’s look at a common example, using full screen mode to watch a video:
<header>
<h2>Web APIs<h2>
</h2>
</h2></header>
<div>
<div>
<div>
Demo - Fullscreen
</div>
<div>
<div></div>
<div>
This API makes fullscreen-mode of our webpage possible. It lets you select the Element you want to view in fullscreen-mode, then it shuts off the browsers window features like URL bar, the window pane, and presents the Element to take the entire width and height of the system.
In Android phones, it will remove the browsers window and the Android UI where the network status, battery status are displayed, and display the Element in full width of the Android system.
</div>
<div>
<video></video>
<button>Toogle Fullscreen</button>
</div>
<div>
This API makes fullscreen-mode of our webpage possible. It lets you select the Element you want to view in fullscreen-mode, then it shuts off the browsers window features like URL bar, the window pane, and presents the Element to take the entire width and height of the system.
In Android phones, it will remove the browsers window and the Android UI where the network status, battery status are displayed, and display the Element in full width of the Android system.
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const l =console.log
function toggle() {
const videoStageEl = document.querySelector(".video-stage")
if(videoStageEl.requestFullscreen) {
if(!document.fullscreenElement){
videoStageEl.requestFullscreen()
}
else {
document.exitFullscreen()
}
} else {
error.innerHTML = "此设备不支持 Fullscreen API"
error.classList.remove("close")
}
}
</script>As you can see, the video element is in the div#video-stage element, with a button Toggle Fullscreen.

When the button is clicked to switch to full screen, we want the element div#video-stage to be displayed in full screen. toggle The implementation of the function is as follows:
function toggle() {
const videoStageEl = document.querySelector(".video-stage")
if(!document.fullscreenElement)
videoStageEl.requestFullscreen()
else
document.exitFullscreen()
}Here, querySelector is used to find the div#video-stage element and save its HTMLDivElement instance in videoStageEl on.
Then, use the document.fullsreenElement property to determine if the document is full screen, so requestFullscreen(() can be called on videoStageEl ). This will make div#video-stage occupy the entire device view.
If you click the Toggle Fullscreen button in full screen mode, exitFullscreen will be called on the document, so that the UI view will return to normal view (exit full screen).

related resources:
3. Web Speech API
Web Speech API 提供了将语音合成和语音识别添加到 Web 应用程序的功能。使用此 API,我们将能够向 Web 应用程序发出语音命令,就像在 Android 上通过其 Google Speech 或在 Windows 中使用 Cortana 一样。
下面来看一个简单的例子,使用 Web Speech API 实现文字转语音和语音转文字:
<header>
<h2>Web APIs<h2>
</h2>
</h2></header>
<div>
<div></div>
<div>
<div>
Demo - Text to Speech
</div>
<div>
<div>
<input>
</div>
<div>
<button>Tap to Speak</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<div>
Demo - Speech to Text
</div>
<div>
<div>
<textarea></textarea>
</div>
<div>
<button>Tap and Speak into Mic</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
try {
var speech = new SpeechSynthesisUtterance()
var SpeechRecognition = SpeechRecognition;
var recognition = new SpeechRecognition()
} catch(e) {
error.innerHTML = "此设备不支持 Web Speech API"
error.classList.remove("close")
}
function speak() {
speech.text = textToSpeech.value
speech.volume = 1
speech.rate=1
speech.pitch=1
window.speechSynthesis.speak(speech)
}
function tapToSpeak() {
recognition.onstart = function() { }
recognition.onresult = function(event) {
const curr = event.resultIndex
const transcript = event.results[curr][0].transcript
speechToText.value = transcript
}
recognition.onerror = function(ev) {
console.error(ev)
}
recognition.start()
}
</script>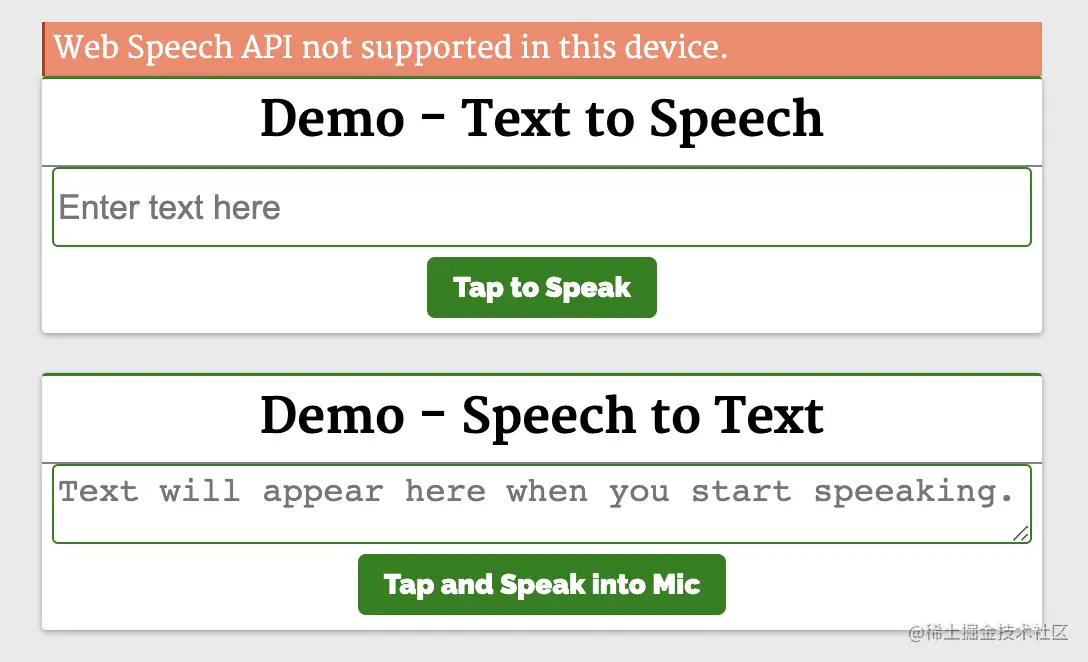
第一个演示 Demo - Text to Speech 演示了使用这个 API 和一个简单的输入字段,接收输入文本和一个按钮来执行语音操作。
function speak() {
const speech = new SpeechSynthesisUtterance()
speech.text = textToSpeech.value
speech.volume = 1
speech.rate = 1
speech.pitch = 1
window.speechSynthesis.speak(speech)
}它实例化了 SpeechSynthesisUtterance() 对象,将文本设置为从输入框中输入的文本中朗读。 然后,使用 speech 对象调用 SpeechSynthesis#speak 函数,在扬声器中说出输入框中的文本。
第二个演示 Demo - Speech to Text 将语音识别为文字。 点击 Tap and Speak into Mic 按钮并对着麦克风说话,我们说的话会被翻译成文本输入框中的内容。
点击 Tap and Speak into Mic 按钮会调用 tapToSpeak 函数:
function tapToSpeak() {
var SpeechRecognition = SpeechRecognition;
const recognition = new SpeechRecognition()
recognition.onstart = function() { }
recognition.onresult = function(event) {
const curr = event.resultIndex
const transcript = event.results[curr][0].transcript
speechToText.value = transcript
}
recognition.onerror = function(ev) {
console.error(ev)
}
recognition.start()
}这里实例化了 SpeechRecognition,然后注册事件处理程序和回调。语音识别开始时调用 onstart,发生错误时调用 onerror。 每当语音识别捕获一条线时,就会调用 onresult。
在 onresult 回调中,提取内容并将它们设置到 textarea 中。 因此,当我们对着麦克风说话时,文字会出现在 textarea 内容中。
相关资源:
4. Web Bluetooth API
Bluetooth API 让我们可以访问手机上的低功耗蓝牙设备,并使用它将网页上的数据共享到另一台设备。
基本 API 是 navigator.bluetooth.requestDevice。 调用它将使浏览器提示用户使用设备选择器,用户可以在其中选择一个设备或取消请求。navigator.bluetooth.requestDevice 需要一个强制对象。 此对象定义过滤器,用于返回与过滤器匹配的蓝牙设备。
下面来看一个简单的例子,使用 navigator.bluetooth.requestDevice API 从 BLE 设备检索基本设备信息:
<header>
<h2>Web APIs<h2>
</h2>
</h2></header>
<div>
<div>
<div>
Demo - Bluetooth
</div>
<div>
<div></div>
<div>
<div>Device Name: <span></span>
</div>
<div>Device ID: <span></span>
</div>
<div>Device Connected: <span></span>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<button>Get BLE Device</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
function bluetoothAction(){
if(navigator.bluetooth) {
navigator.bluetooth.requestDevice({
acceptAllDevices: true
}).then(device => {
dname.innerHTML = device.name
did.innerHTML = device.id
dconnected.innerHTML = device.connected
}).catch(err => {
error.innerHTML = "Oh my!! Something went wrong."
error.classList.remove("close")
})
} else {
error.innerHTML = "Bluetooth is not supported."
error.classList.remove("close")
}
}
</script>这里会显示设备信息。 单击 Get BLE Device 按钮会调用 bluetoothAction 函数:
function bluetoothAction(){
navigator.bluetooth.requestDevice({
acceptAllDevices: true
}).then(device => {
dname.innerHTML = device.name
did.innerHTML = device.id
dconnected.innerHTML = device.connected
}).catch(err => {
console.error("Oh my!! Something went wrong.")
})
}bluetoothAction 函数调用带有 acceptAllDevices:true 选项的 navigator.bluetooth.requestDevice API,这将使其扫描并列出所有附近的蓝牙活动设备。 它返回了一个 promise,所以将它解析为从回调函数中获取一个参数 device,这个 device 参数将保存列出的蓝牙设备的信息。这是我们使用其属性在设备上显示信息的地方。
相关资源:
5. Vibration API
Vibration API 可以使我们的设备振动,作为对我们应该响应的新数据或信息的通知或物理反馈的一种方式。
执行振动的方法是 navigator.vibrate(pattern)。pattern 是描述振动模式的单个数字或数字数组。
这将使设备振动在 200 毫秒之后停止:
navigator.vibrate(200) navigator.vibrate([200])
这将使设备先振动 200 毫秒,再暂停 300 毫秒,最后振动 400 毫秒并停止:
navigator.vibrate([200, 300, 400])
可以通过传递 0、[]、[0,0,0] 来消除振动。
下面来看一个简单的例子:
<header>
<h2>Web APIs<h2>
</h2>
</h2></header>
<div>
<div>
<div>
Demo - Vibration
</div>
<div>
<div></div>
<div>
<input>
</div>
<div>
<button>Vibrate</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
if(navigator.vibrate) {
function vibrate() {
const time = vibTime.value
if(time != "")
navigator.vibrate(time)
}
} else {
error.innerHTML = "Vibrate API not supported in this device."
error.classList.remove("close")
}
</script>这里有一个输入框和一个按钮。 在输入框中输入振动的持续时间并按下按钮。我们的设备将在输入的时间内振动。
相关资源:
6. Broadcast Channel API
Broadcast Channel API 允许从同源的不同浏览上下文进行消息或数据的通信。其中,浏览上下文指的是窗口、选项卡、iframe、worker 等。
BroadcastChannel 类用于创建或加入频道:
const politicsChannel = new BroadcastChannel("politics")politics 是频道的名称,任何使用 politics 始化 BroadcastChannel 构造函数的上下文都将加入 politics 频道,它将接收在频道上发送的任何消息,并可以将消息发送到频道中。
如果它是第一个具有 politics 的 BroadcastChannel 构造函数,则将创建该频道。可以使用 BroadcastChannel.postMessage API 来将消息发布到频道。使用 BroadcastChannel.onmessage API 要订阅频道消息。
下面来看一个简单的聊天应用:
<header>
<h2>Web APIs<h2>
</h2>
</h2></header>
<div>
<div>
<div>
Demo - BroadcastChannel
</div>
<div>
<div>Open this page in another <i>tab</i>, <i>window</i> or <i>iframe</i> to chat with them.</div>
<div></div>
<div>
</div>
<div>
<input>
<button>Send Msg to Channel</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const l = console.log;
try {
var politicsChannel = new BroadcastChannel("politics")
politicsChannel.onmessage = onMessage
var userId = Date.now()
} catch(e) {
error.innerHTML = "BroadcastChannel API not supported in this device."
error.classList.remove("close")
}
input.addEventListener("keydown", (e) => {
if(e.keyCode === 13 && e.target.value.trim().length > 0) {
sendMsg()
}
})
function onMessage(e) {
const {msg,id}=e.data
const newHTML = "<div class='chat-msg'><span><i>"+id+": "+msg+""
displayMsg.innerHTML = displayMsg.innerHTML + newHTML
displayMsg.scrollTop = displayMsg.scrollHeight
}
function sendMsg() {
politicsChannel.postMessage({msg:input.value,id:userId})
const newHTML = "<div class='chat-msg'><span><i>Me: "+input.value+""
displayMsg.innerHTML = displayMsg.innerHTML + newHTML
input.value = ""
displayMsg.scrollTop = displayMsg.scrollHeight
}
</script>这里有一个简单的文本和按钮。 输入消息,然后按按钮发送消息。下面初始化了politicalChannel,并在 politicalChannel 上设置了一个 onmessage 事件监听器,这样它就可以接收和显示消息。
点击按钮就会调用sendMsg 函数。 它通过 BroadcastChannel#postMessage API 将消息发送到 politics 频道。任何初始化此脚本的选项卡、iframe 或工作程序都将接收从此处发送的消息,因此此页面将接收从其他上下文发送的消息。相关资源:
7. Clipboard API
复制、剪切和粘贴等剪贴板操作是应用程序中最常见的一些功能。 Clipboard API 使 Web 用户能够访问系统剪贴板并执行基本的剪贴板操作。
以前,可以使用 document.execCommand 与系统剪贴板进行交互。 现代异步剪贴板 API 提供了直接读取和写入剪贴板内容的访问权限。
从剪贴板读取内容:
navigator.clipboard.readText().then(clipText =>
document.getElementById("outbox").innerText = clipText
);将内容写入剪贴板:
function updateClipboard(newClip) {
navigator.clipboard.writeText(newClip).then(function() {
/* clipboard successfully set */
}, function() {
/* clipboard write failed */
});
}相关资源:
8. Web Share API
Share API 可帮助我们在 web 应用上实现共享功能。它给人以移动原生共享的感觉。它使共享文本、文件和指向设备上其他应用程序的链接成为可能。
可通过 navigator.share 方法访问 Web Share API:
if (navigator.share) {
navigator.share({
title: '百度',
text: '百度一下',
url: '<https:></https:>',
})
.then(() => console.log('分享成功'))
.catch((error) => console.log('分享失败', error));
}上面的代码使用原生 JavaScript 实现了文本共享。需要注意,我们只能使用 onclick 事件调用此操作:
function Share({ label, text, title }) {
const shareDetails = { title, text };
const handleSharing = async () => {
if (navigator.share) {
try {
await navigator.share(shareDetails).then(() => console.log("Sent"));
} catch (error) {
console.log(`Oops! I couldn't share to the world because: ${error}`);
}
} else {
// fallback code
console.log(
"Web share is currently not supported on this browser. Please provide a callback"
);
}
};
return (
<button>
<span>{label}</span>
</button>
);
}相关资源:
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
The above is the detailed content of 8 Web APIs you may not know about but are very useful. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools. In today's era of rapid development of the Internet, front-end development has become increasingly important. As users have higher and higher requirements for the experience of websites and applications, front-end developers need to use more efficient and flexible tools to create responsive and interactive interfaces. As two important technologies in the field of front-end development, PHP and Vue.js can be regarded as perfect tools when paired together. This article will explore the combination of PHP and Vue, as well as detailed code examples to help readers better understand and apply these two
 Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
In front-end development interviews, common questions cover a wide range of topics, including HTML/CSS basics, JavaScript basics, frameworks and libraries, project experience, algorithms and data structures, performance optimization, cross-domain requests, front-end engineering, design patterns, and new technologies and trends. . Interviewer questions are designed to assess the candidate's technical skills, project experience, and understanding of industry trends. Therefore, candidates should be fully prepared in these areas to demonstrate their abilities and expertise.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 Is Django front-end or back-end? check it out!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Is Django front-end or back-end? check it out!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Django is a web application framework written in Python that emphasizes rapid development and clean methods. Although Django is a web framework, to answer the question whether Django is a front-end or a back-end, you need to have a deep understanding of the concepts of front-end and back-end. The front end refers to the interface that users directly interact with, and the back end refers to server-side programs. They interact with data through the HTTP protocol. When the front-end and back-end are separated, the front-end and back-end programs can be developed independently to implement business logic and interactive effects respectively, and data exchange.
 What is a front-end modular ESM?
Feb 25, 2024 am 11:48 AM
What is a front-end modular ESM?
Feb 25, 2024 am 11:48 AM
What is front-end ESM? Specific code examples are required. In front-end development, ESM refers to ECMAScriptModules, a modular development method based on the ECMAScript specification. ESM brings many benefits, such as better code organization, isolation between modules, and reusability. This article will introduce the basic concepts and usage of ESM and provide some specific code examples. The basic concept of ESM In ESM, we can divide the code into multiple modules, and each module exposes some interfaces for other modules to
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service









